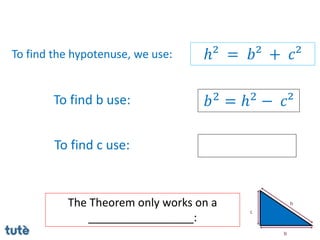
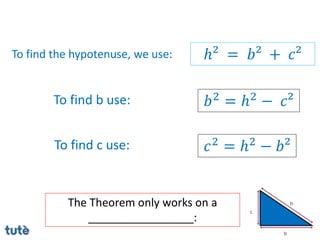
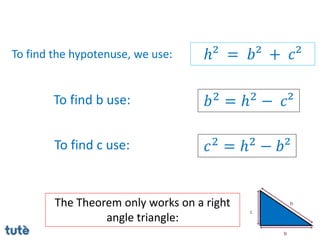
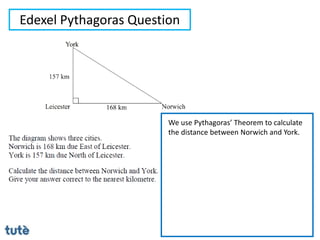
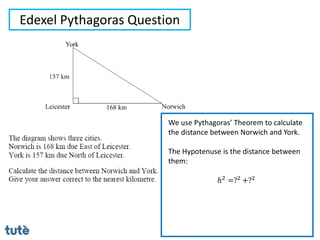
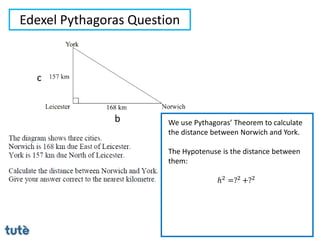
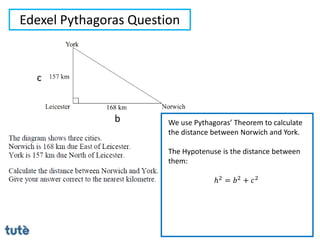
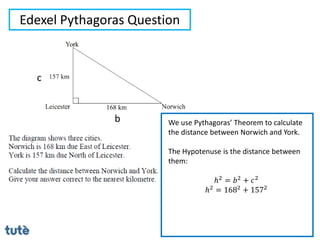
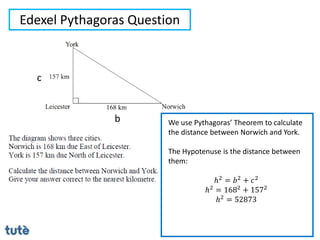
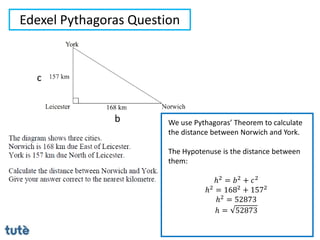
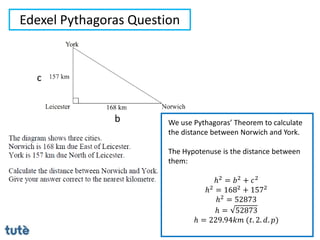
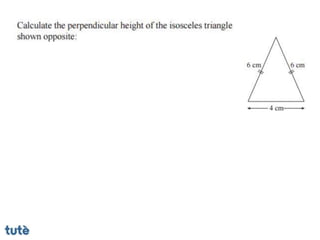
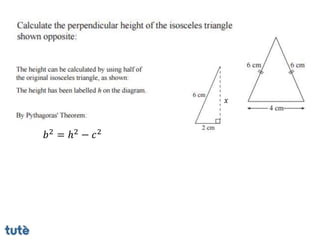
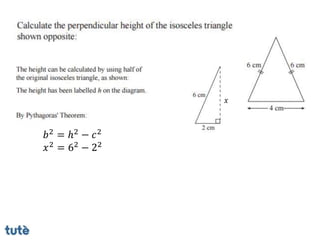
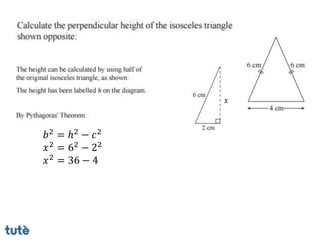
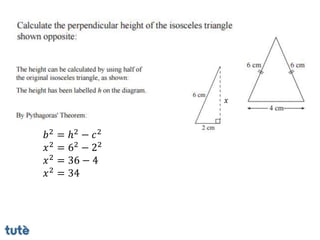
