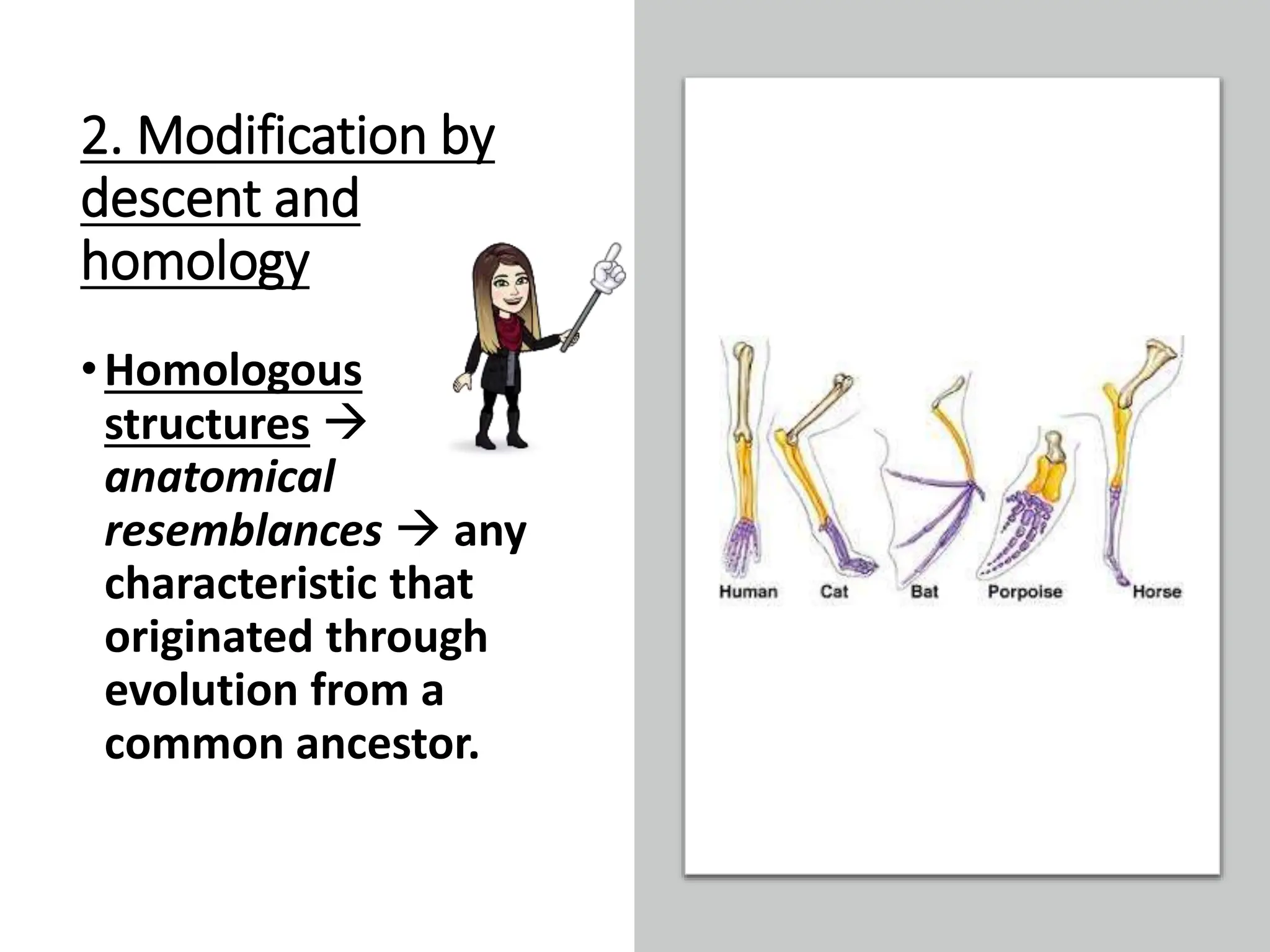
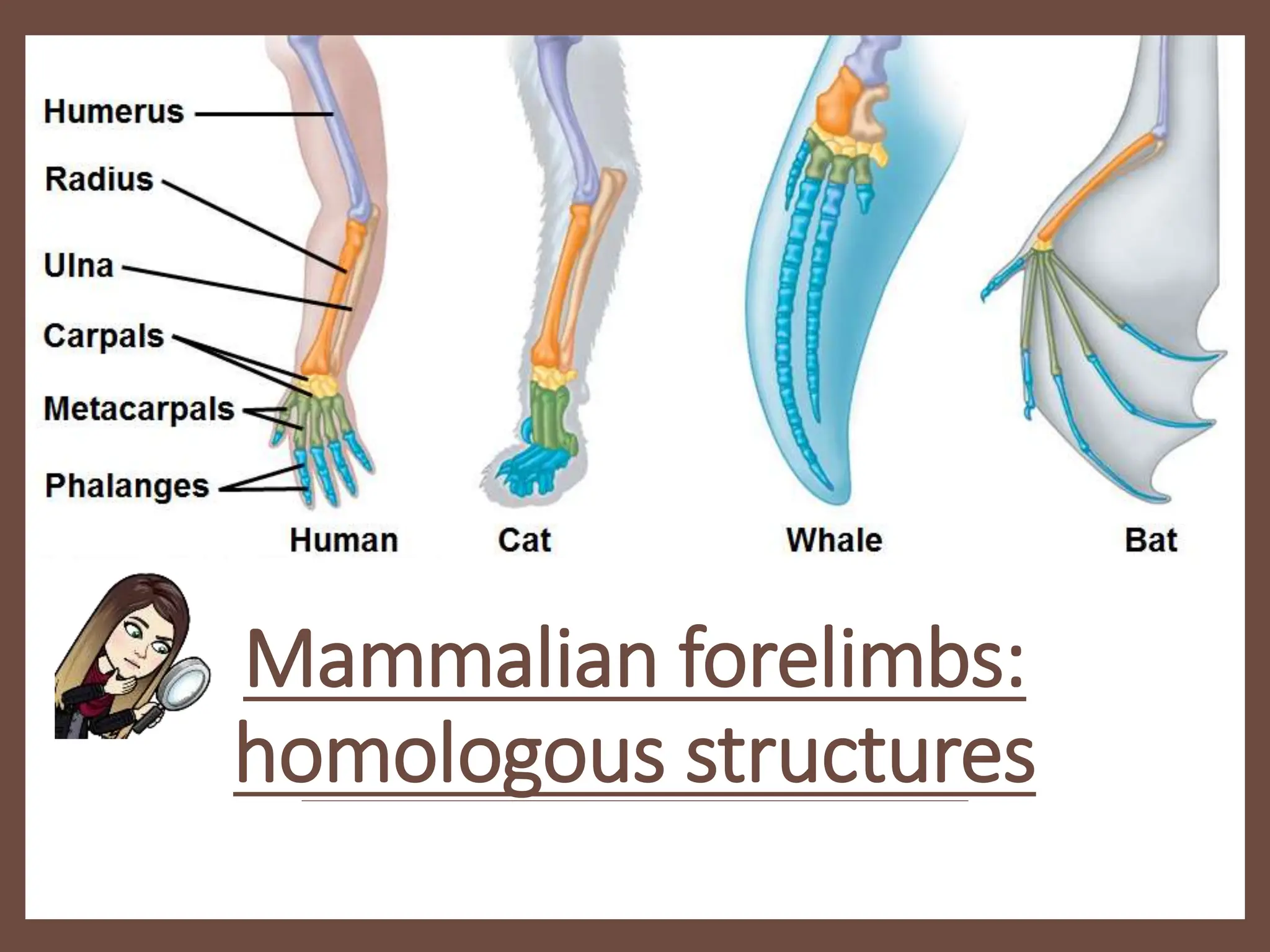
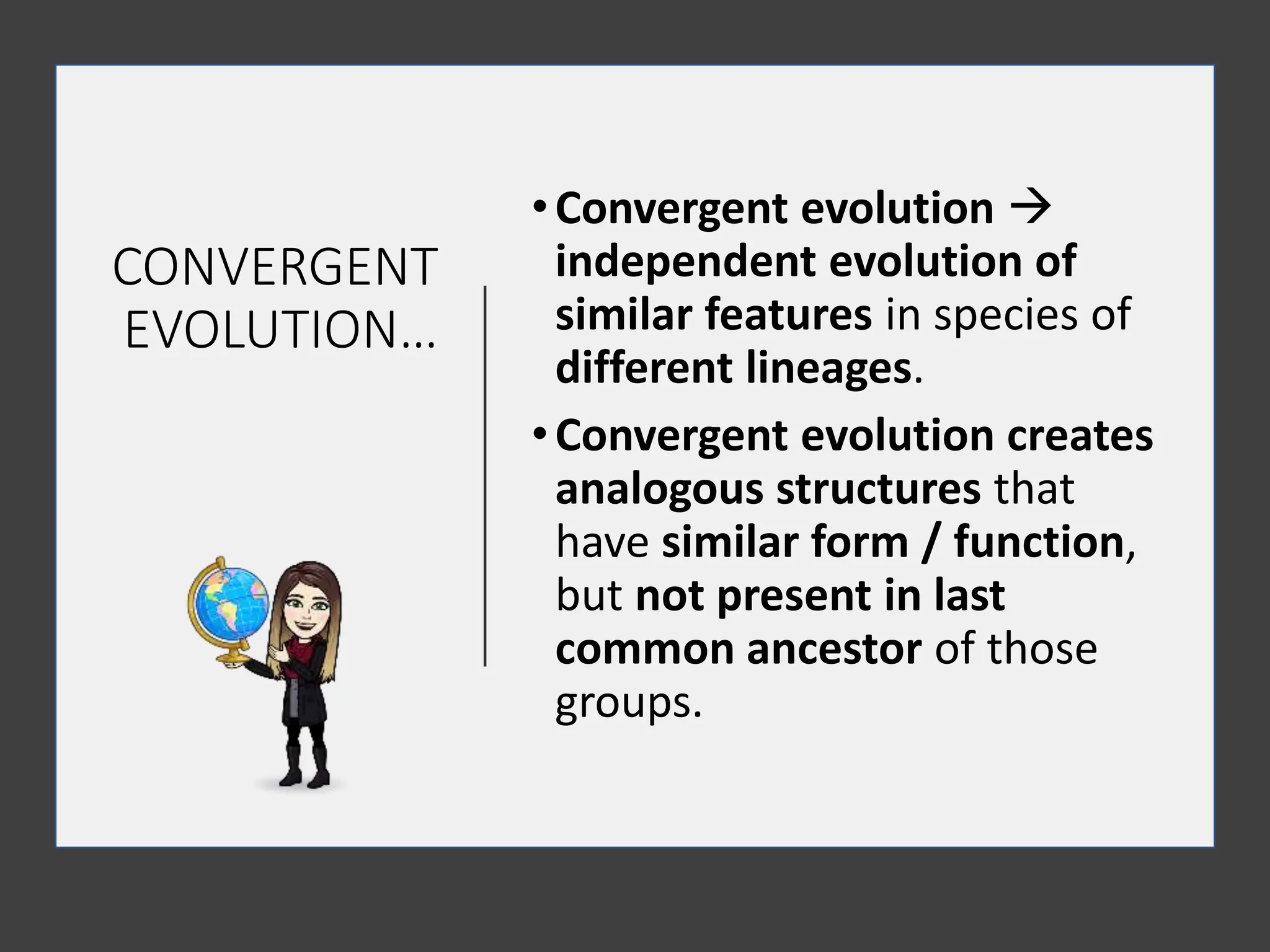
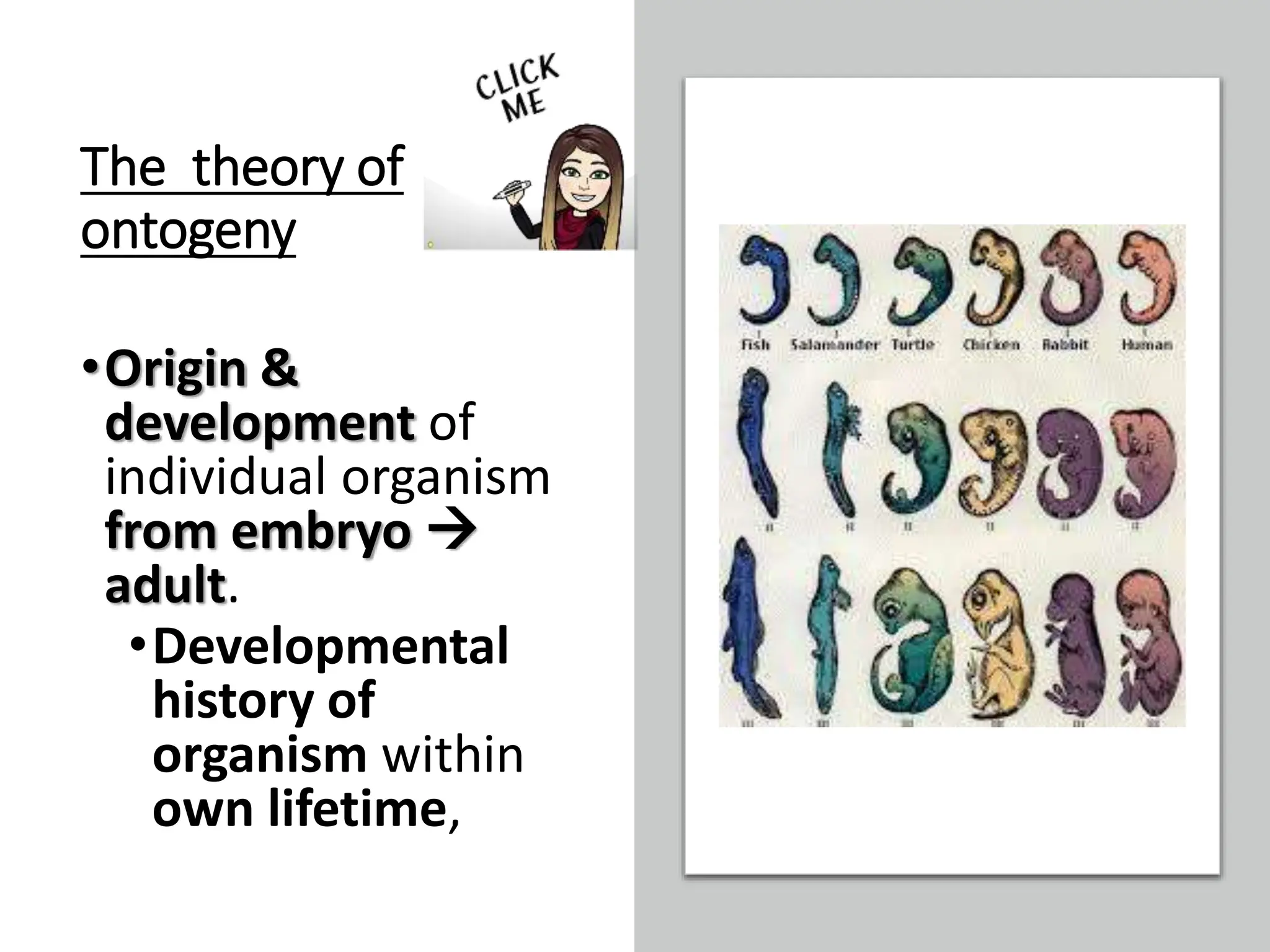
