The document is a set of lecture notes on gears that discusses various topics including:
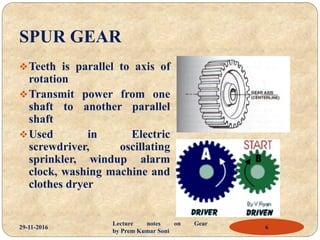
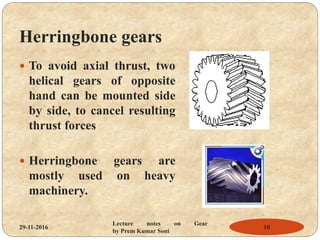
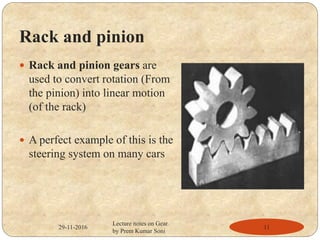
- Types of gears like spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, and worm gears.
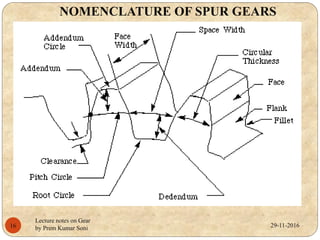
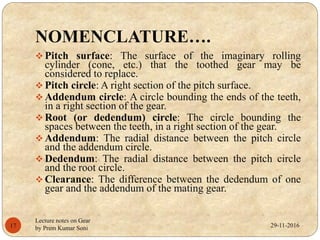
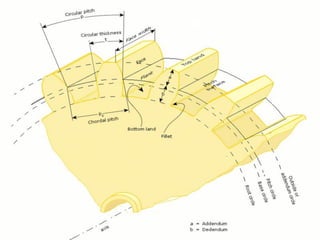
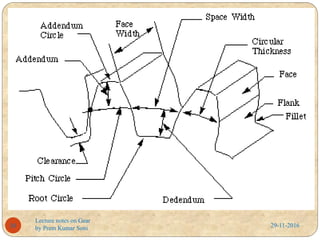
- Gear terminology like pitch circle, addendum, dedendum, and module.
- Applications of different gears in devices like electric screwdrivers, steering systems, and material handling equipment.
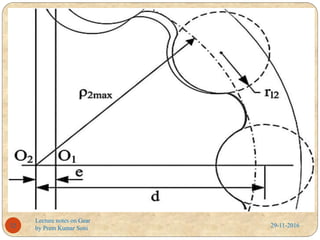
- Factors that affect gear performance like backlash, which is the play between meshing gear teeth that can cause imprecision.