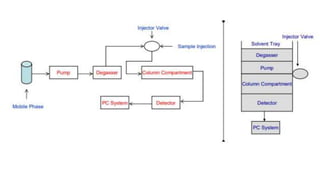
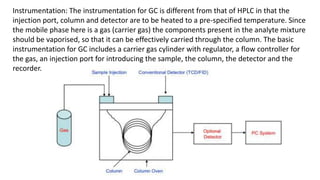
Chromatography is a technique used to separate chemical components in a complex mixture. It works by carrying components through a stationary phase at different rates using a mobile phase, usually liquid or gas. Liquid chromatography uses high pressure to push a liquid mobile phase through a column, while gas chromatography uses an inert gas and higher temperatures. Different detectors can be used to analyze the separated components as they exit the column. Common detectors measure properties like thermal conductivity, ionization, or light emission to identify the separated chemicals. Chromatography is a powerful analytical and preparative separation method.