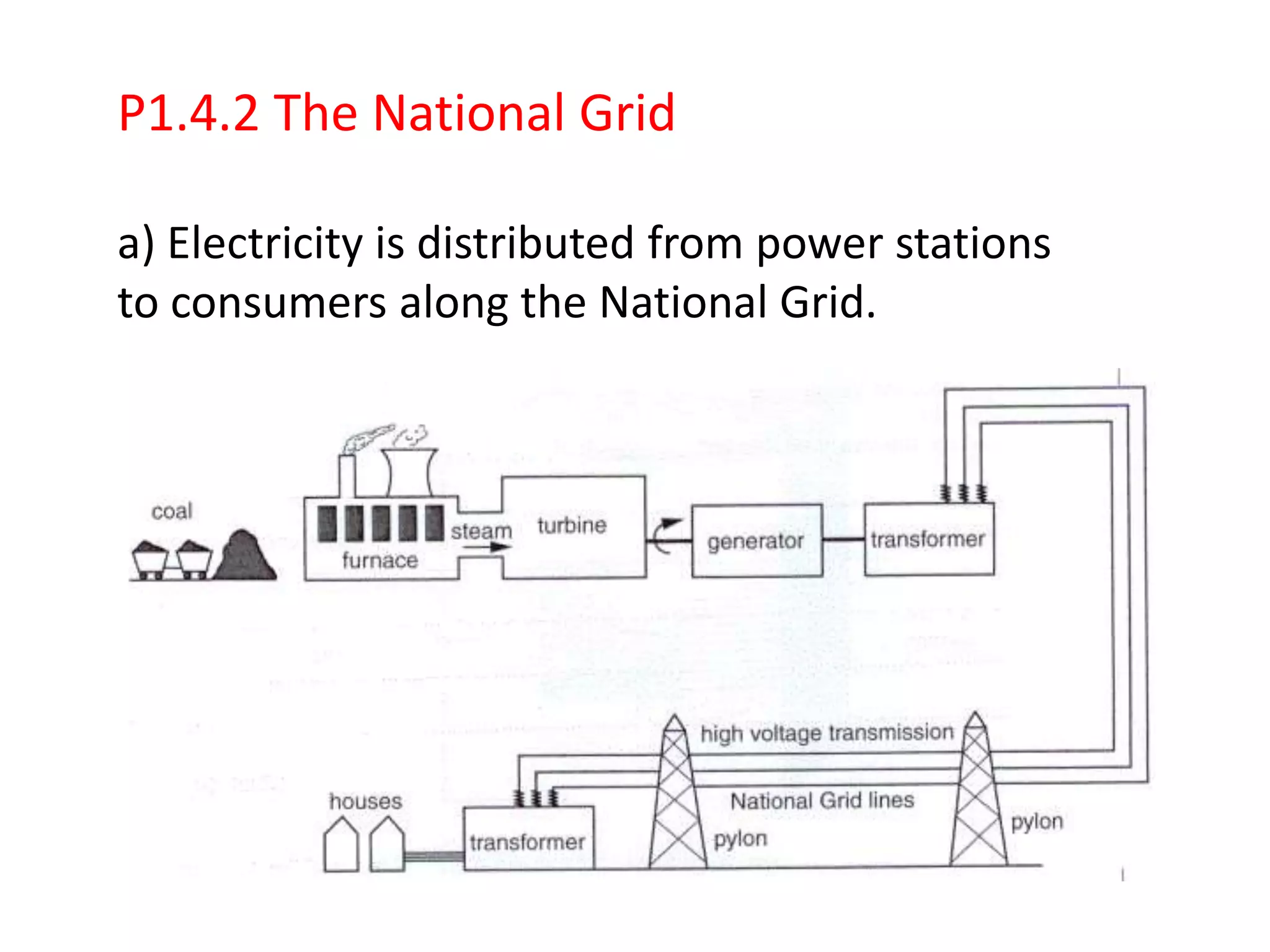
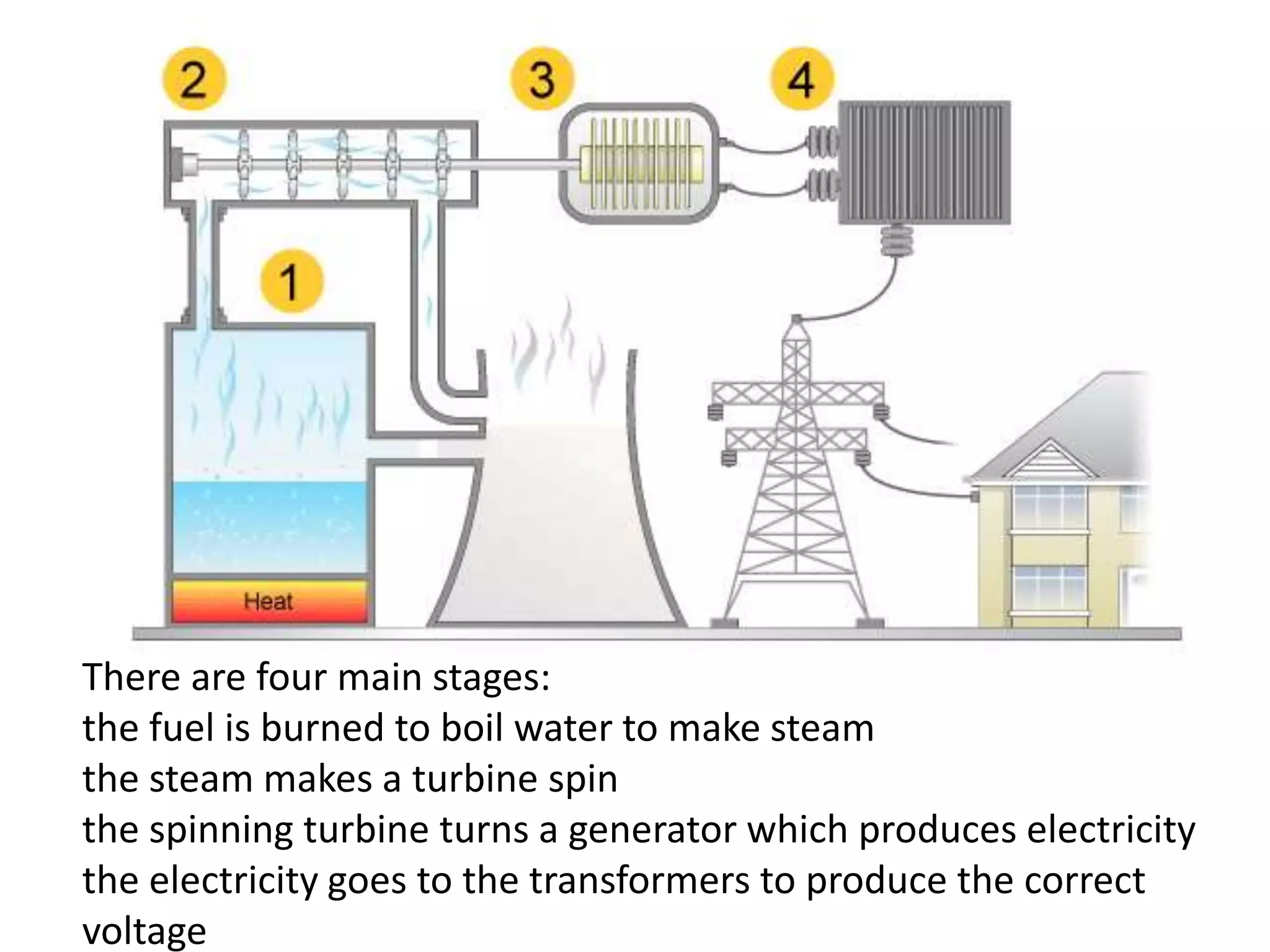
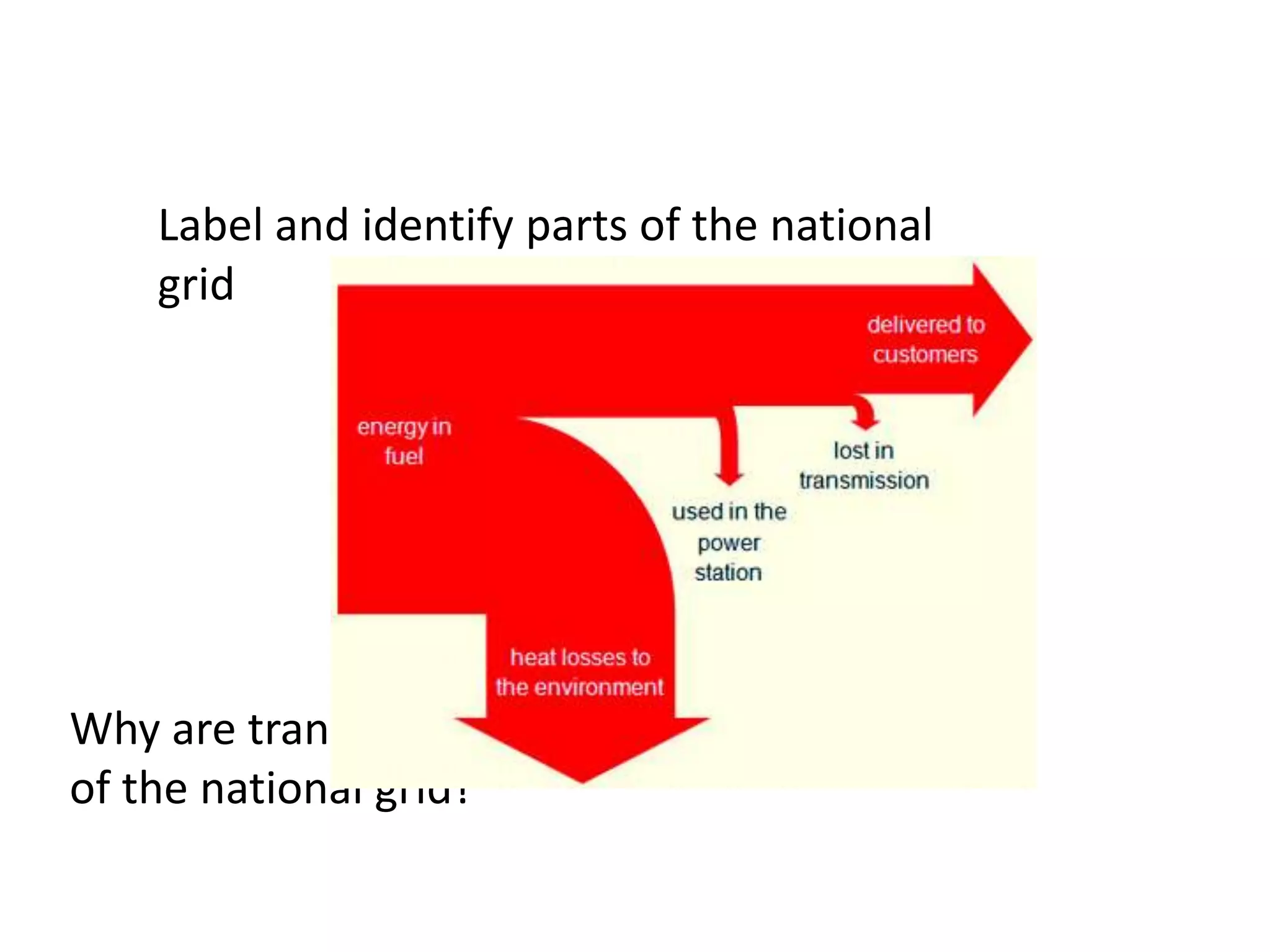
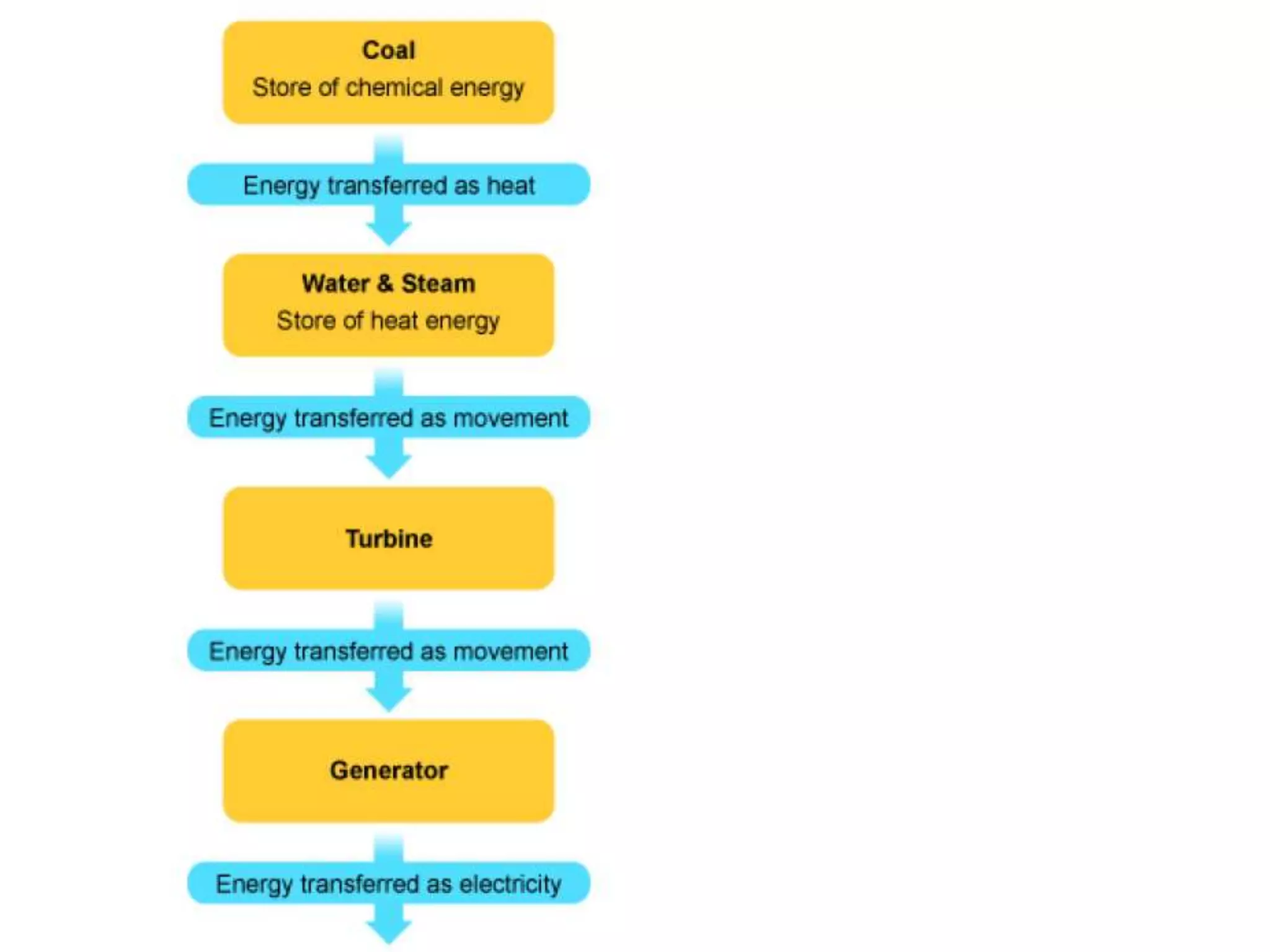
The document discusses different methods for generating electricity, including using fossil fuels, nuclear energy, water, wind, solar power, and geothermal energy to heat water and power turbines connected to generators. It also describes the national grid system for distributing electricity from power stations to consumers via high voltage transmission lines and transformers. Key points covered include the advantages and disadvantages of different electricity generation methods and the role of step-up and step-down transformers in increasing or decreasing voltage levels on the national grid.