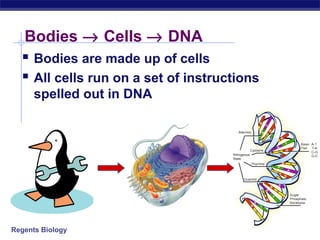
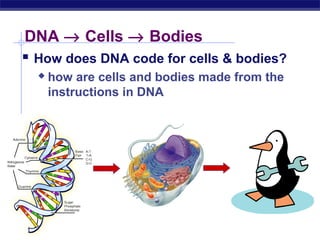
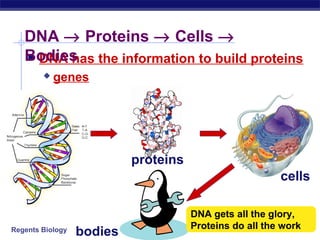
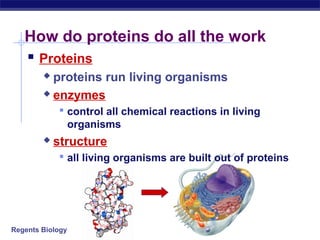
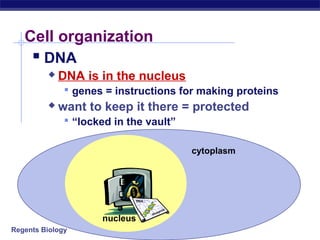
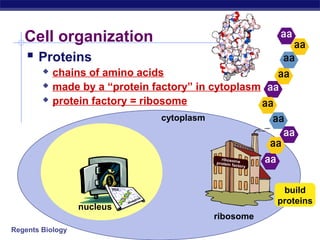
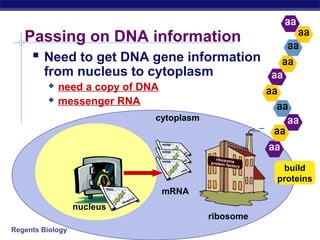
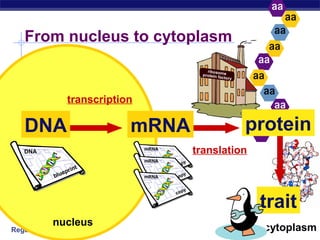
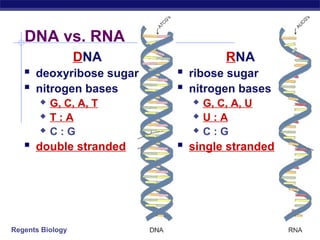
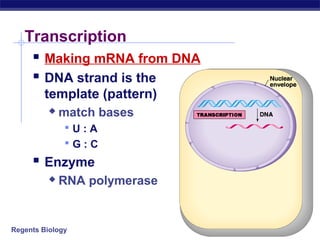
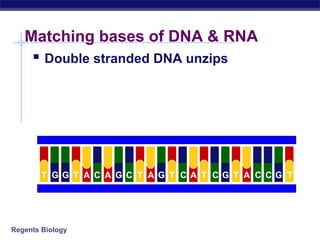
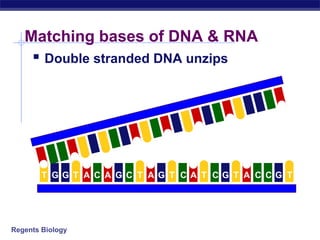
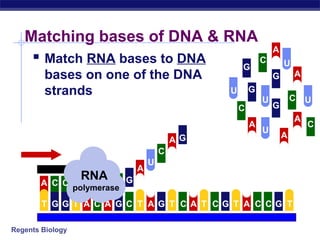
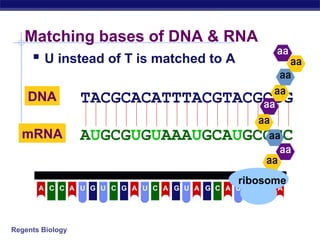
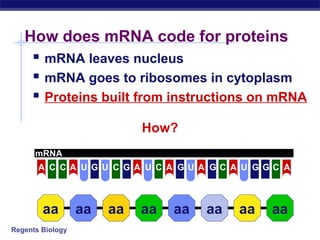
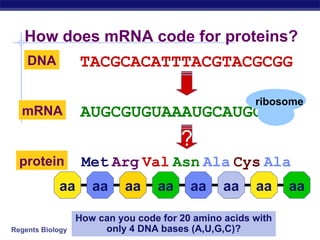
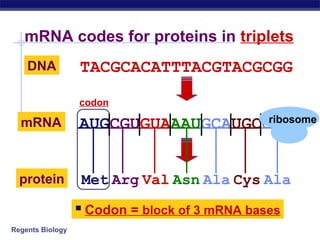
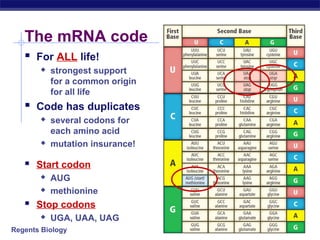
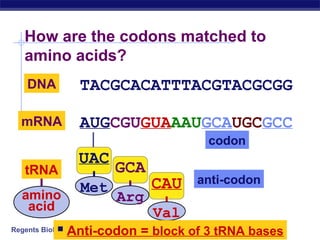
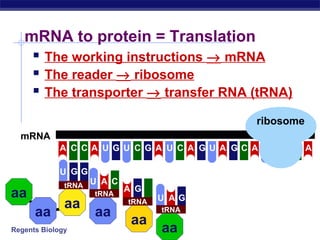
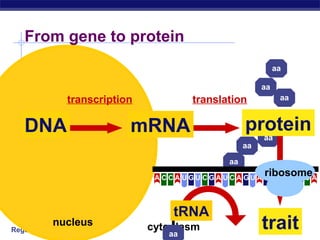
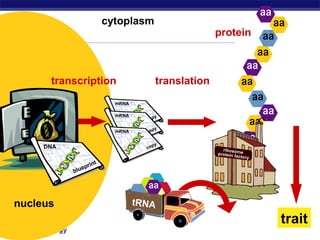
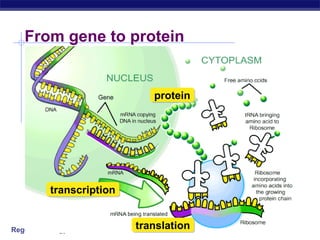
The document outlines the process of how genetic information in DNA is used to produce proteins. It discusses how DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus, and then how mRNA is translated into proteins with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The mRNA code uses three-letter combinations called codons to specify which of 20 amino acids should be included in the protein chain.