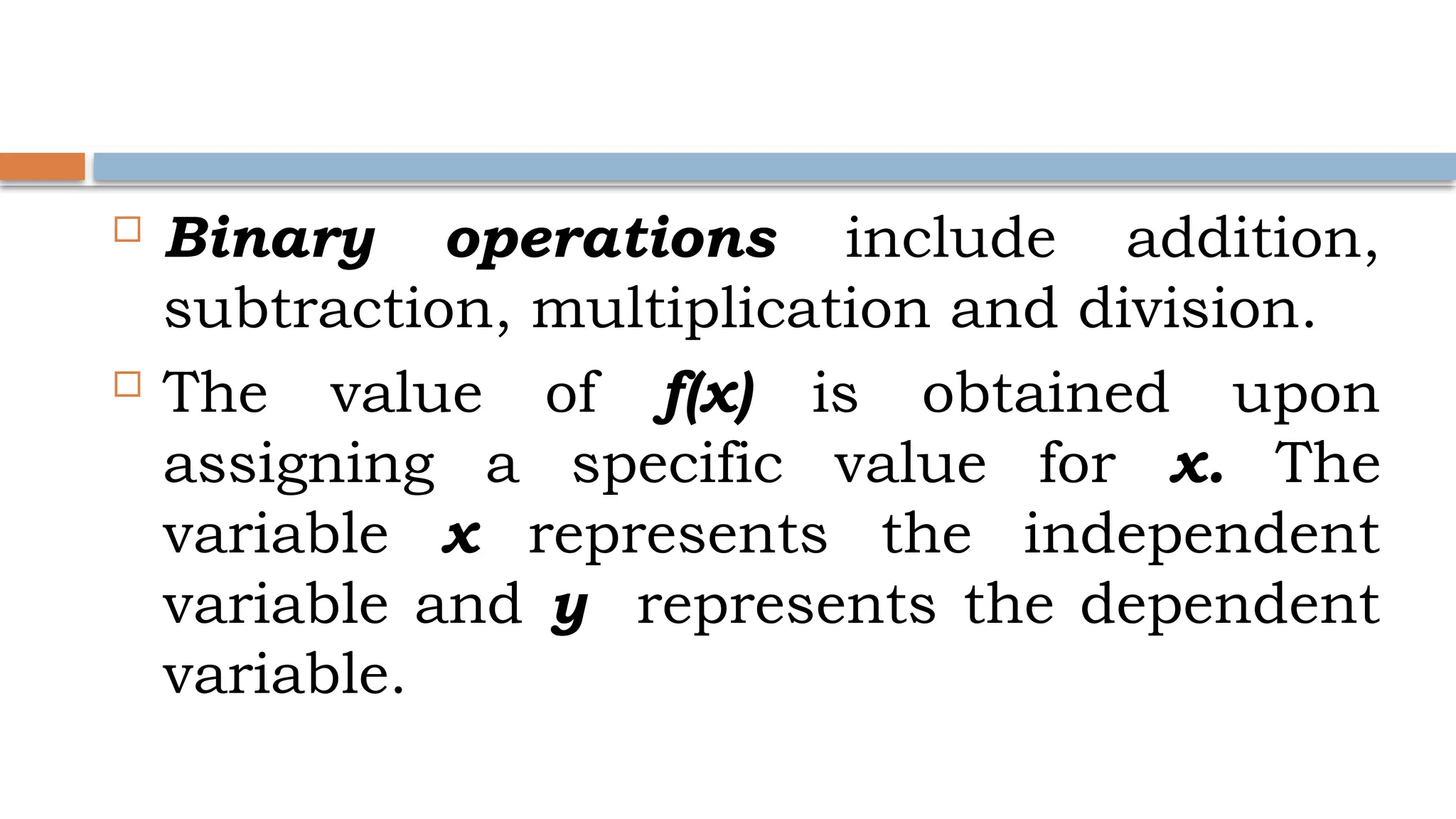
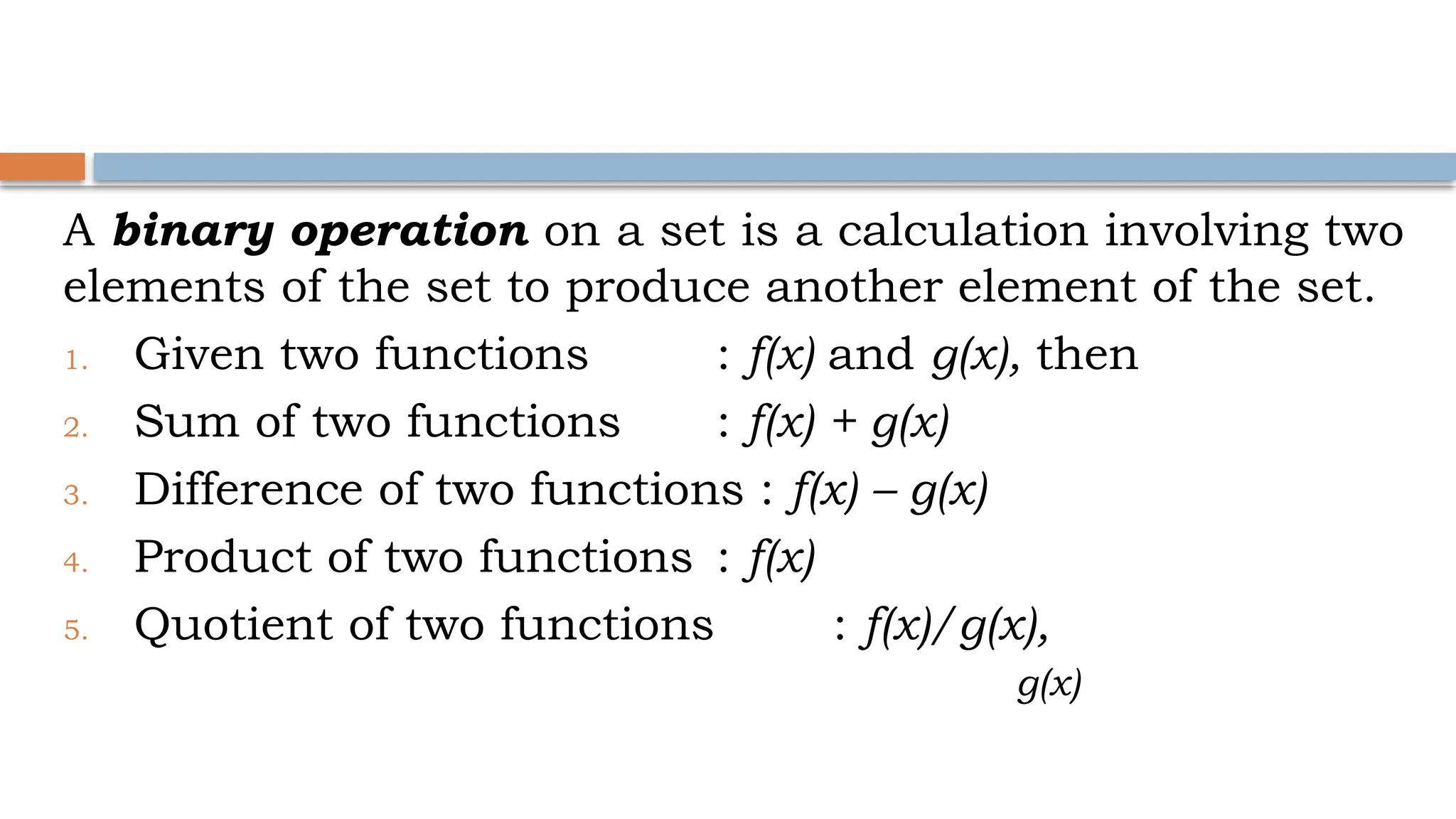