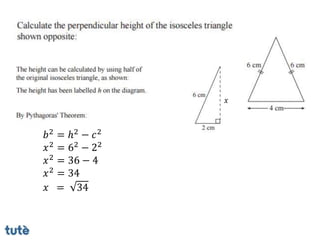
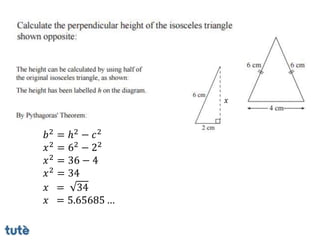
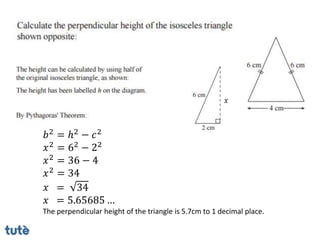
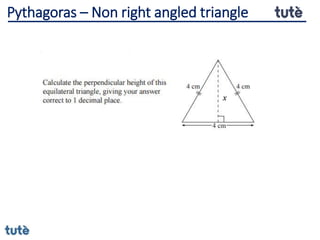
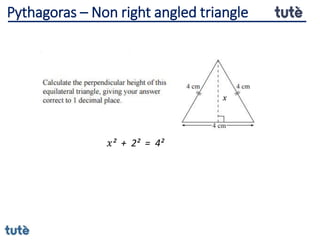
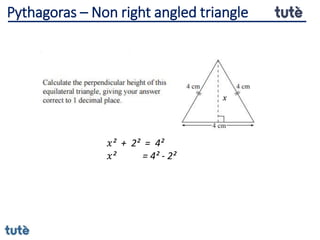
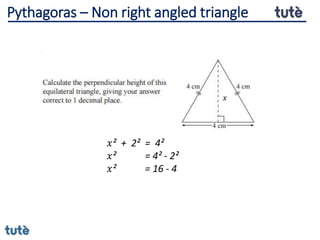
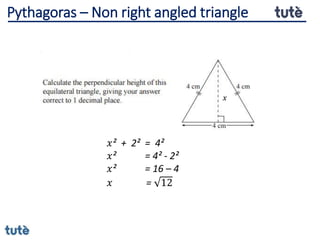
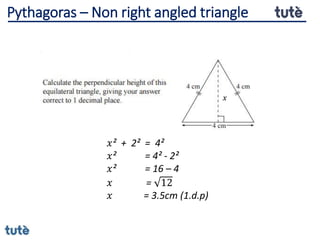
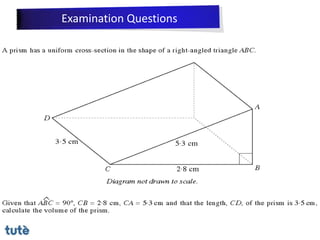
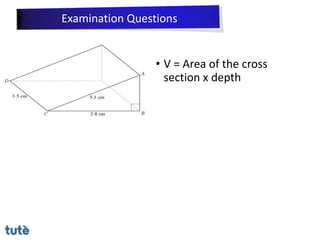
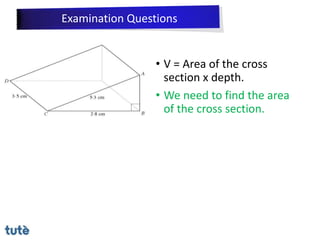
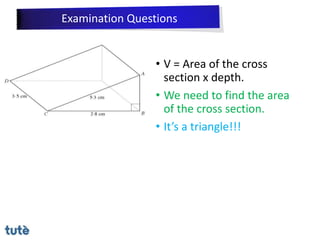
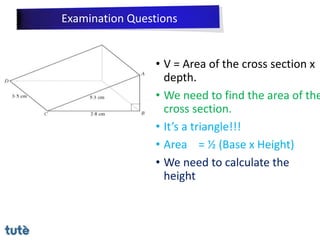
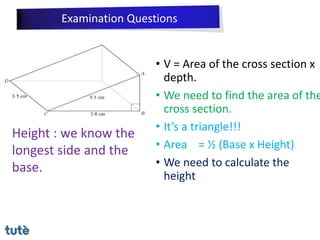
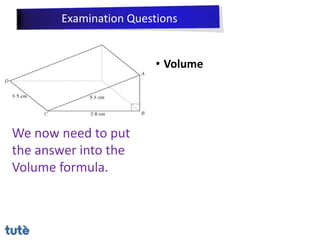
