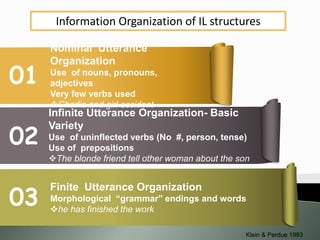
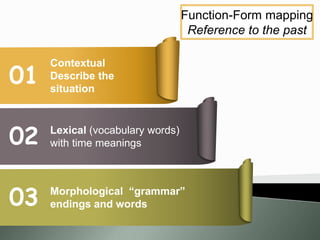
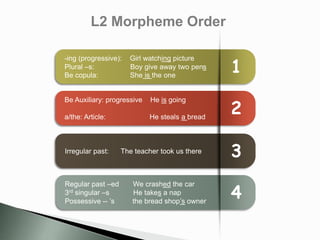
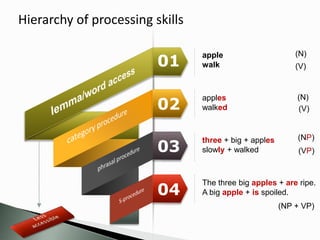
The document discusses the significance of awareness in second language (L2) learning, emphasizing that learners often prioritize meaning over grammatical structures. It outlines developmental stages in language acquisition, such as simplifications and overgeneralizations, and introduces the concept of processability theory, which illustrates how learners process language based on complexity. Additionally, it highlights the influence of first language (L1) on L2 development and the importance of a balanced instructional approach that includes both form-focused and meaning-focused strategies.










![Hierarchy of Internal Clause reordering
(S1 + S2)
01
02
03
04
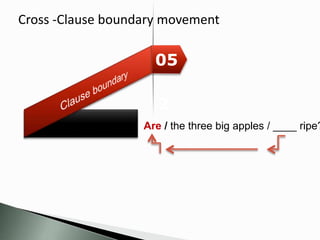
That’s the man [who
ran away].
That’s the truck [that I
sold yesterday].
That’s the man [to whom I
gave the letter].
That’s the book [that I told you
about],
or [about which I told you]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2interlanguagedevelopment-150314134835-conversion-gate01/85/L2-interlanguage-development-16-320.jpg)



![ French speaker: The boy kiss her mother. (French
possessive determiners agree with object possessed.)
Spanish speaker: He no speak e-Spanish. (Spanish has
no initial consonant clusters [sp-].)
German speaker: Like you ice cream? (At Stage 4/5 of
question formation, learner hypothesizes that full verbs
can be inverted in questions.)
Arabic speaker: The boy that I saw him was running fast.
(In relative clauses, Arabic does not delete the pronoun
from its ‘original’ place.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2interlanguagedevelopment-150314134835-conversion-gate01/85/L2-interlanguage-development-20-320.jpg)









![ Subject
That’s the man [who ran away].
Direct object
That’s the truck [that I sold yesterday].
Indirect object
That’s the man [to whom I gave the letter].
Object of preposition
That’s the book [that I told you about].
Genitive
That’s the man [whose sister I know].
Object of comparison
He’s the only man [whom I am taller than].
Less
accessible](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2interlanguagedevelopment-150314134835-conversion-gate01/85/L2-interlanguage-development-31-320.jpg)