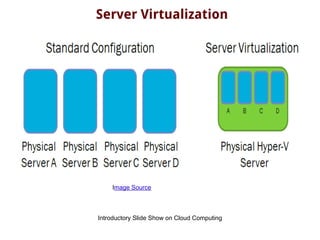
The document discusses cloud virtualization technology, defining virtualization as an abstraction layer that separates physical hardware from operating systems, resulting in benefits such as cost savings and improved resource utilization. It outlines various virtualization techniques, server virtualization approaches, and key components like hypervisors and logical partitioning. The importance of backend infrastructure requirements and detailed design for successful implementation is also highlighted.