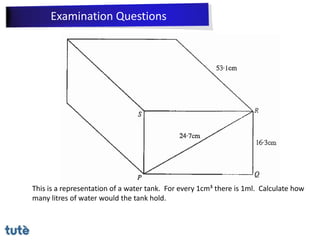
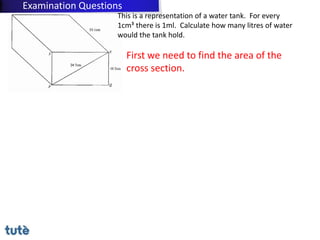
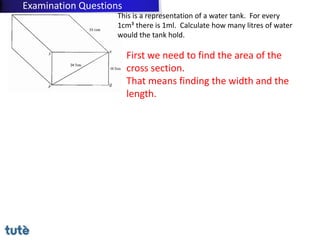
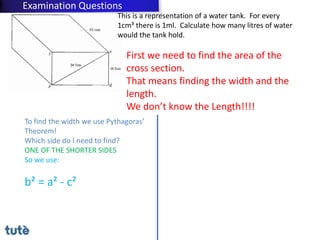
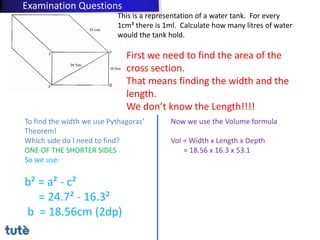
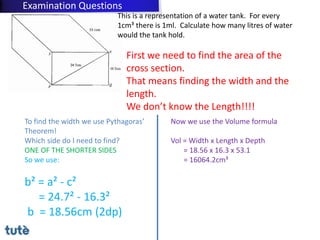
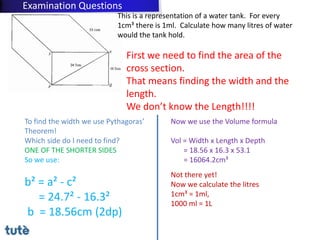
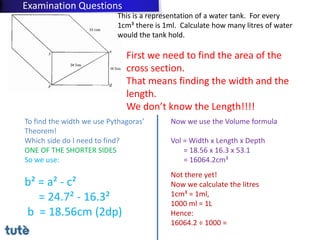
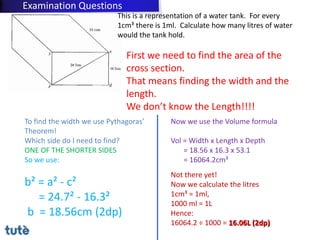
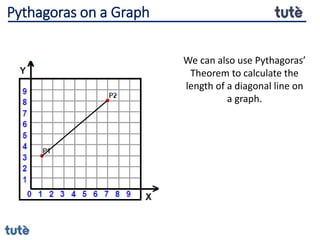
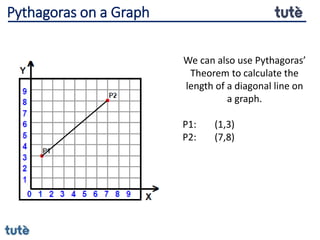
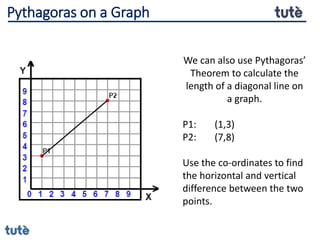
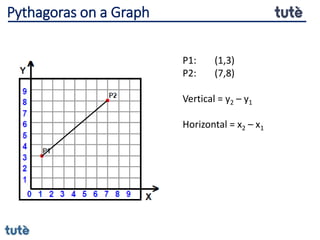
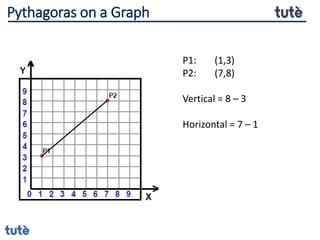
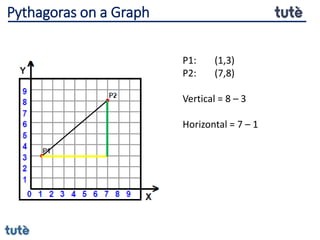
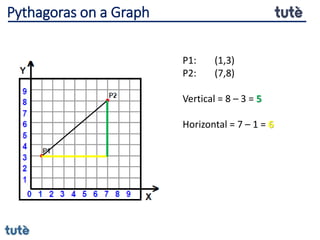
