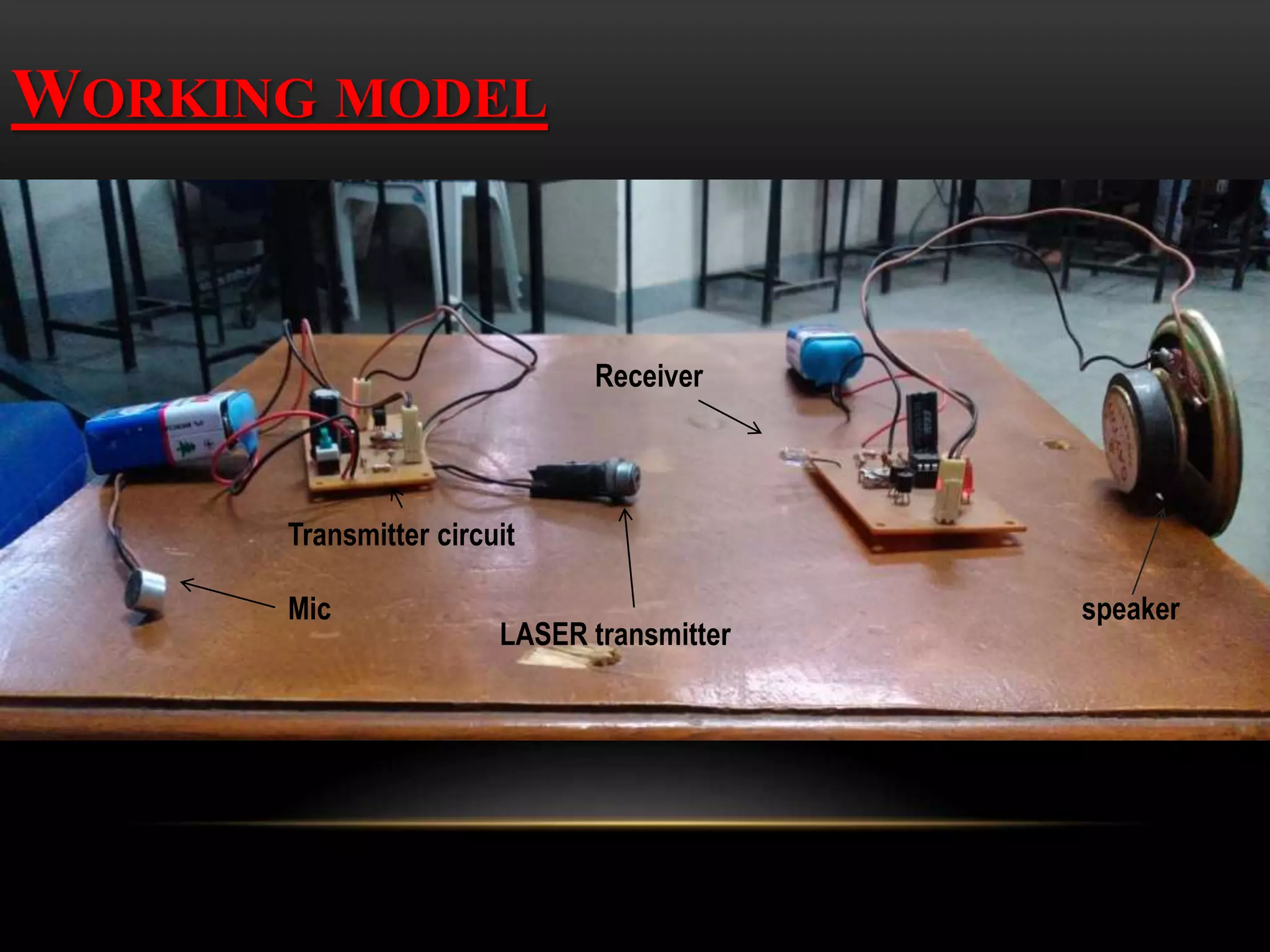
This document provides an overview of free-space optical communication (FSO) technology. FSO uses lasers and photo detectors to transmit data wirelessly through free space, similar to fiber optic links but without the fiber. The document discusses the history and development of FSO, how FSO systems work by transmitting laser beams between a transmitter and receiver section, applications such as communication with satellites, and advantages over radio frequency technologies like greater bandwidth and more secure communication through beam directionality.