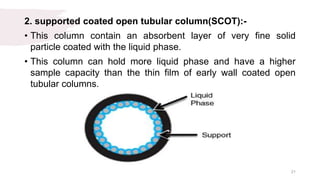
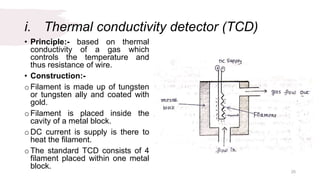
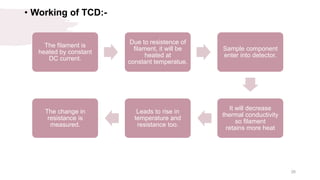
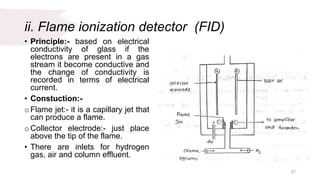
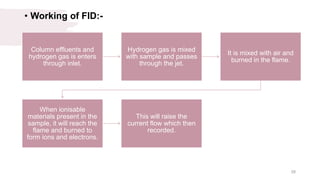
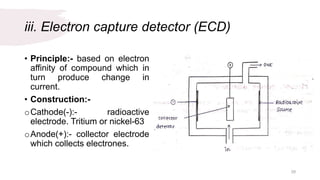
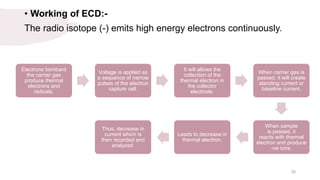
The document provides an overview of gas chromatography (GC), detailing its principles, mobile and stationary phases, instrumentation, derivatization, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. GC is a widely used technique for separating components of a mixture by partitioning them between a gaseous mobile phase and a stationary phase, with applications in fields such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and forensics. It highlights different types of columns, detectors, and sample preparation methods, as well as the process of derivatization to enhance analyte properties for better analysis.