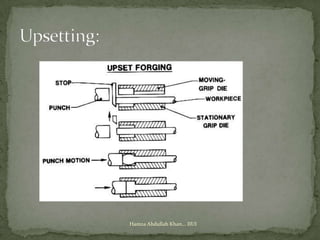
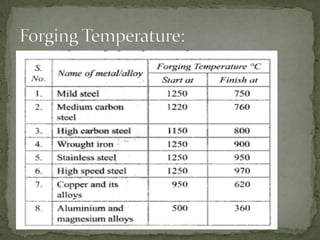
Forging is a process that involves shaping metal by heating and hammering. It increases strength and toughness by producing directional grains that refine the metal's structure, eliminating defects like cracks and pores. Forged components can withstand high loads, be produced to close tolerances, and require less machining than casted parts, reducing costs. Common forging operations include upsetting, drawing down, bending, punching, drifting, and swaging.