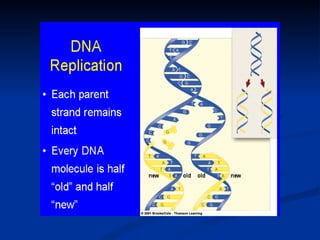
DNA replication is the process where DNA separates into two strands and uses free nucleotides to form an exact copy of each strand, resulting in two complete DNA molecules. Transcription is where one strand of DNA is copied into a similar strand of RNA, with some differences in RNA. There are three types of RNA: mRNA which acts as a pattern for protein amino acids, tRNA which carries amino acids to ribosomes, and rRNA found in ribosomes. Translation is where the bases on mRNA act as a code read by ribosomes to bring the correct amino acids carried by tRNA, building a protein chain.