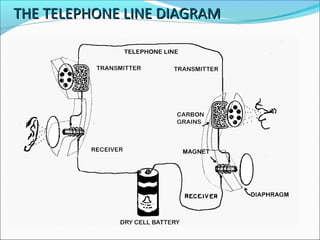
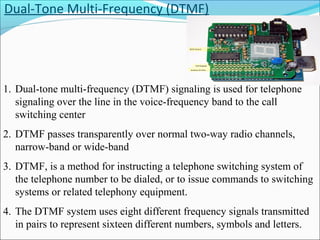
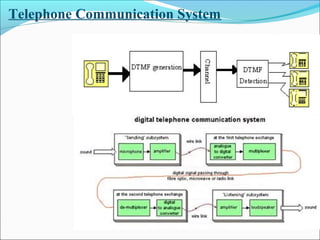
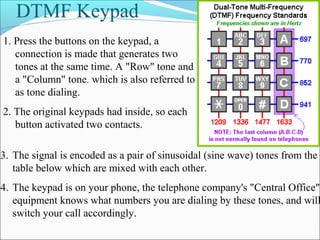
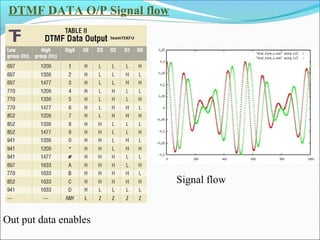
This presentation provides an overview of touch tone dial telephones and their components. It discusses the basic components of a telephone set including the transmitter, receiver, and electrical network. It then explains the essential components of a touch tone dial telephone such as the ringer circuit, on/off hook circuit, and hybrid network. The presentation describes how dual-tone multi-frequency signaling works to generate tones from a telephone keypad that are interpreted by the telephone switching system to route calls. It concludes with advantages and applications of telephone systems.