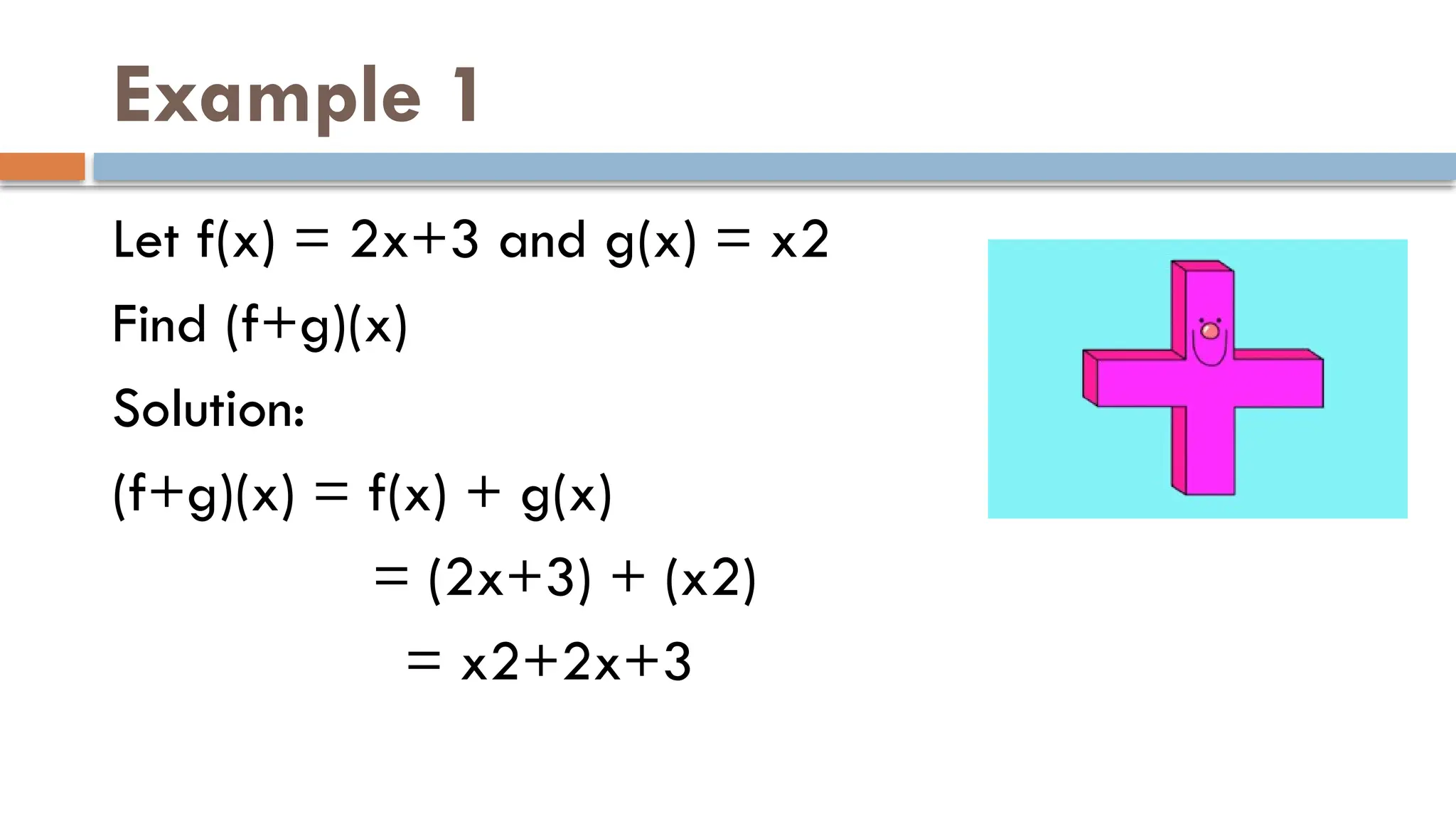
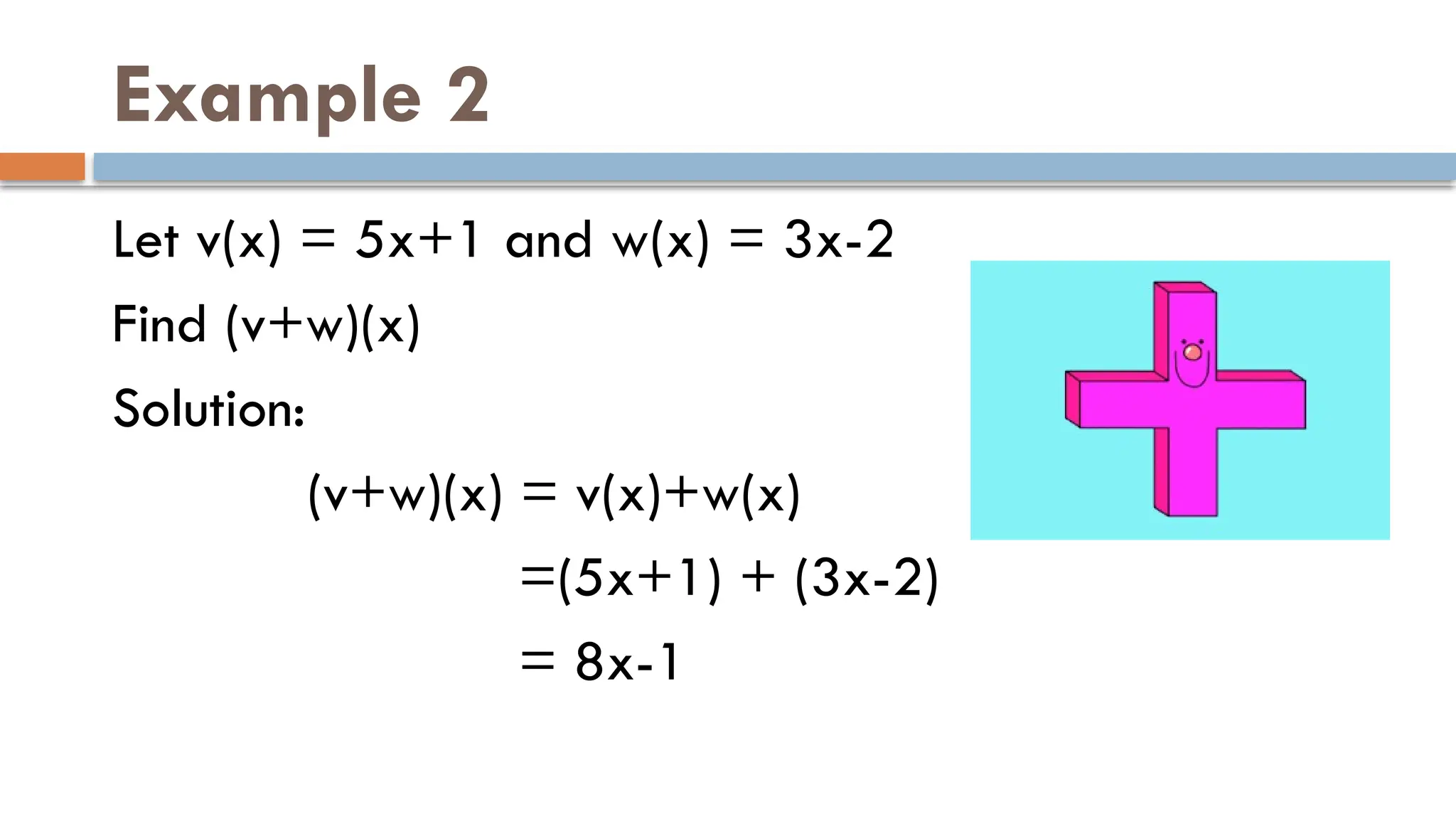
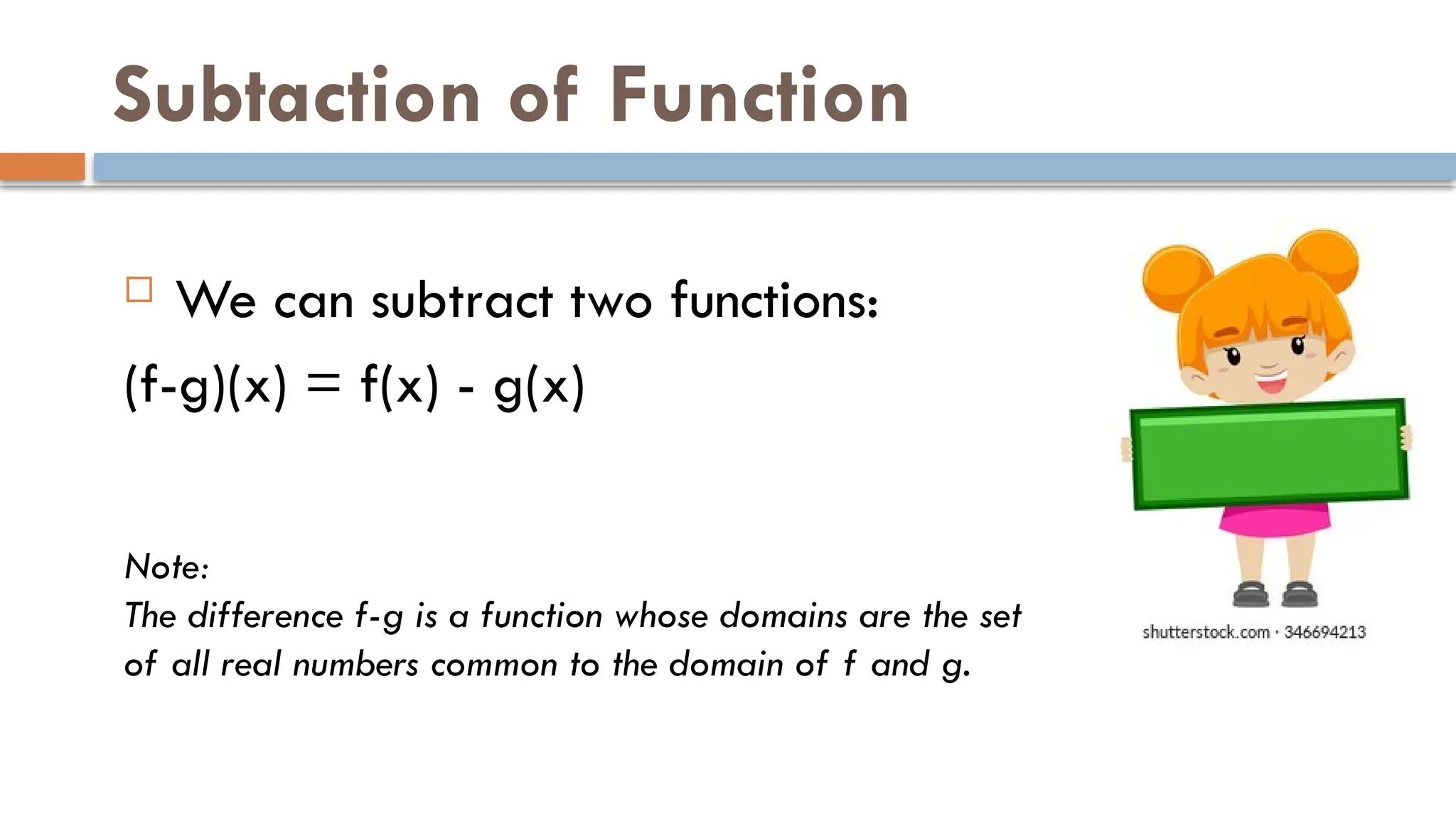