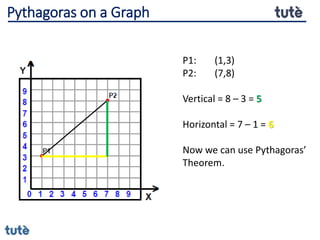
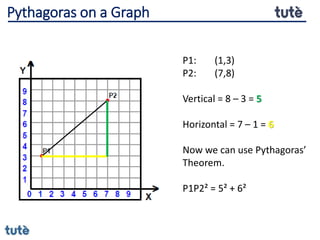
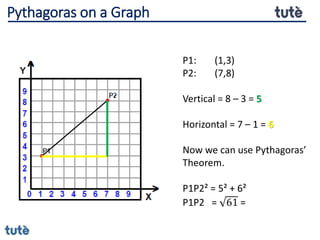
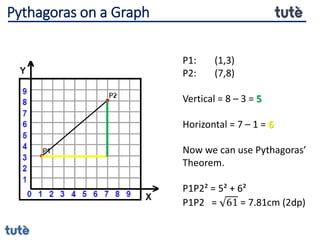
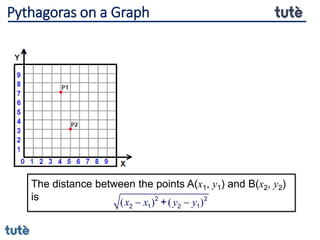
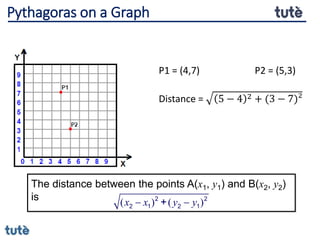
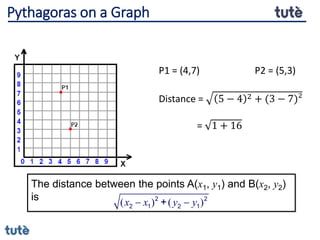
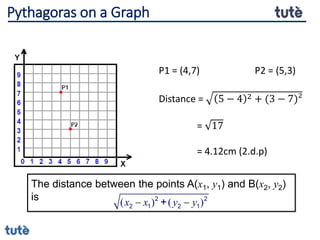
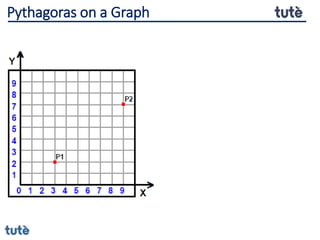
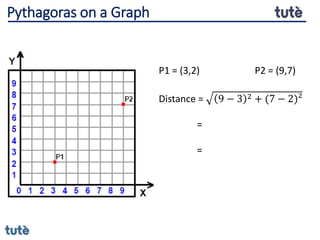
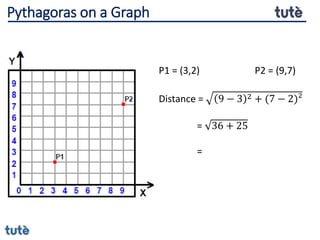
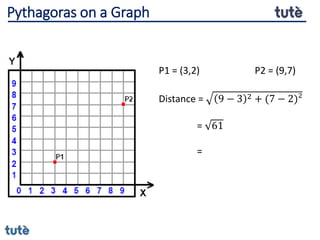
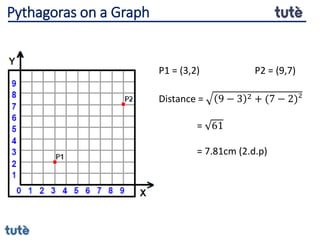
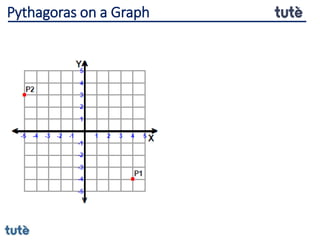
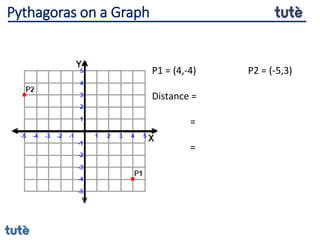
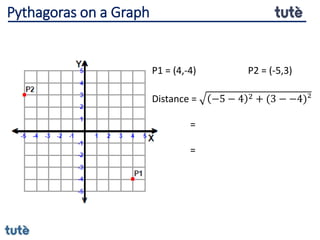
