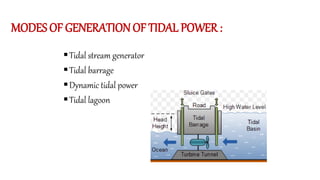
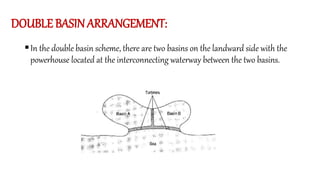
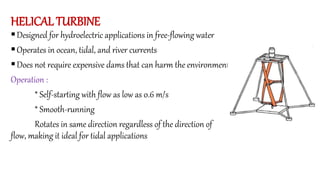
Tidal energy is a form of hydropower that converts the gravitational energy of tides into electricity using tidal energy generators, turbines, and barrages. The potential for tidal power hinges on the gravitational forces of the moon and sun, with various generation methods including tidal stream generators and dynamic tidal power plants. Despite advantages like being inexhaustible and environmentally friendly, challenges such as high construction costs and ecological impacts limit its widespread adoption.