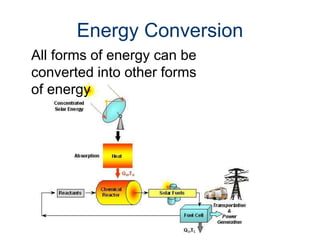
Energy exists in many forms and can be transferred and transformed, but not created or destroyed. The document outlines six main forms of energy: mechanical, chemical, electrical, heat/thermal, light/radiant, and nuclear. It provides examples of each type of energy and explains concepts like potential and kinetic energy. Potential energy is stored energy in an object at rest, while kinetic energy is energy in motion.