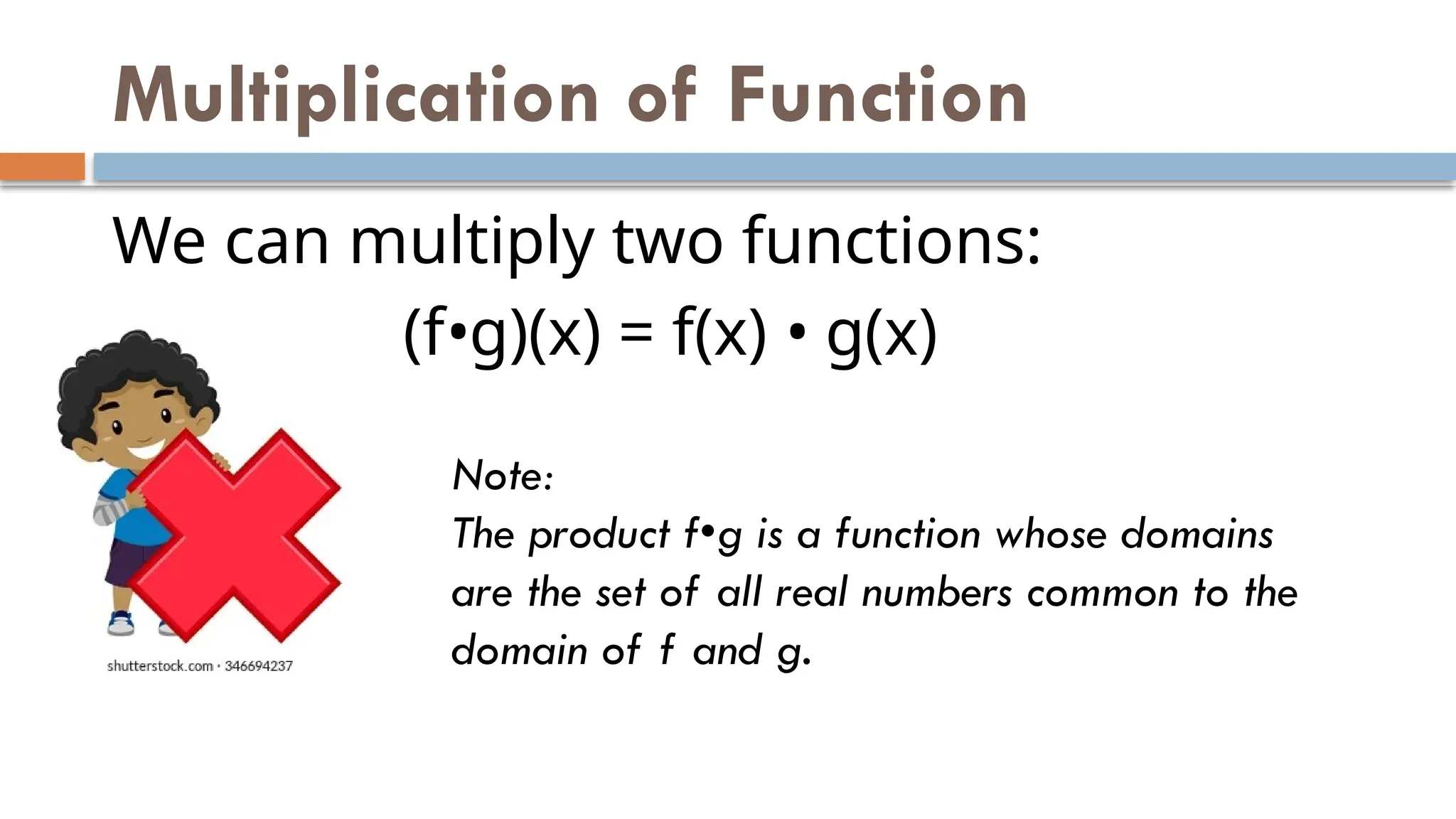
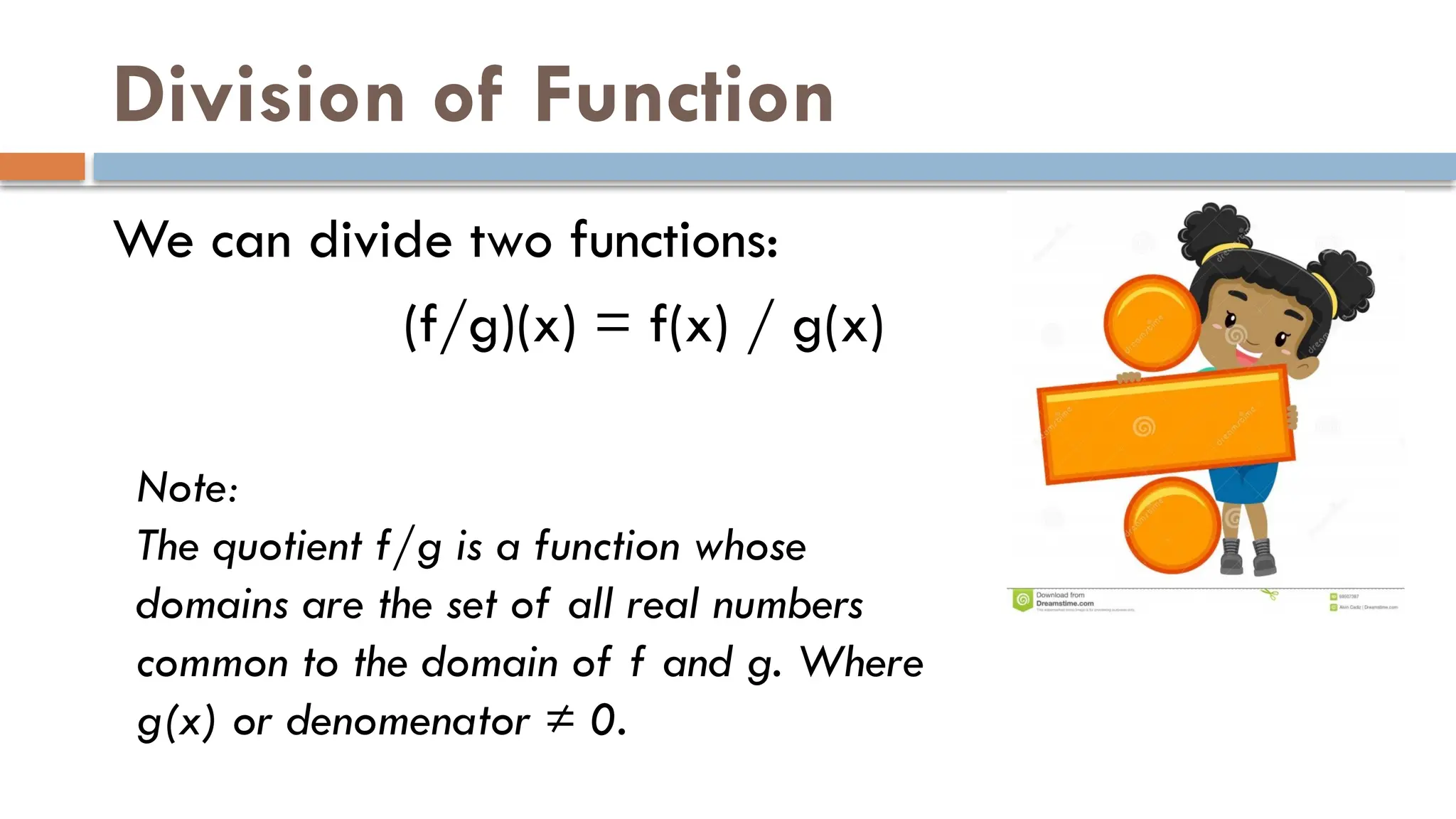
