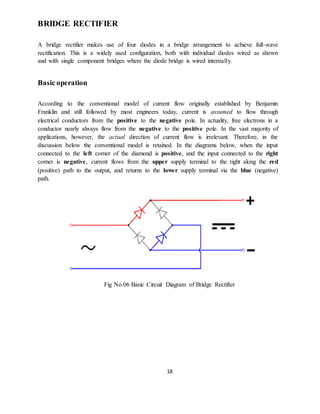
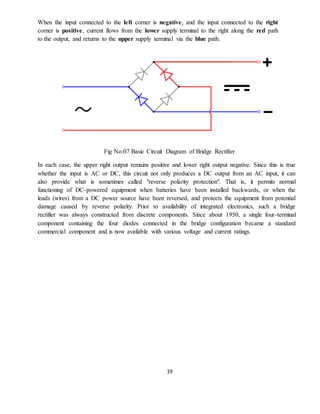
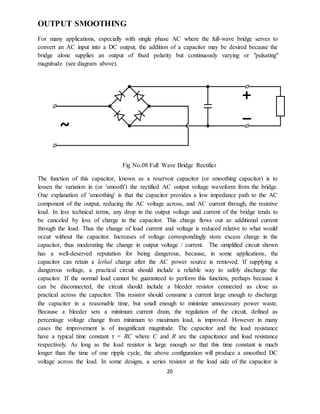
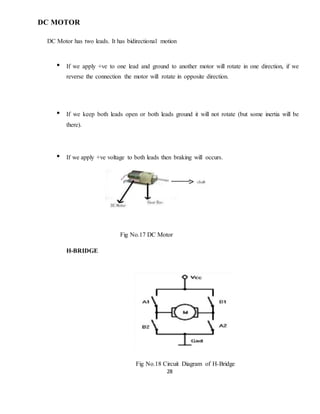
This document is a project report submitted by Mr. Pankaj Rai for a diploma in electronics and telecommunications engineering. The project is on a DTMF based mobile controlled robot. The report includes an introduction describing how the robot is controlled via DTMF tones sent from a mobile phone, block diagrams of the system components, descriptions of the hardware used including the power supply, transformer, rectifier, regulator, motors, and a circuit diagram. It also includes testing procedures and potential applications and future improvements. The overall purpose is to describe the design and implementation of a robot that can be remotely controlled via a mobile phone call.









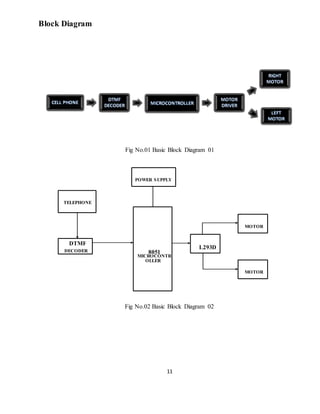


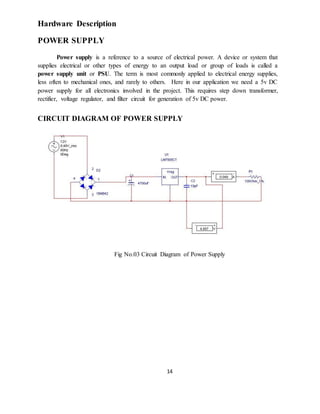

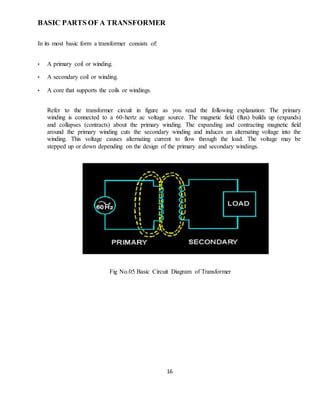










![36
Component List
R1 - 10K [BROWN, BLACK, ORANGE]
R2 - 270K [RED, VIIOLET, YELLOW]
R3 - 220E [RED, RED, BROWN]
R4 - 22K [RED, RED, ORANGE]
R6 - 1K [BROWN, BLACK, RED]
R5 - 500K PRESET
C1 - 10UF / 25V Electrolytic
C2, 6, 9, 10 - 100KPF DISC (0.1UF / 104) (4 NOS)
C3 - 100KPF POLY (0.1UF / 104)
C4, 5 - 33PF Ceramic Disc (2 NOS)
C7 - 1000UF / 16V Electrolytic
C8 - 47UF / 25V Electrolytic
X1 - 3.579545 MHZ Crystal
X2 - 11.0592 MHZ Crystal
D1 - 1N4007 Diode
L1 - 3 mm OR 5 mm RED LED
L2 - 3 mm OR 5 mm GREEN LED
U1 - AT89C2051 - MICROCONTROLLER (Pre Programmed MCU)
U2 - MT8870 - DTMF DECODER
U3 - L293 MOTOR DRIVER
U4 - LM7805 - +5V Voltage Regulator
CN1 ~ 4 - 2 PIN SCREW TERMINALS BLOCK (4 NOS)
1 nos - 20 PIN IC SOCKET FOR U1
1 nos - 18 PIN IC SOCKET FOR U2
1 nos - 16 PIN IC SOCKET FOR U3
1 nos - standard NOKIA Head phone Pin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05pankajprojectreport-160412062506/85/Pankaj-project-report-36-320.jpg)






