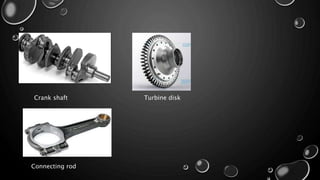
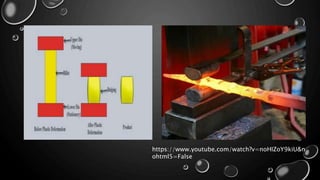
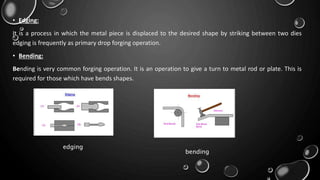
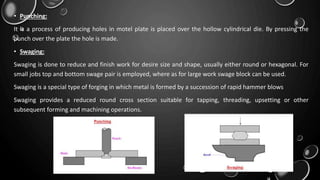
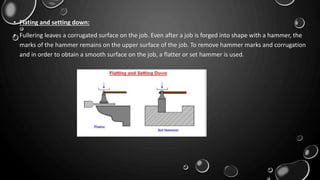
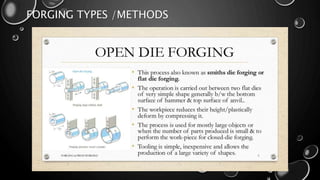
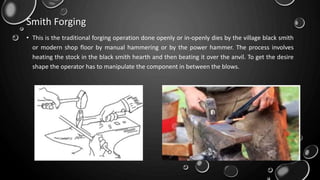
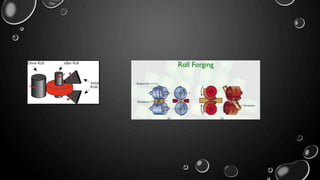
Forging is a metalworking process that uses compressive forces to shape materials by plastic deformation. It is carried out either hot or cold. The material is heated and shaped by hammer blows or presses. It produces stronger parts than casting or machining due to improved grain structure and lack of defects. Common forging applications include bolts, gears, crankshafts, and connecting rods. Forging can be classified by loading type, operating temperature, or die arrangement and involves steps like heating, shaping, heat treatment, and inspection.