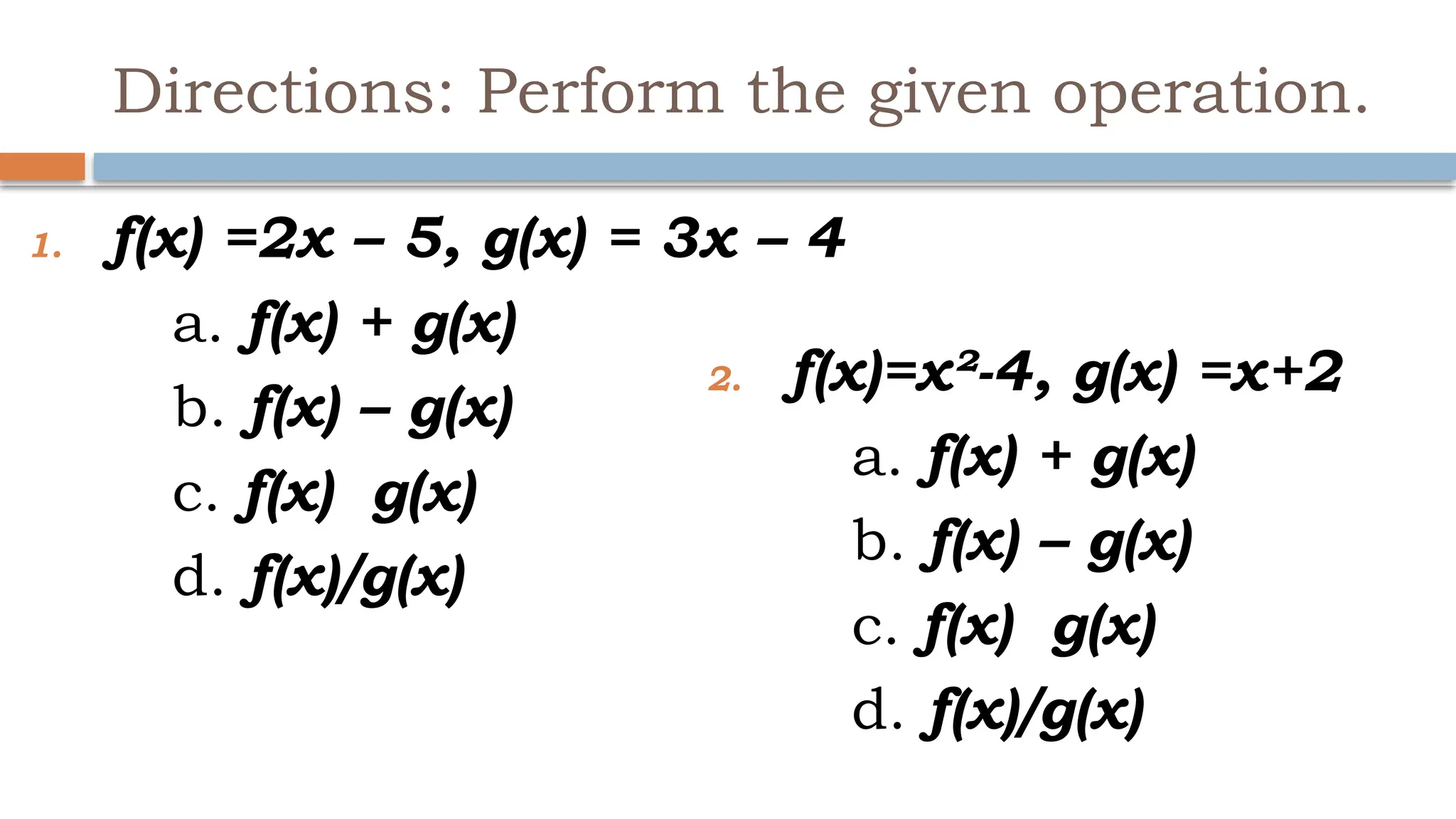
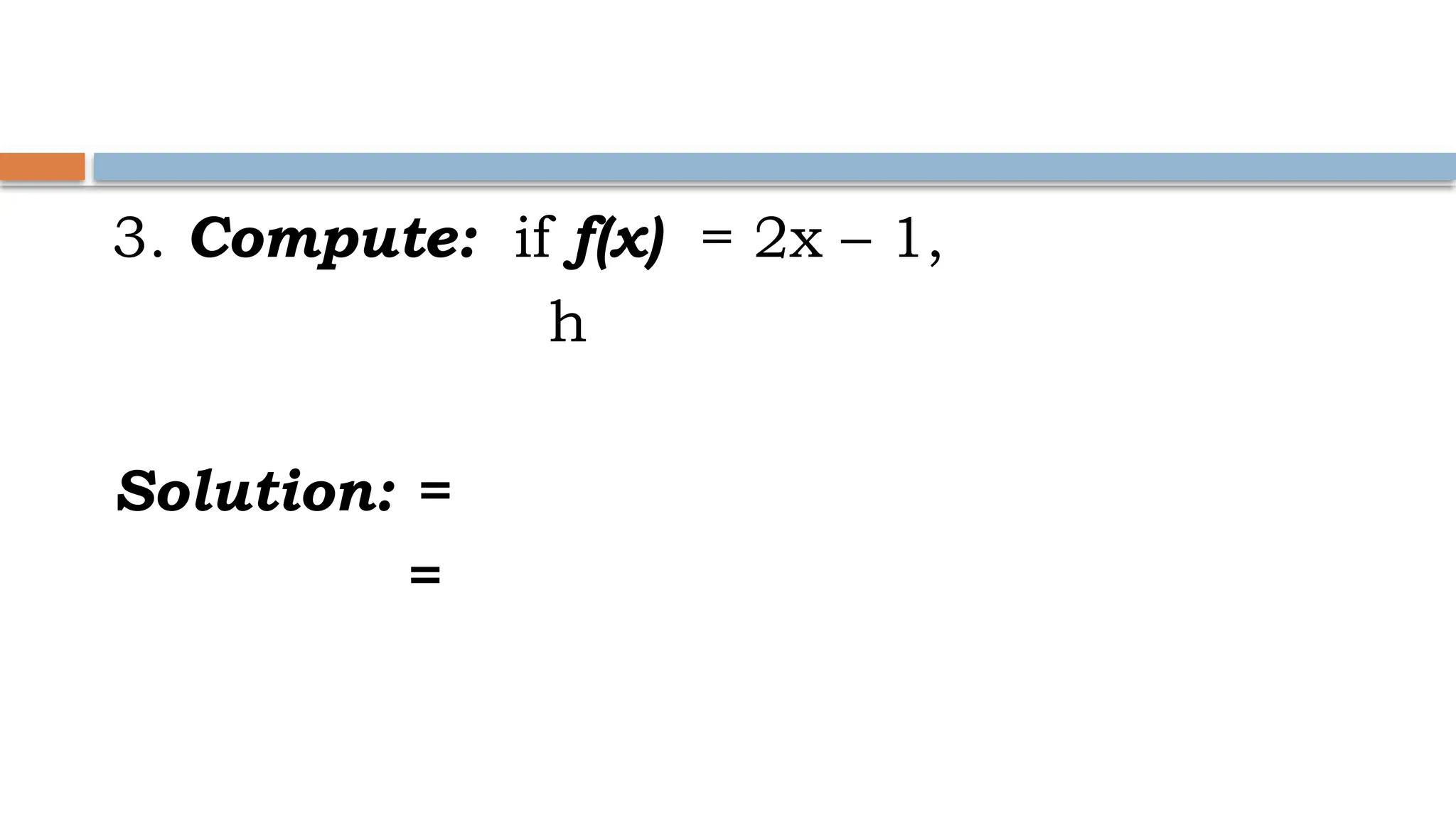