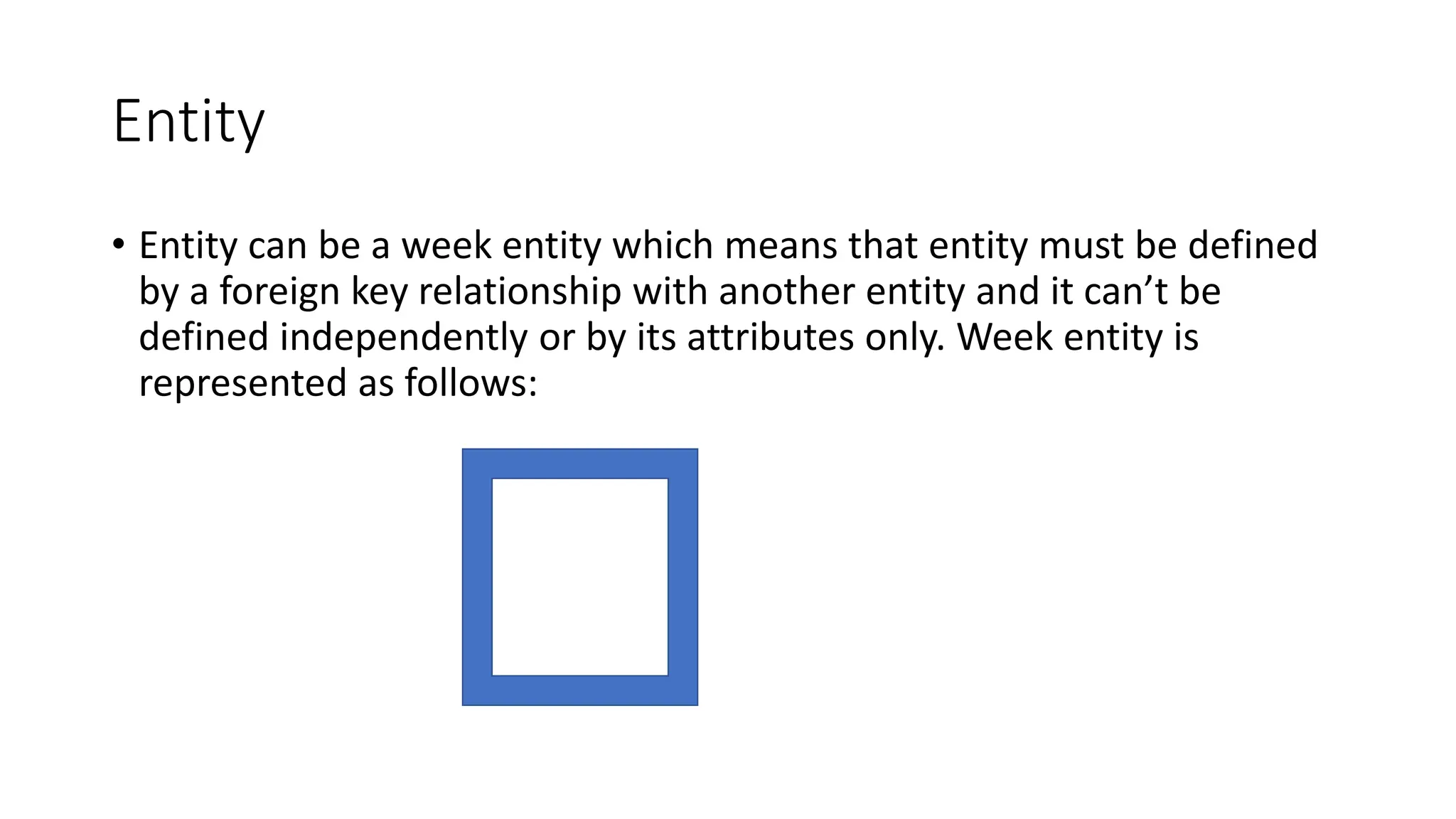
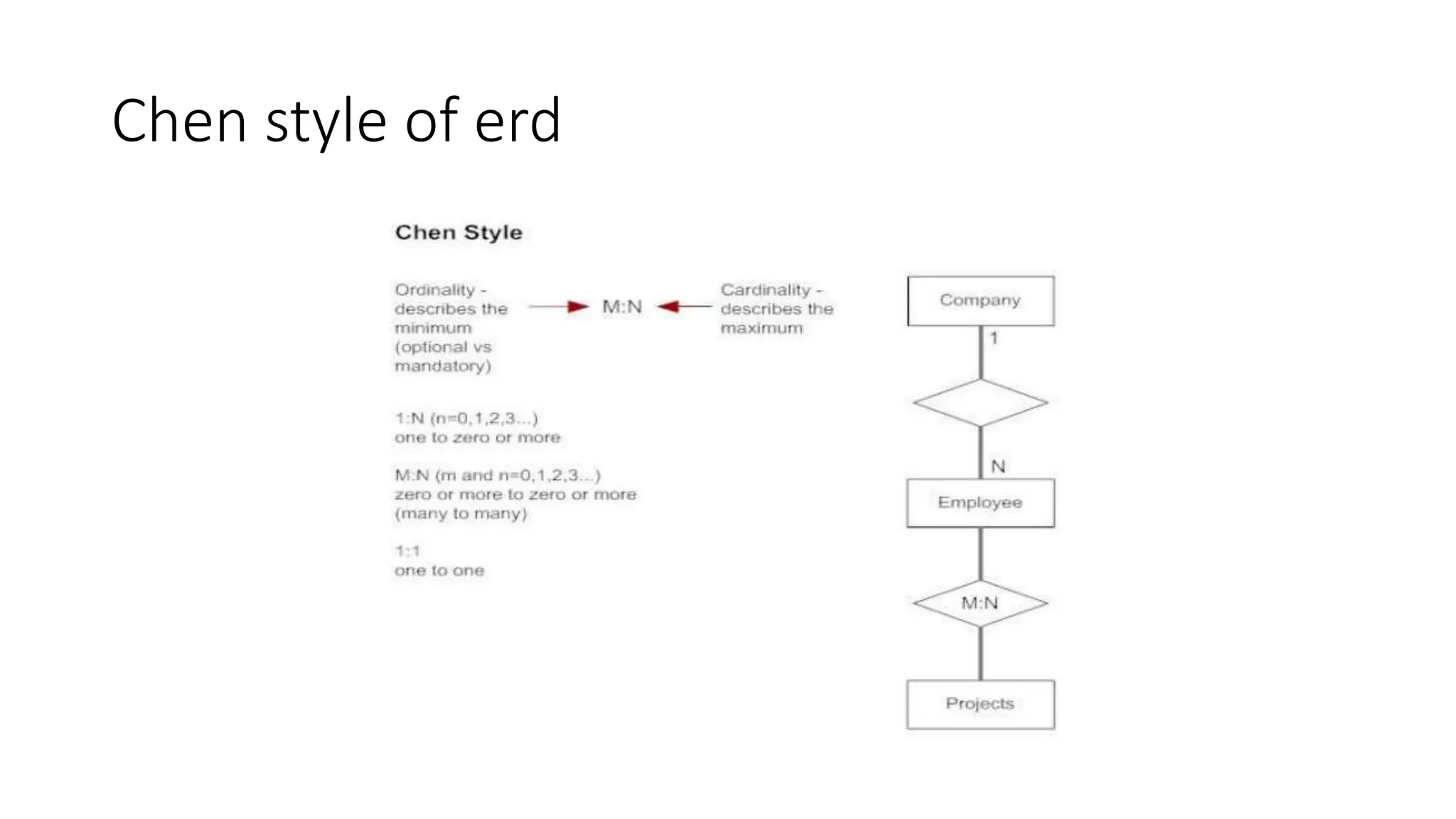
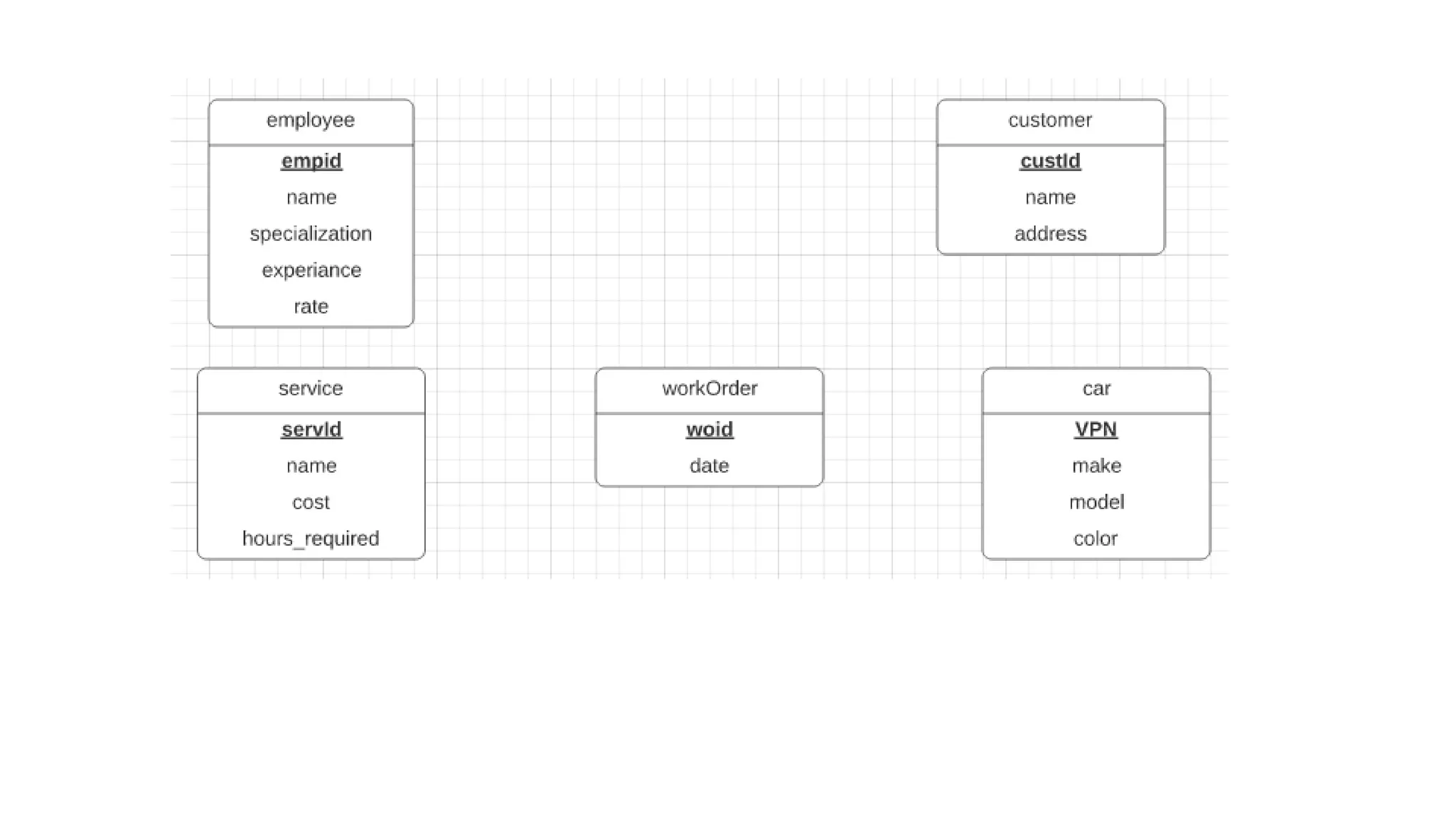
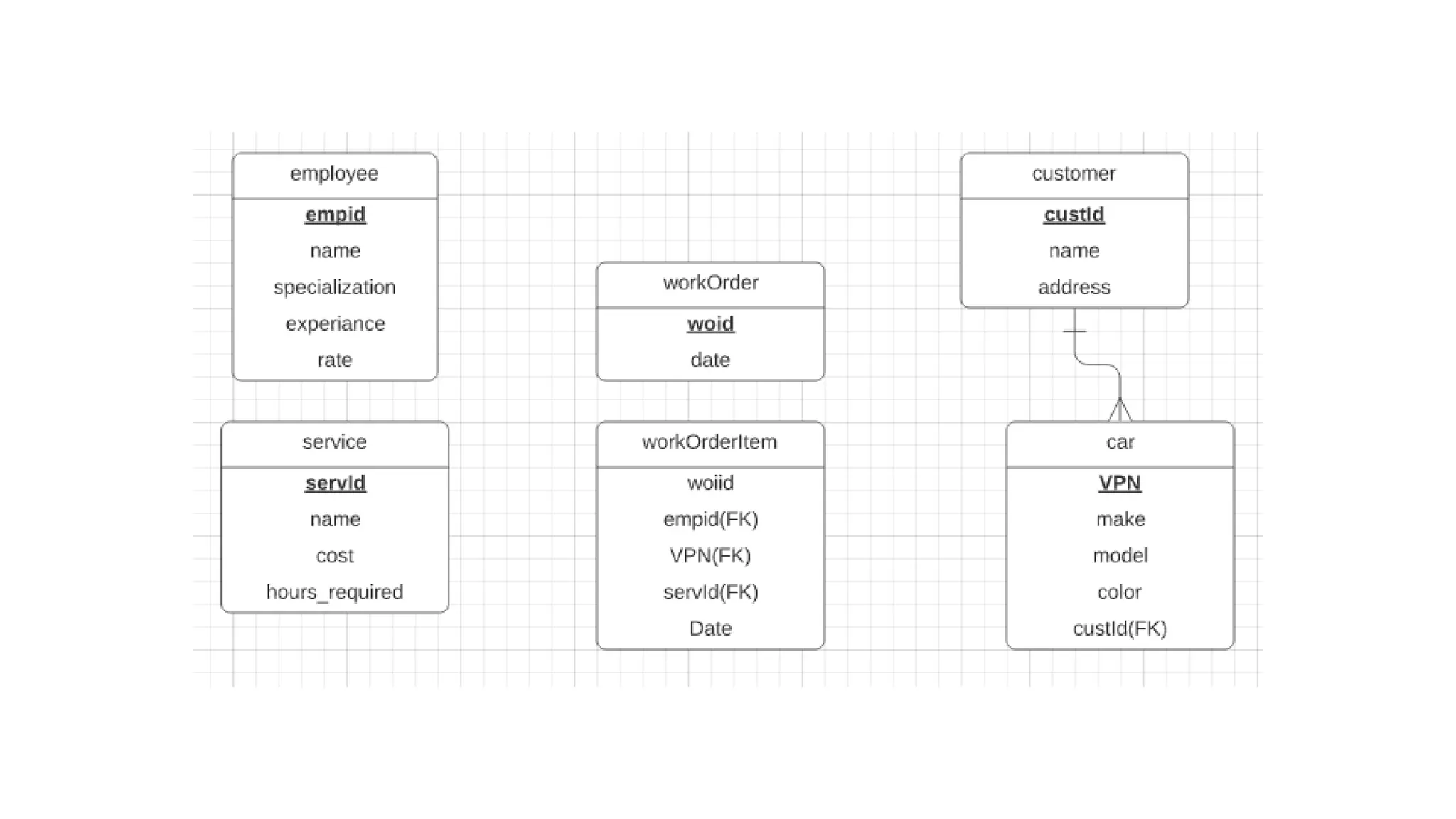
