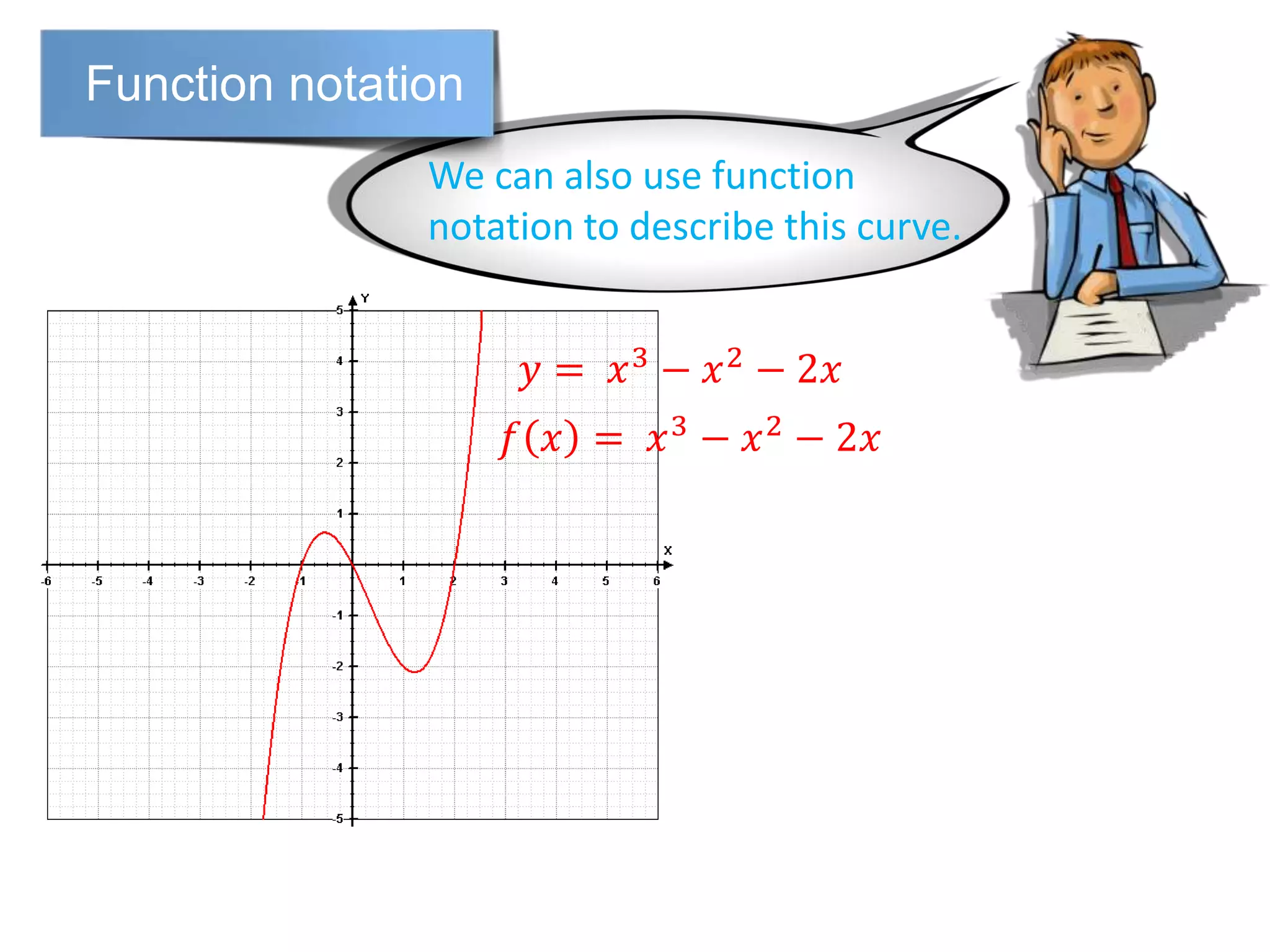
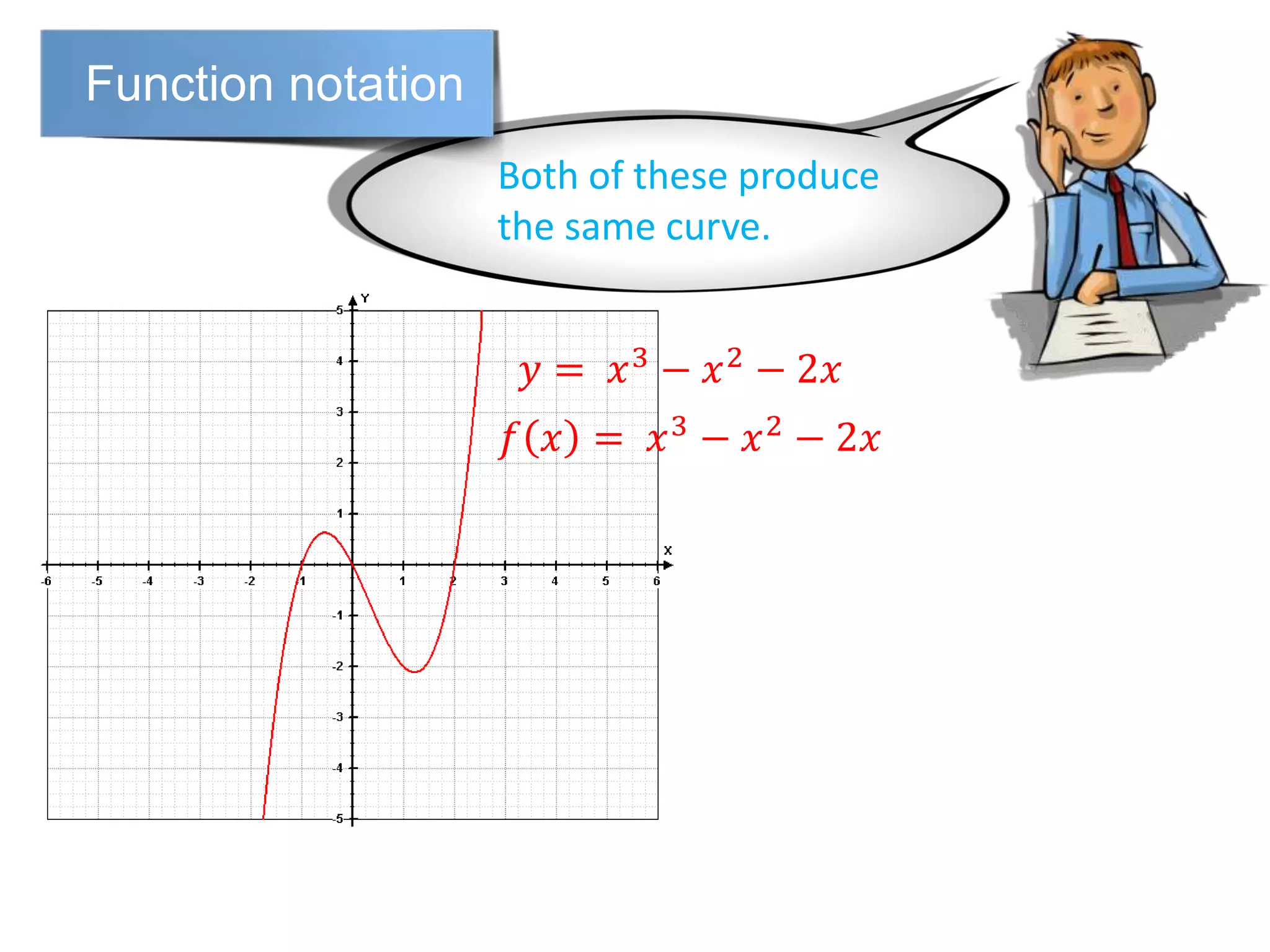
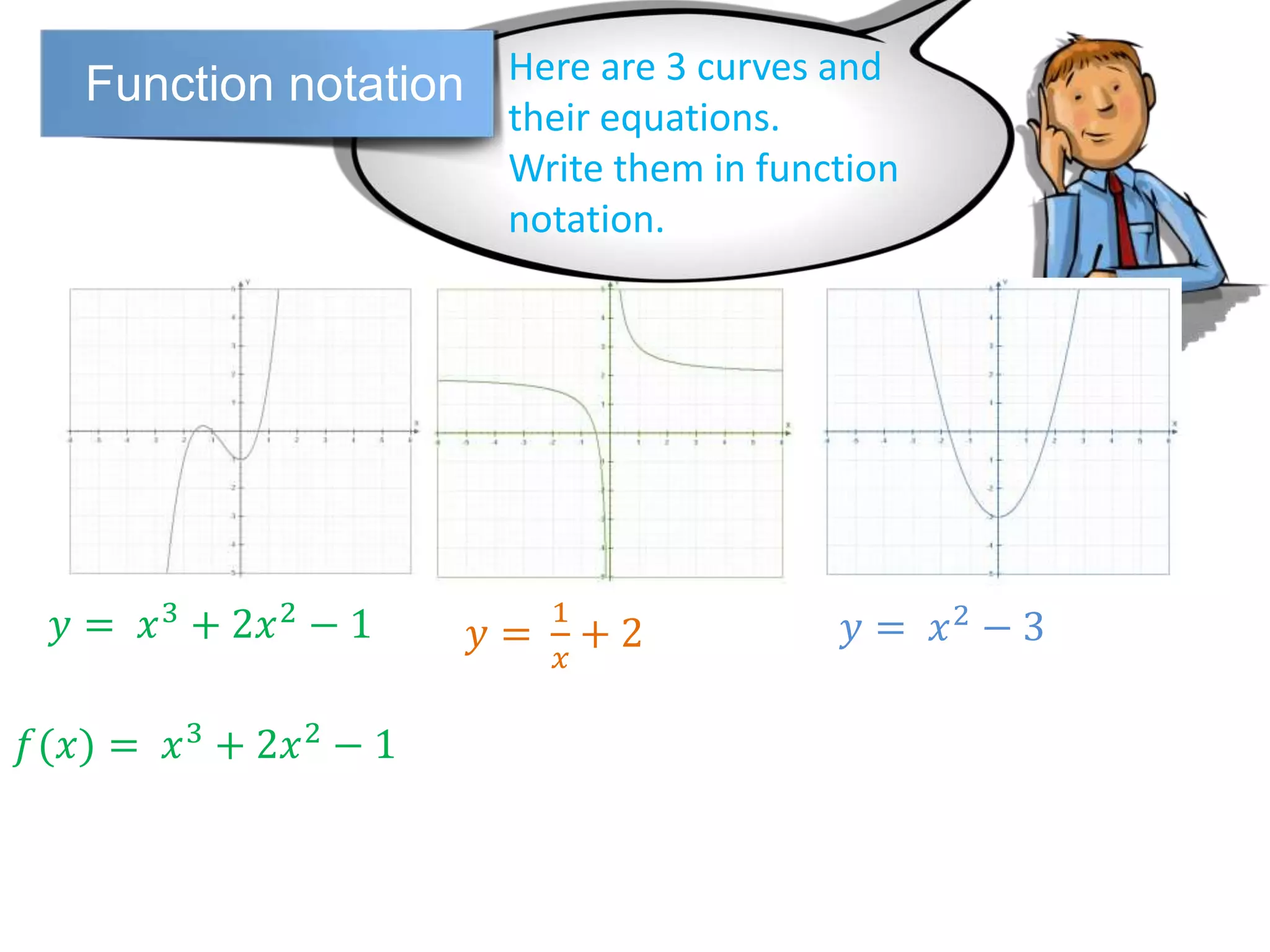