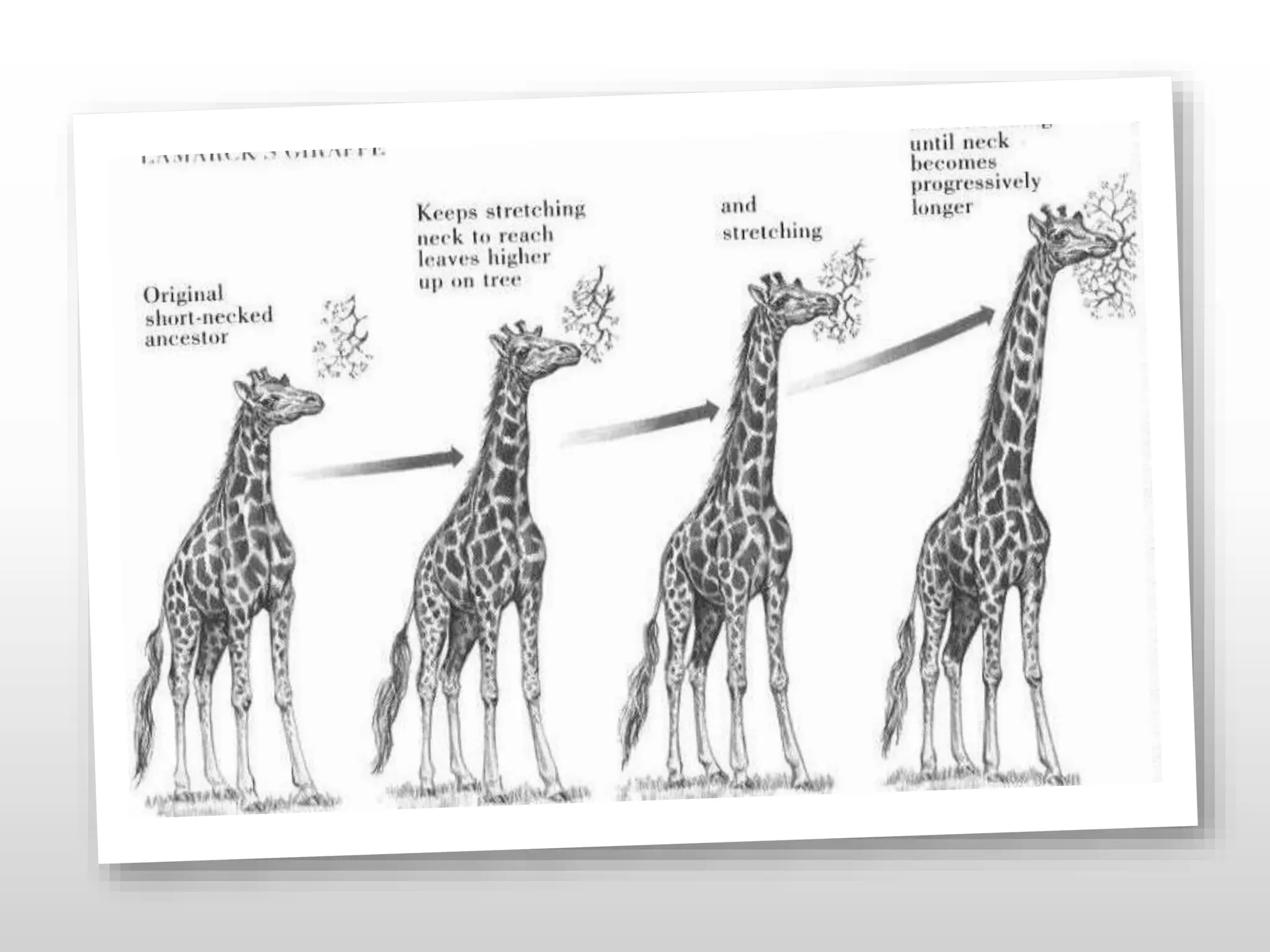
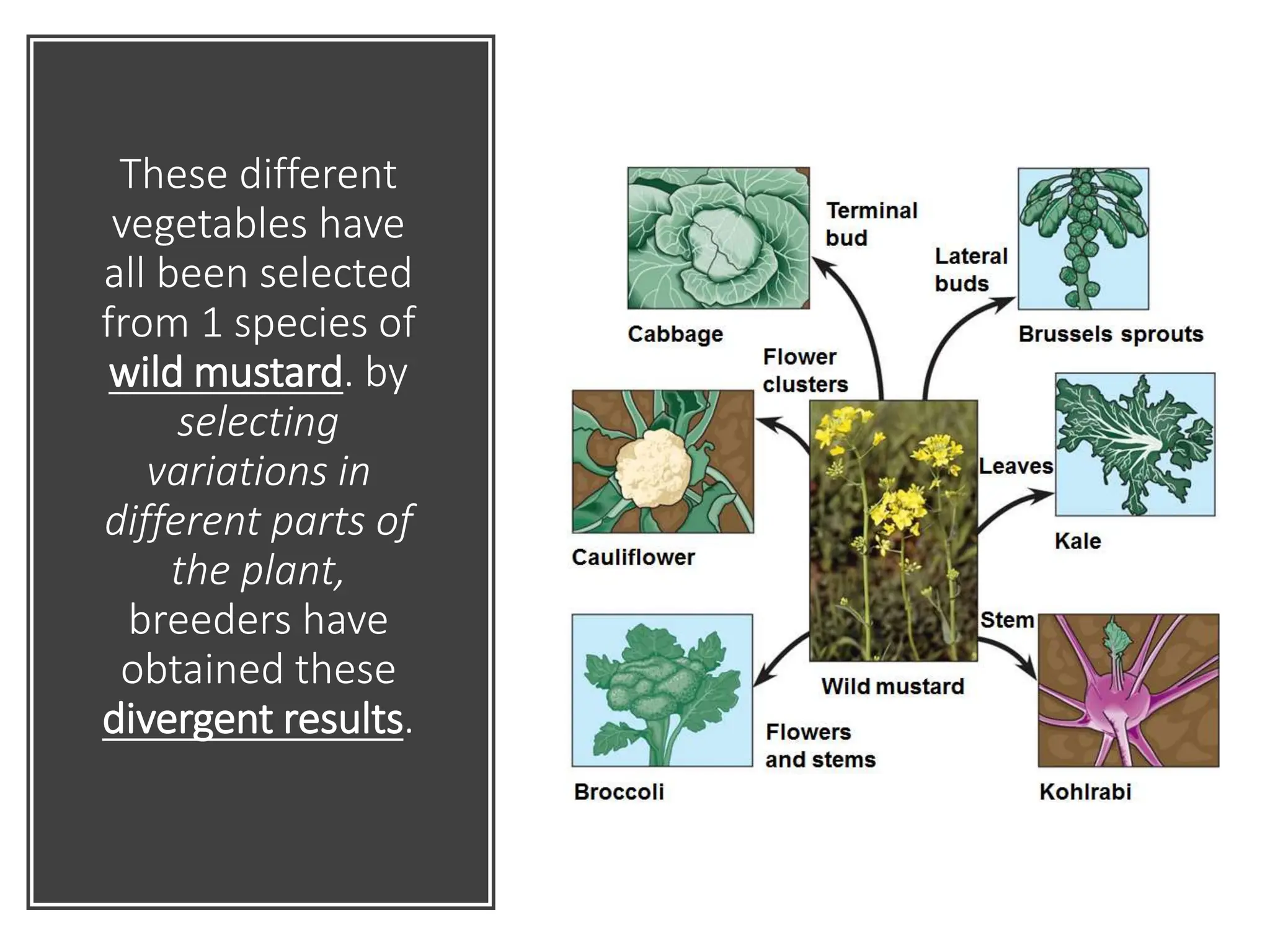
1. Evidence for evolution comes from fossil records, homologous