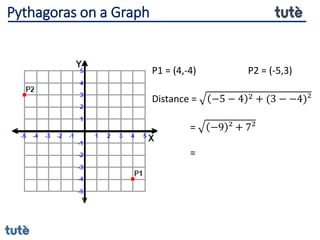
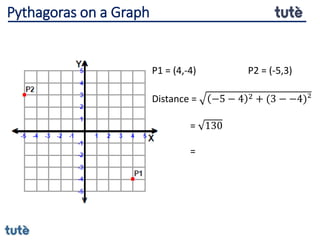
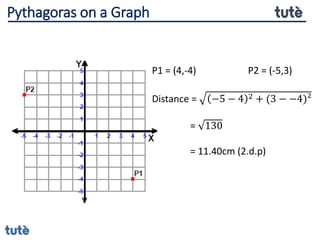
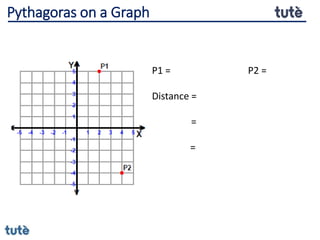
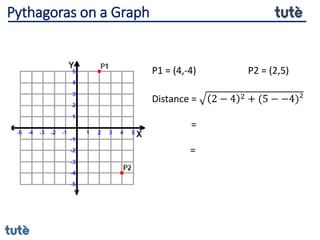
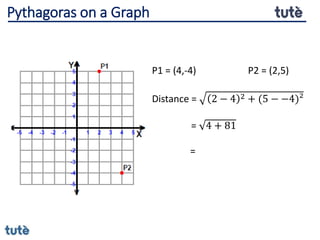
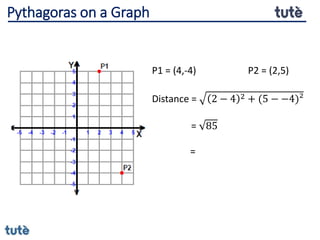
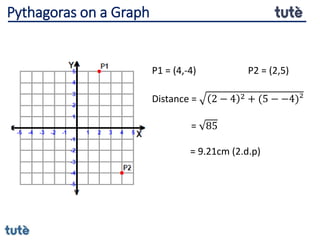
This document discusses how to apply Pythagoras' theorem to calculate distances and lengths in triangles, both right-angled and non-right angled. It provides examples of using the theorem to solve examination questions involving finding lengths, areas, perimeters, volumes, and calculating how much water a tank can hold.