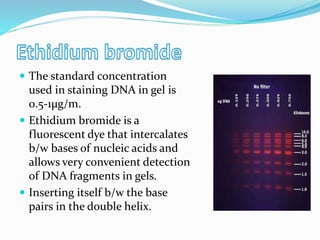
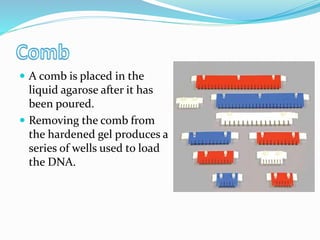
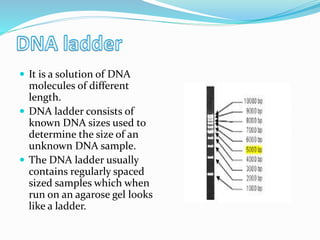
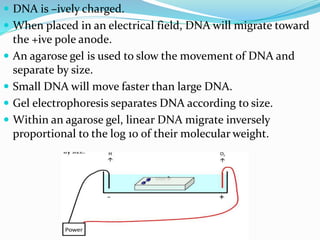
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method for separating DNA or RNA molecules by size using an electric field through an agarose matrix, with shorter molecules migrating faster than longer ones. The process involves casting a gel with a buffer system and staining agents such as ethidium bromide for visualization of DNA fragments. The technique is commonly used for analyzing DNA fragments, with separation based on size, charge, and shape, and requires careful control of voltage during the process.