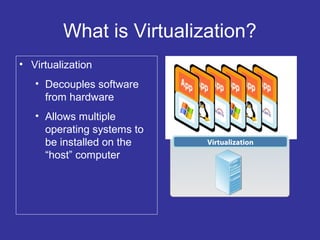
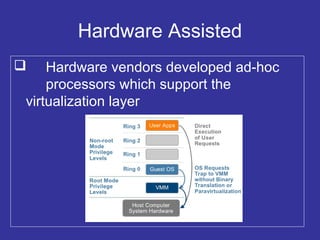
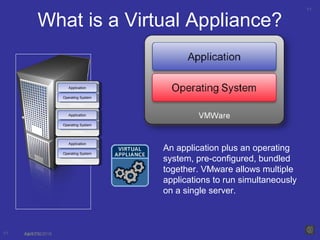
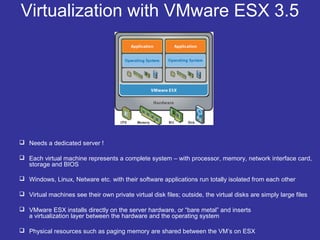
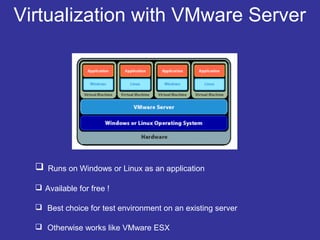
Virtualization is a technique that separates a service from the underlying physical hardware. It allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on a single computer by decoupling the software from the hardware. There are two main approaches - hosted virtualization runs atop an operating system, while hypervisor-based virtualization installs directly on the hardware for better performance and scalability. A virtualization layer called a VMM manages and partitions CPU, memory, and I/O access for the guest operating systems. Virtualization overcomes the challenge that x86 operating systems assume sole ownership of the hardware through techniques like binary translation, para-virtualization with OS assistance, or newer hardware-assisted virtualization.