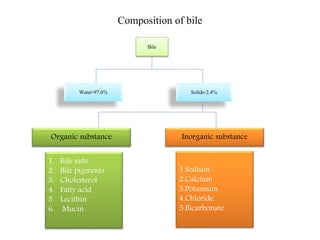
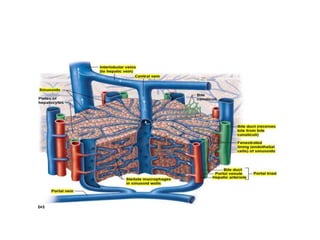
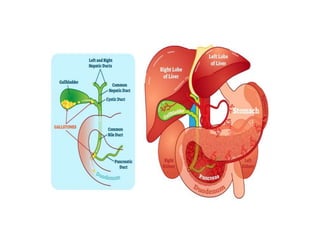
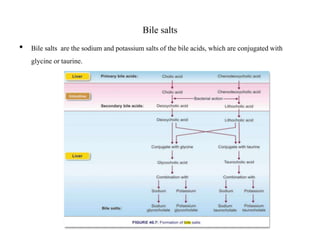
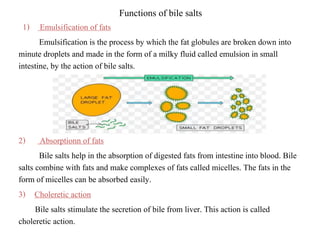
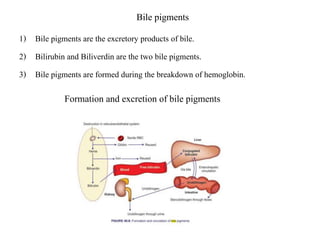
Bile is a thick, yellow-green fluid produced by the liver that aids in fat digestion. It is composed primarily of water, bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Bile is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder before being released into the small intestine in response to food. In the intestine, bile salts act to emulsify and absorb fats, stimulate bile secretion from the liver, and induce bowel movements. Bile also plays roles in excreting waste, maintaining pH, preventing gallstone formation, and lubricating the intestines.