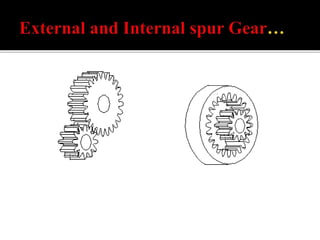
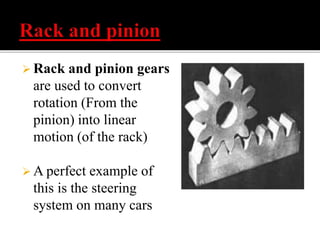
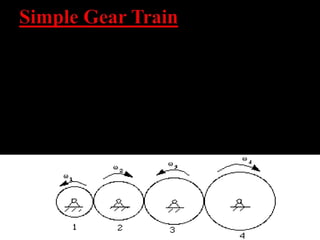
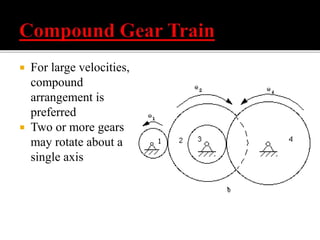
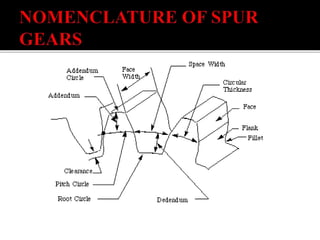
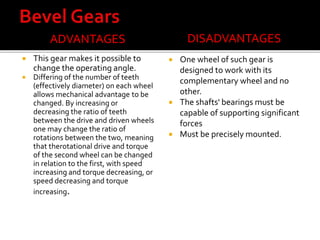
The document discusses different types of gears including spur gears, helical gears, herringbone gears, rack and pinion gears, bevel gears, worm gears, and planetary gears. It describes the design and function of each gear type, their advantages and disadvantages, and common applications. Spur gears transmit power between parallel shafts and are used in machines, power plants, and automobiles. Helical gears operate more quietly than spur gears and are used in automobile transmissions. Planetary gears can produce different gear ratios and are commonly used in automatic transmissions.