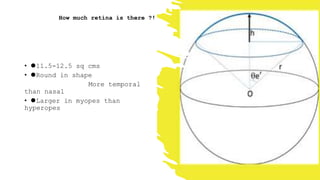
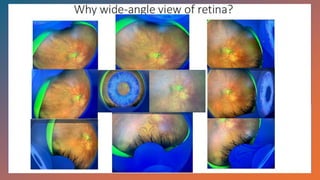
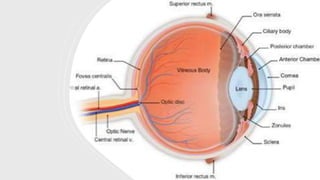
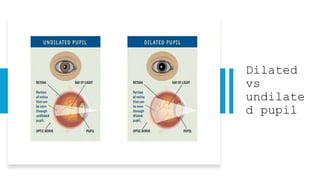
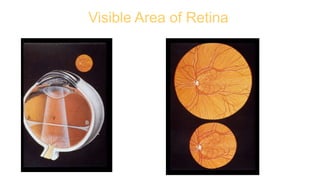
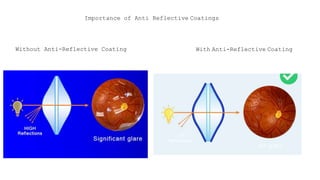
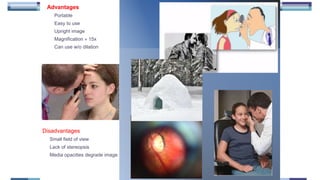
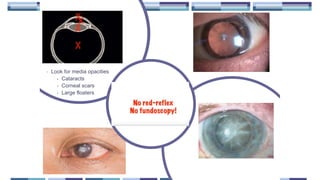
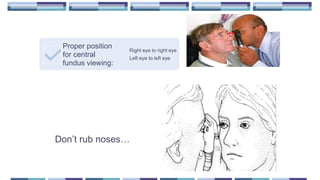
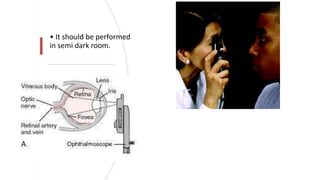
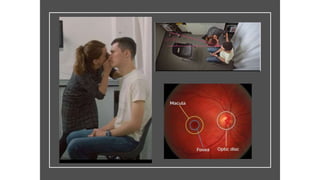
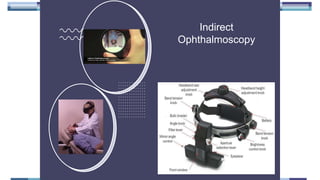
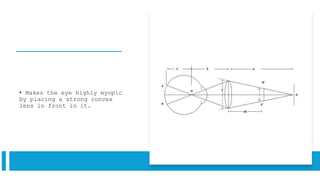
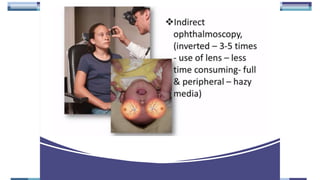
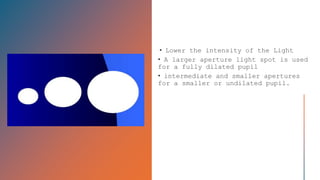
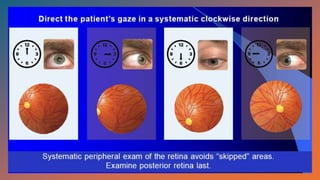
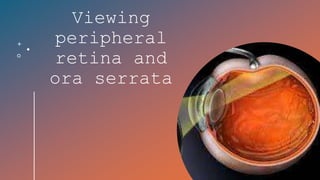
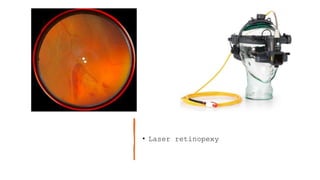
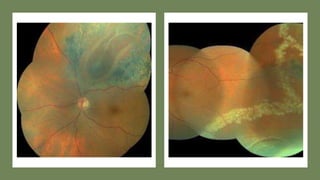
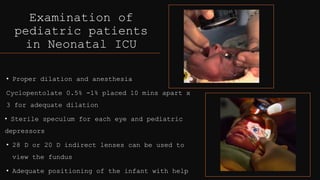
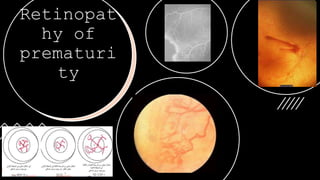
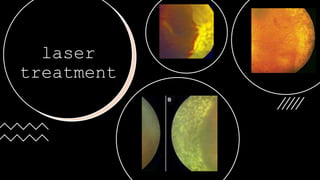
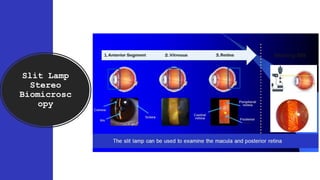
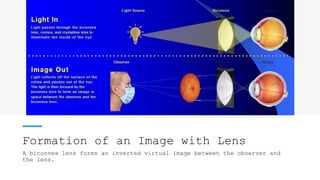
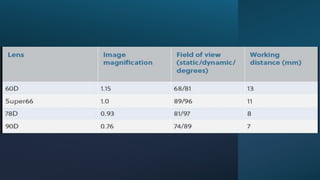
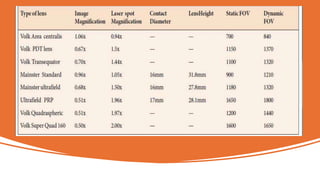
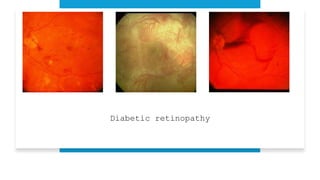
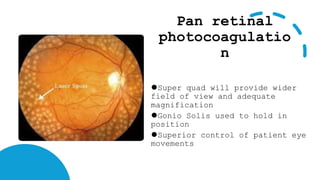
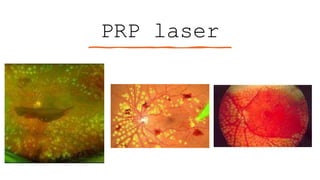
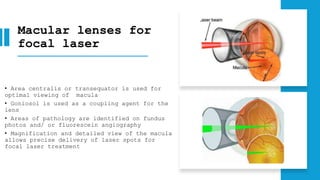
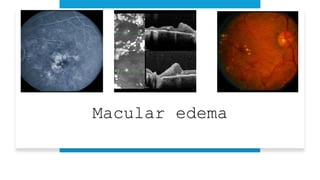
The document outlines techniques and considerations for fundoscopic examinations, including the purpose and methods for assessing the retina. It discusses dilation medications, different lenses for indirect and direct ophthalmoscopy, and the importance of patient cooperation and proper positioning. Various lenses are described for specific retinal examinations, along with their features and applications in conditions like diabetic retinopathy.