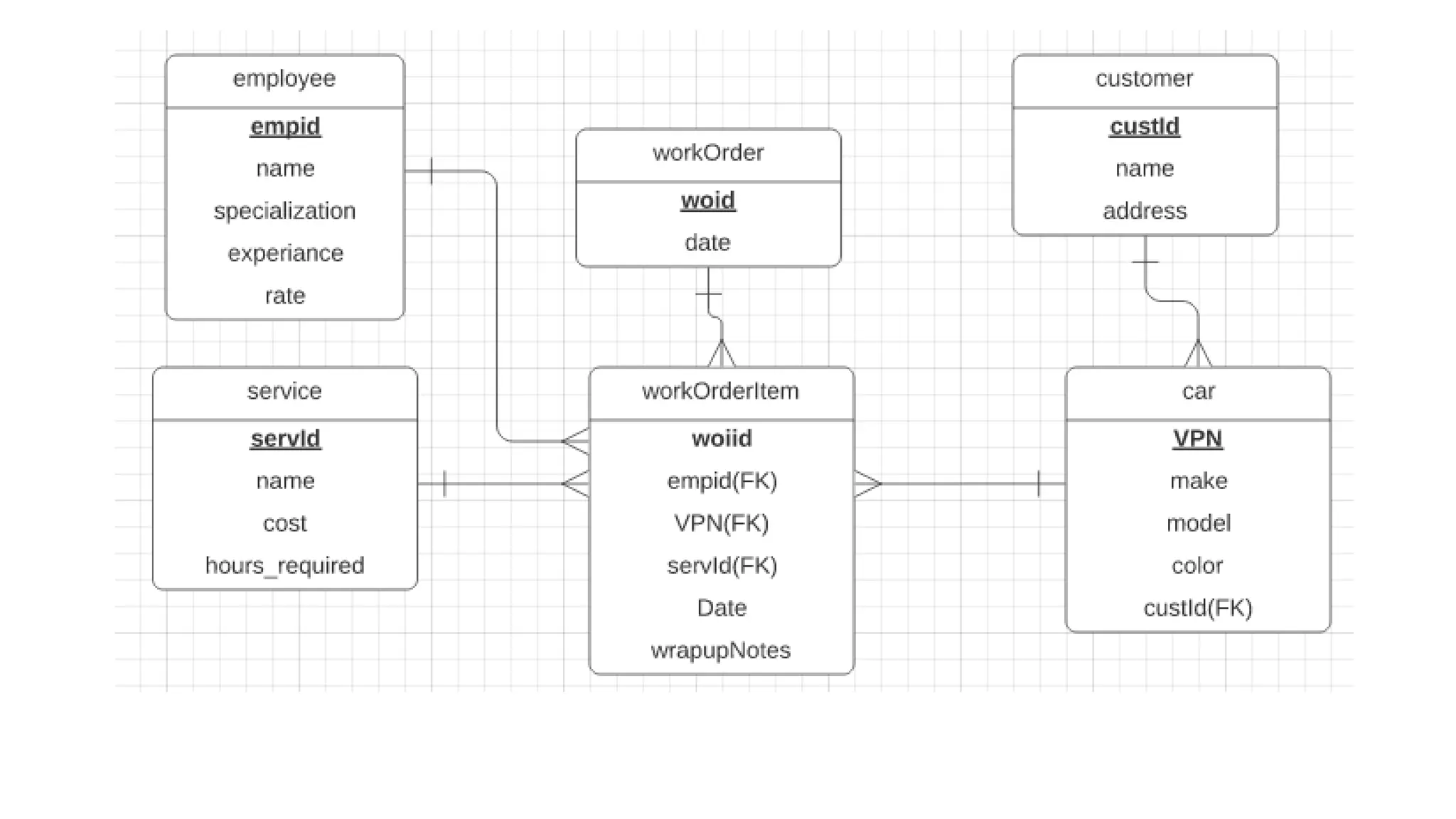
The document discusses entity relationship modeling concepts including:
- Entities represent real-world objects or concepts that can exist independently
- Attributes describe entities with properties like simple or multi-valued attributes
- Relationships exist between entities when one entity's attribute refers to another's attribute
- Keys like primary keys and foreign keys are used to uniquely identify and relate entities
- Cardinality defines relationship types as one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many
- Examples demonstrate applying these concepts to model systems like a university admissions system.