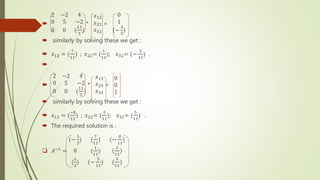The document discusses inverting a matrix. It explains that to invert a matrix A, we let X be the inverse of A such that AX = I, where I is the identity matrix. We then form an augmented matrix of A and I and use Gaussian elimination to put it in upper triangular form. This allows us to solve for the elements of X, which are the entries of the inverse matrix. As an example, it shows inverting a 3x3 matrix A through this process and obtaining its inverse A-1.

![INVERSSION OF MATRIX :
Let us consider we have a matrix [A] & we have to find the inverse of that matrix
. Let [x] be the inverse of matrix [A].
we know that : A ∗ 𝐴−1 = [𝐼]
now : [A]*[X]=[I] as we considered that : [X]= 𝐴−1
Then we convert the system into an augmented matrix
in the form of [A|I ].
then we have to use elementary row operation on the
augmented matrix to get upper triangular matrix by using
Gauss Elimination Method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inverssionofmatrix-181103023534/85/INVERSION-OF-MATRIX-BY-GAUSS-ELIMINATION-METHOD-2-320.jpg)
![ After that using : [A]*[X]=[I]
the relation we have to find the elements of [X] ; which is our required answer .
For example we take a matrix and try to find it’s inverse :
A =
2 −2 4
2 3 2
−1 4 −1
consider the augmented matrix is :
2 −2 4
2 3 2
−1 4 −1
: 1 0 0
: 0 1 0
: 0 0 1
=
2 −2 4
0 5 −2
0 3 1
: 1 0 0
: −1 1 0
: (
1
2
) 0 1
[using 𝑅′2 = 𝑅2 −
2
2
∗ 𝑅1; 𝑅′
3 = 𝑅3 − (
1
2
)𝑅1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inverssionofmatrix-181103023534/85/INVERSION-OF-MATRIX-BY-GAUSS-ELIMINATION-METHOD-3-320.jpg)
![ =
2 −2 4
0 5 −2
0 0 (
11
5
)
: 1 0 0
: −1 1 0
: (
11
10
) −(
3
5
) 1
[using 𝑅′′3 = 𝑅3 −
3
5
∗ 𝑅2]
The inverse matrix is given as : X=
𝑥11 𝑥12 𝑥13
𝑥21 𝑥22 𝑥23
𝑥31 𝑥32 𝑥33
Thus we have an equivalent system of three equation :
2 −2 4
0 5 −2
0 0 (
11
5
)
*
𝑥11
𝑥21
𝑥31
=
1
−1
(
11
10
)
which gives :2𝑥 − 2𝑦 + 4𝑧 = 1;
5𝑦 − 2𝑧 = −1;
11
5
∗ 𝑧 = (
11
10
)
Solving by back substitution method we get ;
𝑥 = −
1
2
; 𝑦 = 0; 𝑧 = (
1
2
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inverssionofmatrix-181103023534/85/INVERSION-OF-MATRIX-BY-GAUSS-ELIMINATION-METHOD-4-320.jpg)