structures, biogeography, and genetics. Fossil records show changes within groups over time, including the origin of new groups and extinction of species. Homologous structures indicate common ancestry. Biogeography, based on patterns of species distribution, allows inferences about when and where groups evolved.
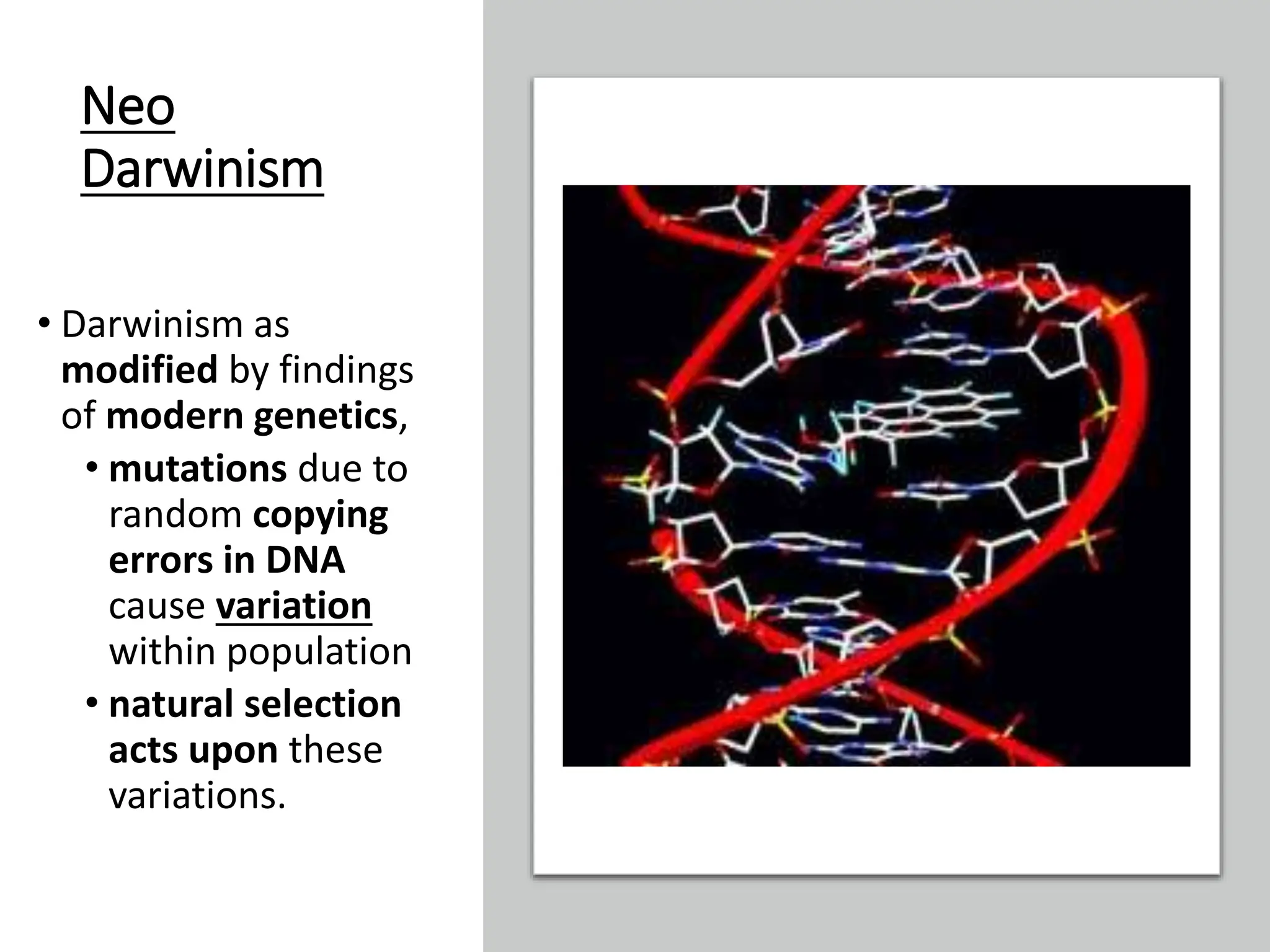
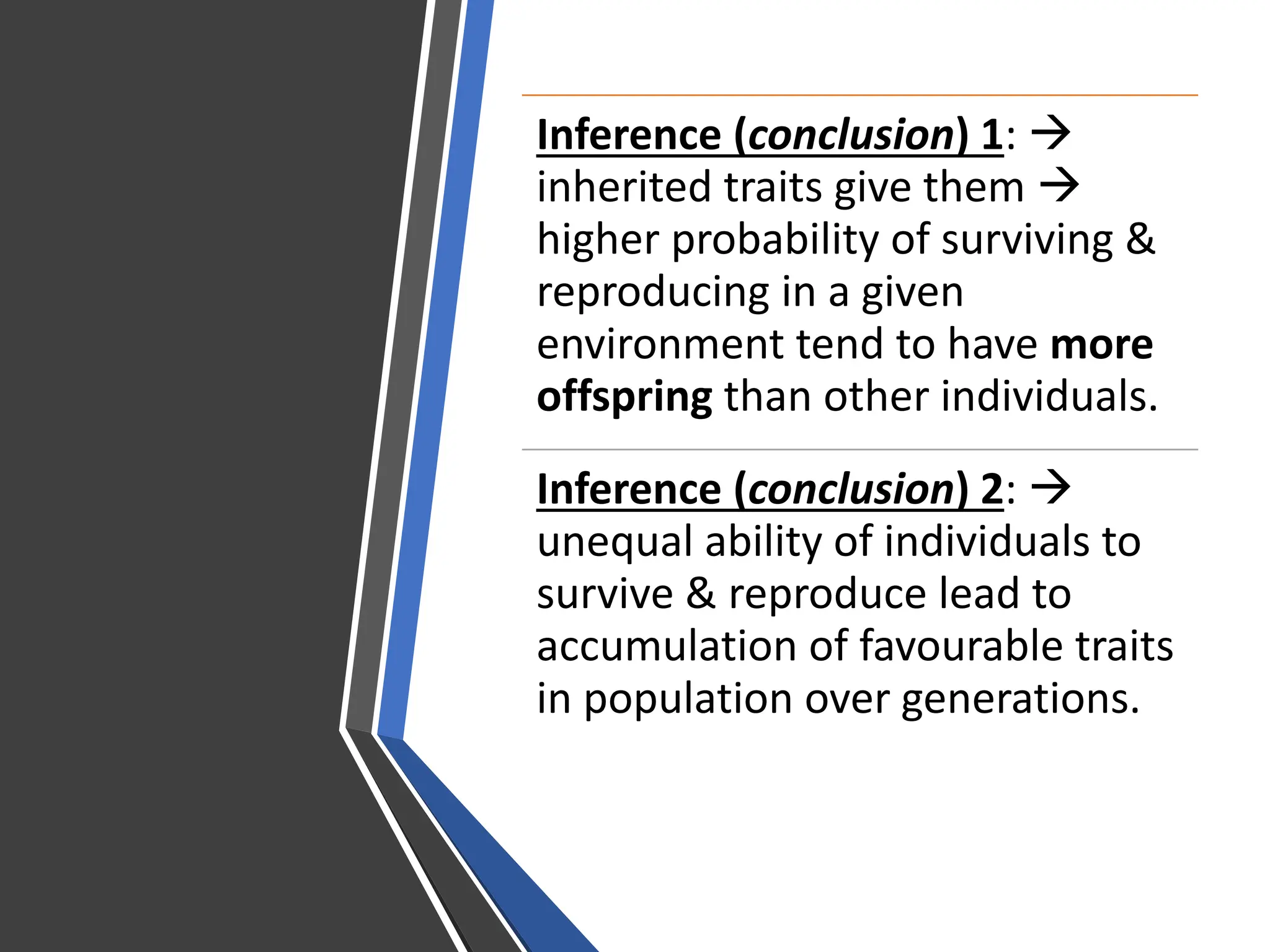
2. Darwin proposed natural selection to explain evolution. He observed variation within populations, inheritance of traits, overproduction of offspring exceeding environmental carrying capacity, and differential survival based on heritable traits. This leads to accumulation of favorable traits and adaptation to the environment over generations.