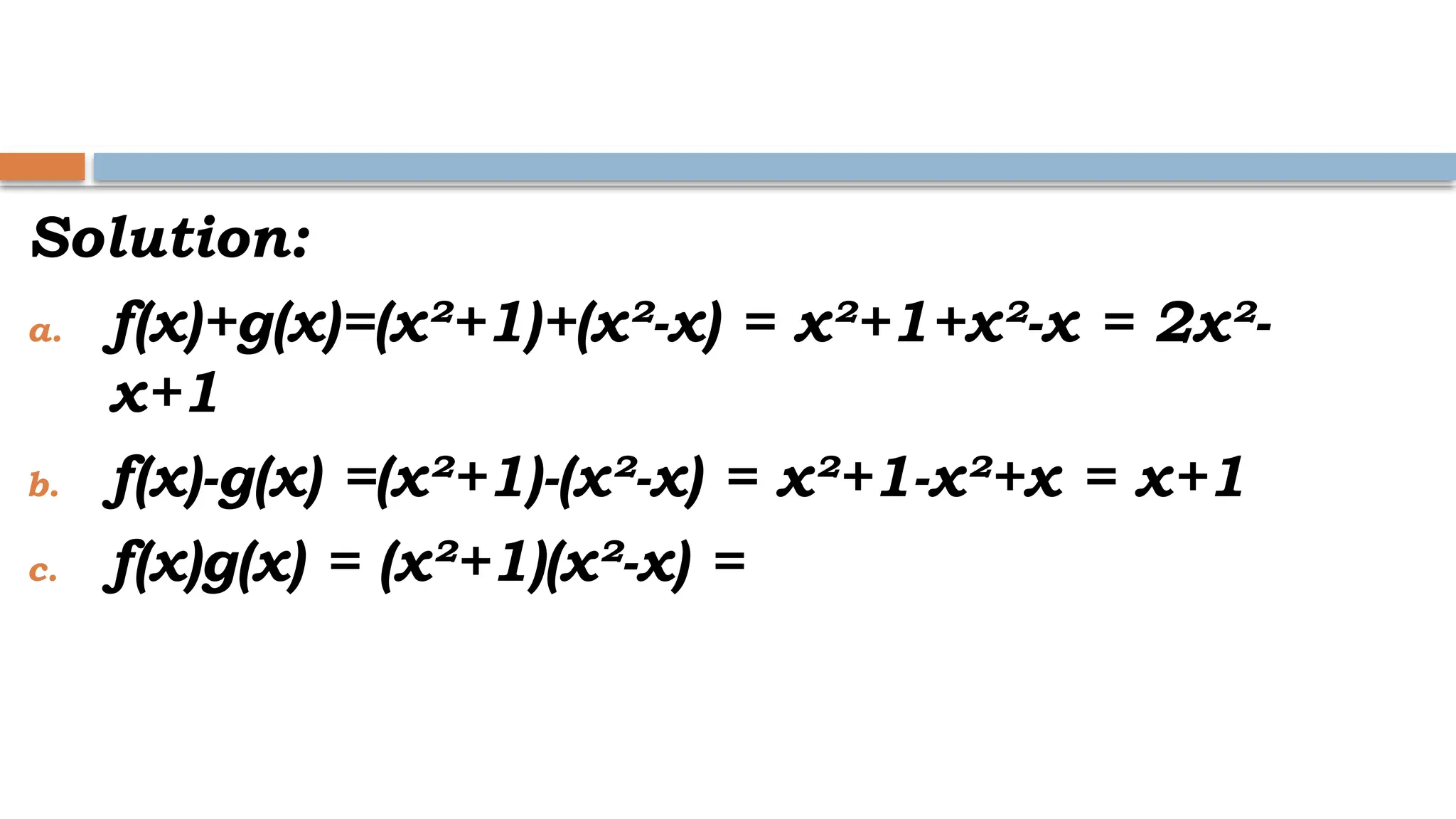The document explains binary operations on a set, describing how each pair of elements produces a unique response also within the set. It outlines operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of functions, providing examples for each. Additionally, it includes specific calculations of function values and operations involving given functions.