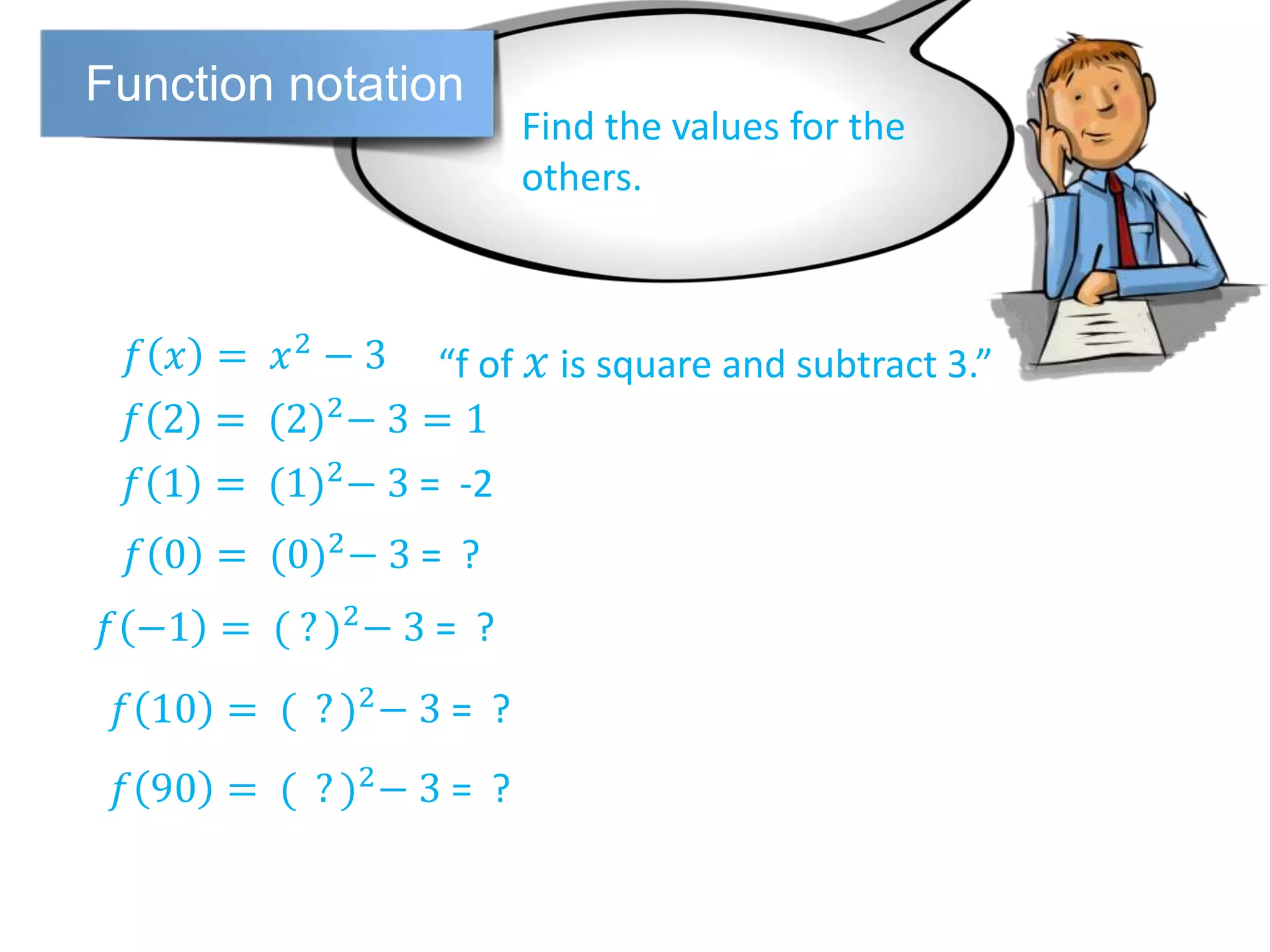
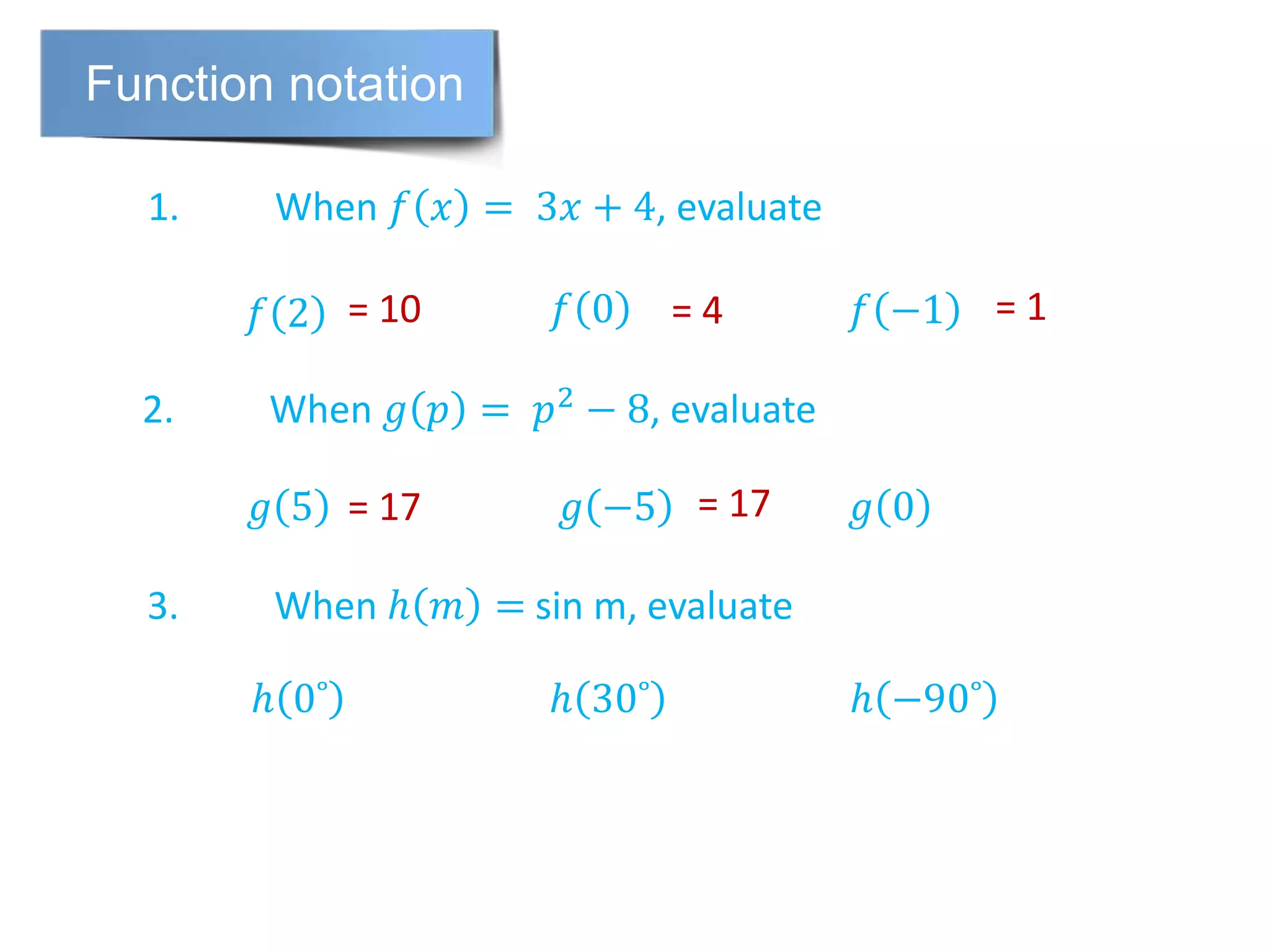
The document discusses function notation and transformations of functions. It provides examples of writing quadratic, cubic, and rational functions in function notation. It also demonstrates how functions are translated vertically by adding or subtracting a number from the original function. Translating a function f(x) by a results in the new function f(x)+a or f(x)-a.