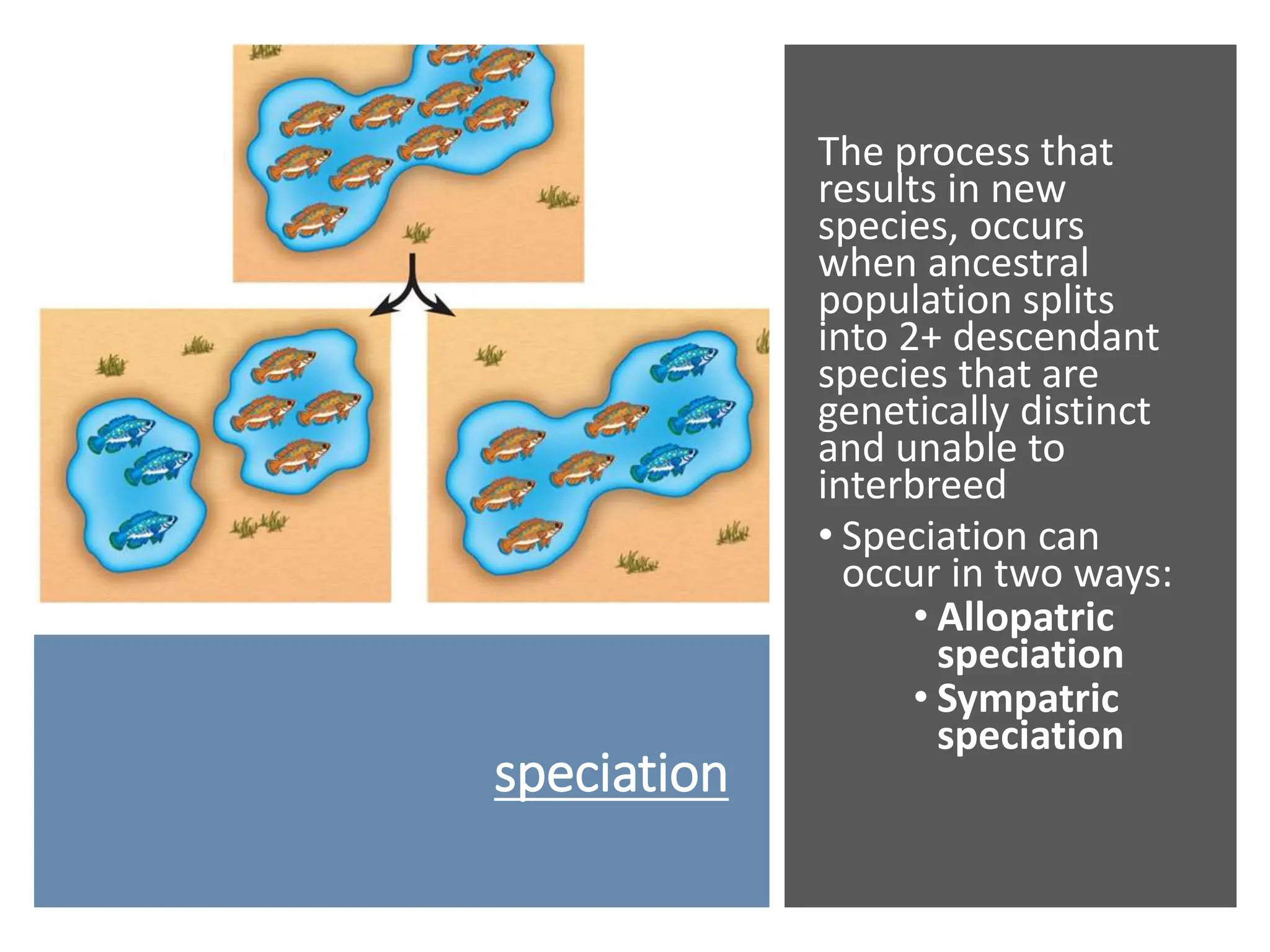
3. Isolation of populations through geographic or reproductive barriers can lead to allopatric or symp