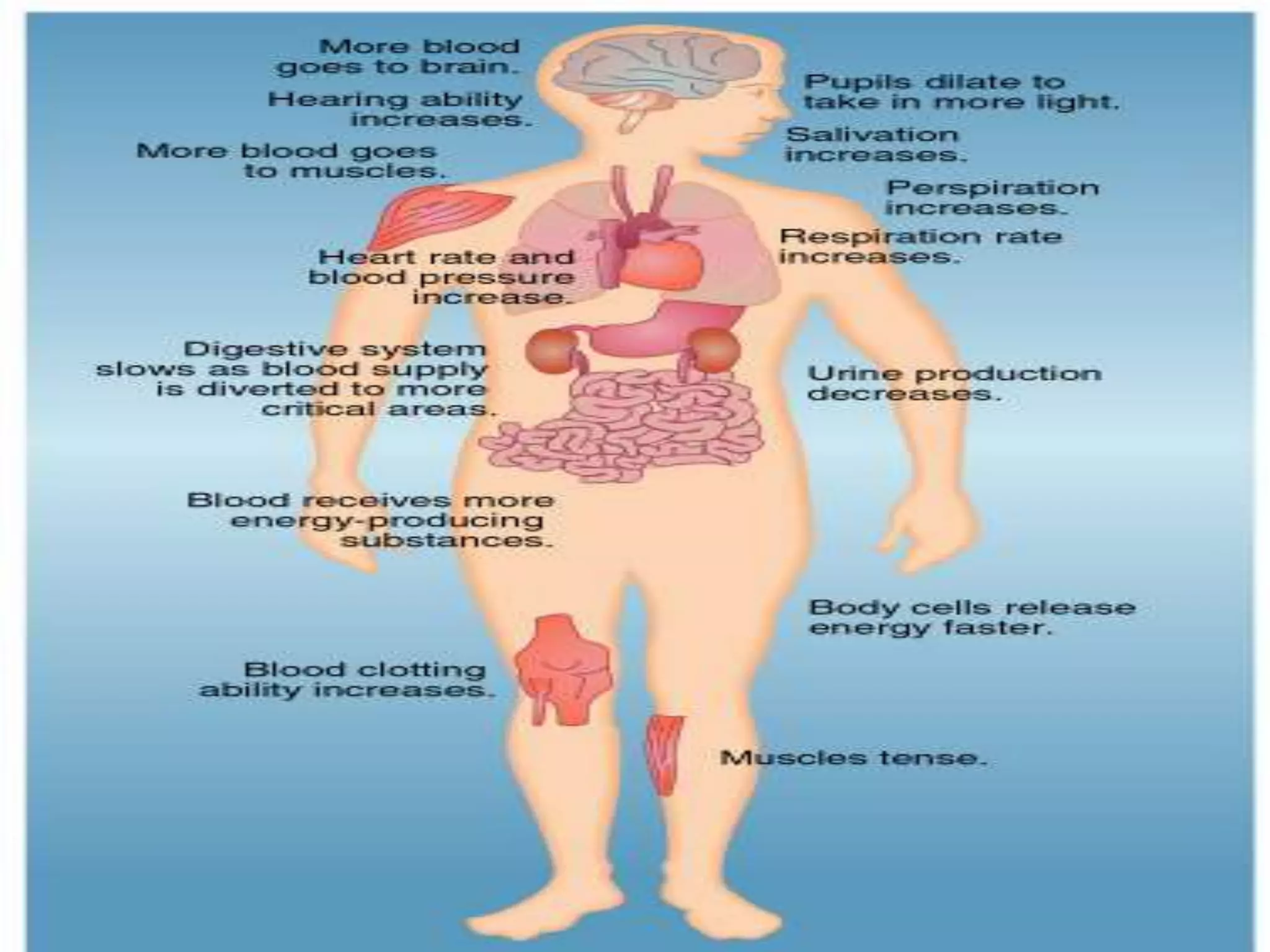
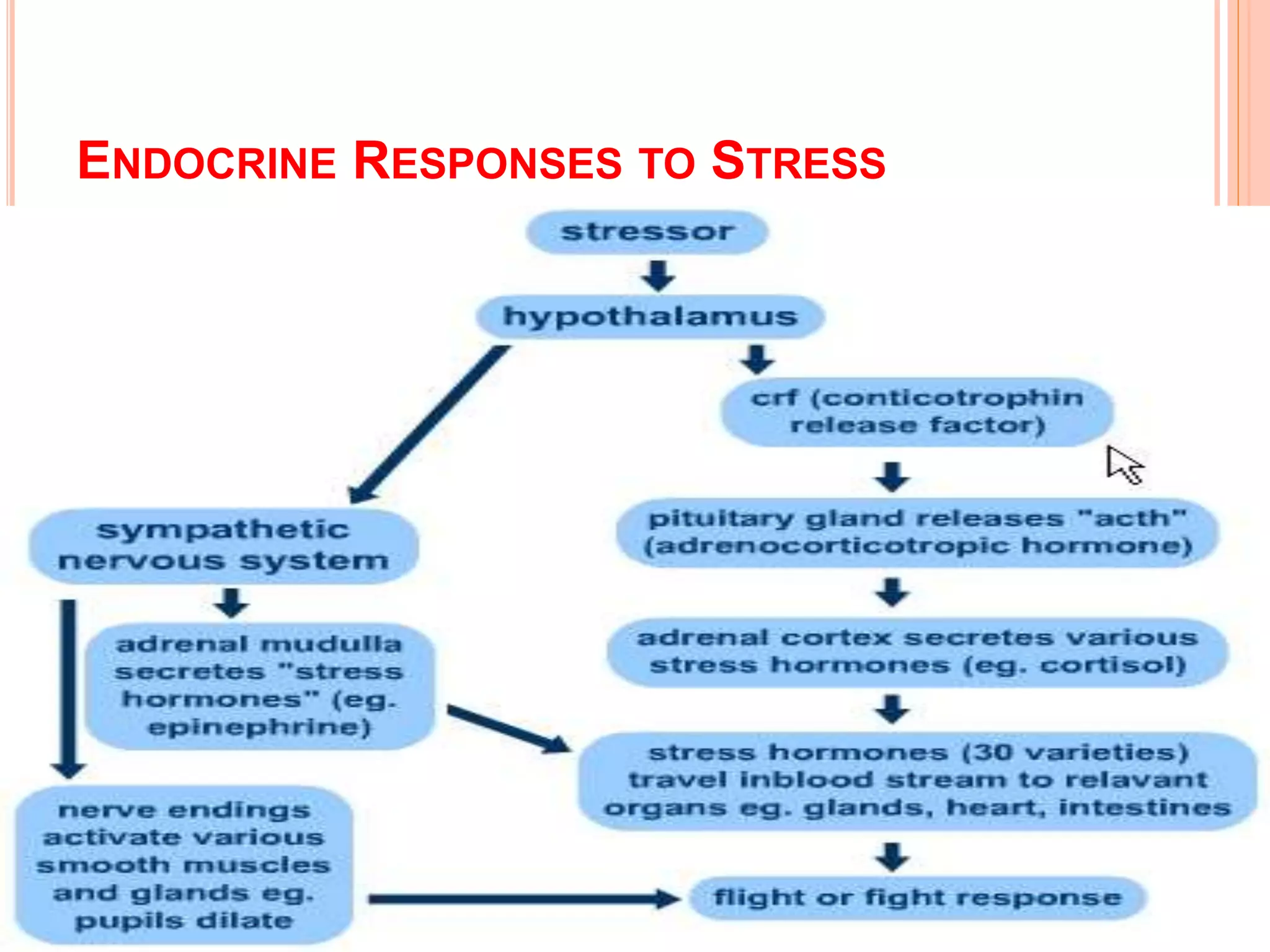
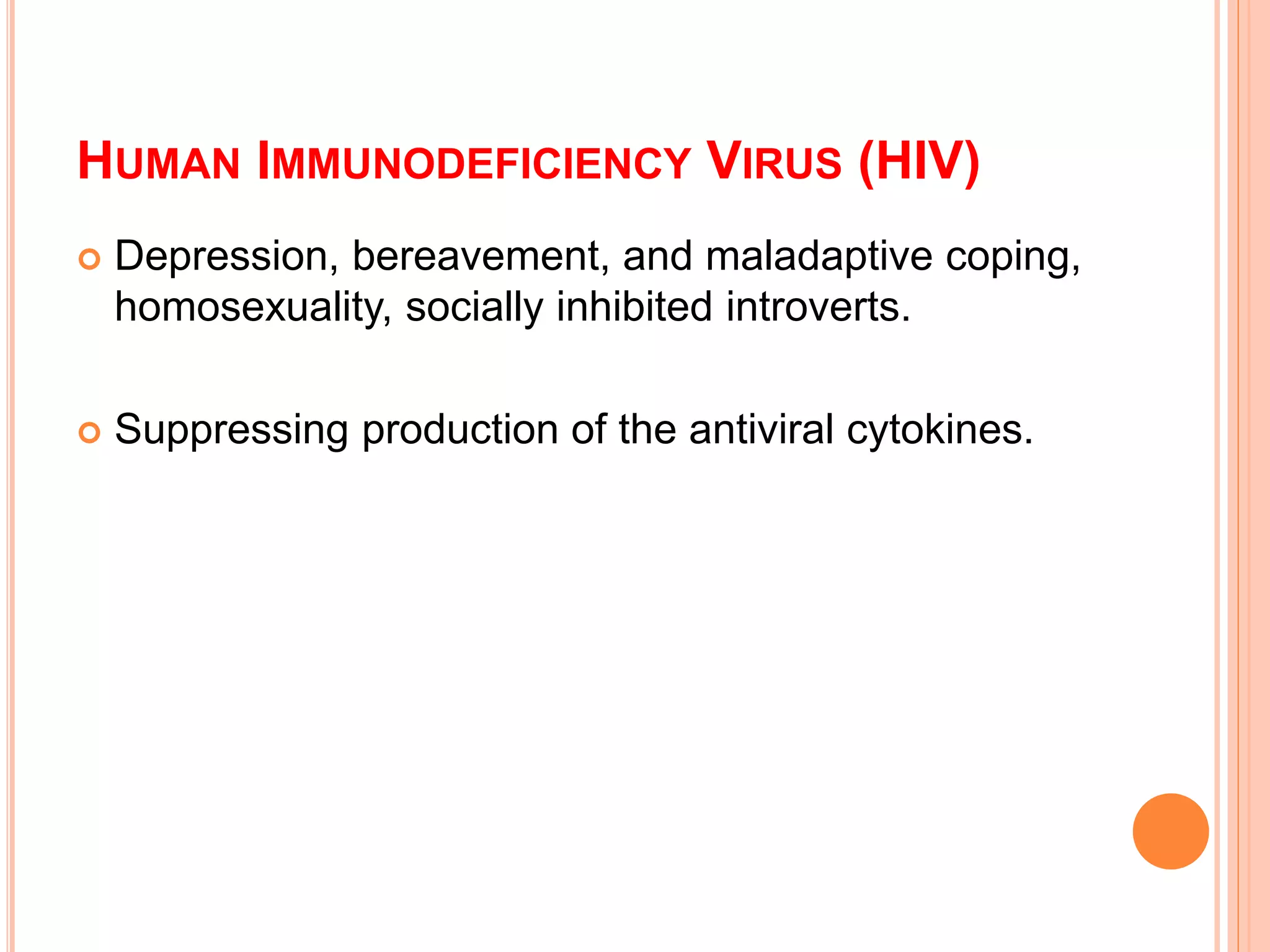
This document discusses stress, its causes and effects. It defines stress as the body's response to real or perceived threats that cause physiological and hormonal changes. Stressors can be traumatic events, uncontrollable events, unpredictable events or events that challenge one's capabilities. Positive or eustress motivates action while negative or distress overwhelms the body and mind. The stress response involves the autonomic nervous system, neuroendocrine and immune systems. Chronic stress can increase inflammation and susceptibility to disease. Managing stress through coping behaviors and interventions can benefit mental and physical health.