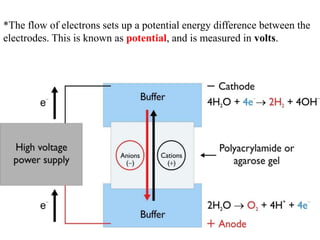
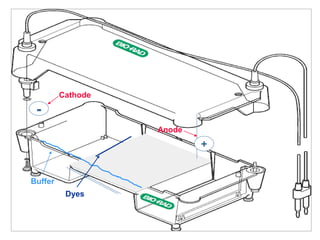
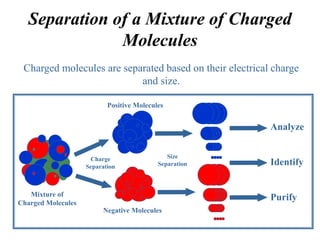
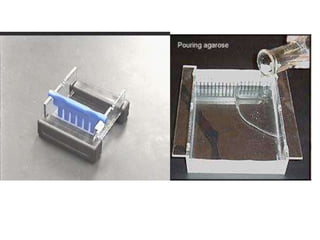
Gel electrophoresis is a method to separate DNA, RNA, and proteins by size and charge through a porous gel using an electric current. Key components include an agarose or polyacrylamide gel matrix, electrophoresis buffer to set and maintain pH, and a power supply. Negatively charged molecules migrate toward the anode, allowing separation by size. Applications include analyzing restriction enzyme digests, PCR products, and estimating size and quantity of nucleic acid samples.