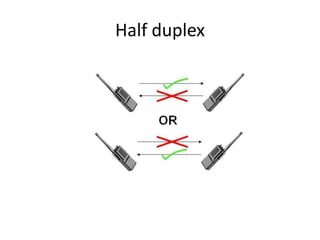
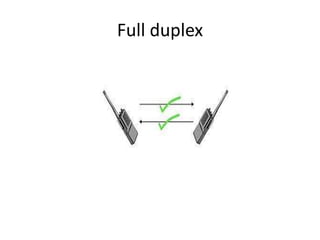
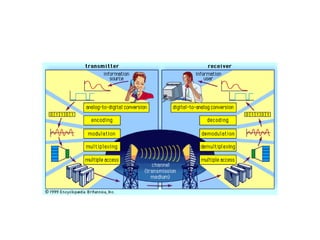
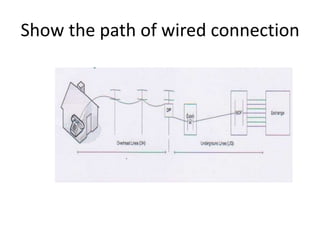
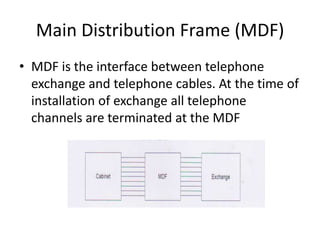
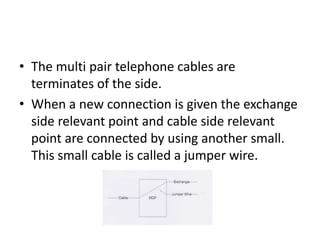
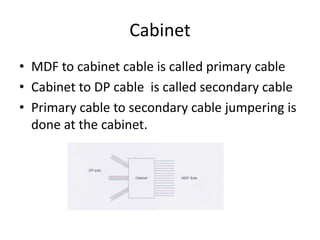
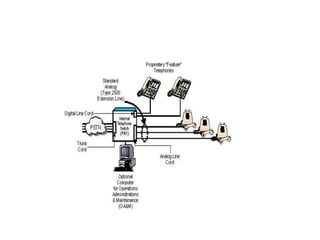
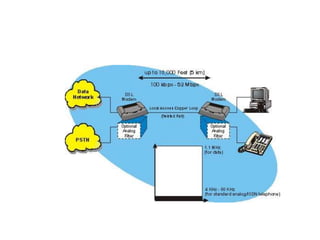
Telecommunication systems allow transmission of information over distances. A basic system includes a transmitter that converts information to signals, a transmission medium like free space to carry the signals, and a receiver to convert signals back to information. Wired telephone connections involve telephone lines connecting to exchanges, distribution points, and homes. Wireless systems use base stations connected to exchanges to transmit radio signals to customer premises equipment like phones. Private branch exchange systems allow internal calling between phone sets and public switched telephone network access, while digital subscriber line systems use existing copper phone lines more efficiently to provide both phone and high-speed internet services.