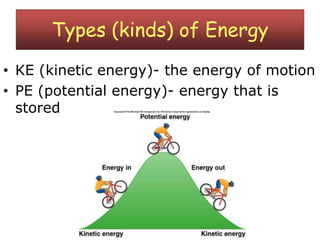
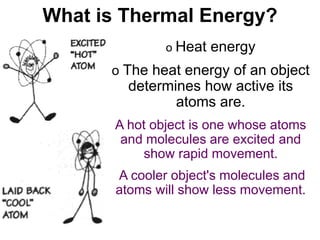
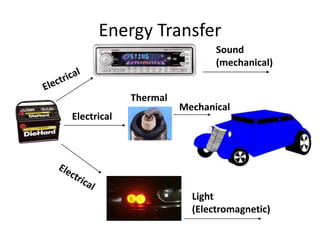
This document examines various forms of energy and energy transformations. It defines energy as the ability to do work. There are two main types of energy: kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy. The document then describes five specific forms of energy - radiant or light, sound, heat/thermal, electrical, and mechanical. For each form, it provides a definition and brief explanation. Finally, it notes that energy can be transferred between forms, such as from mechanical to thermal or electrical to light.