Embed presentation
Download to read offline
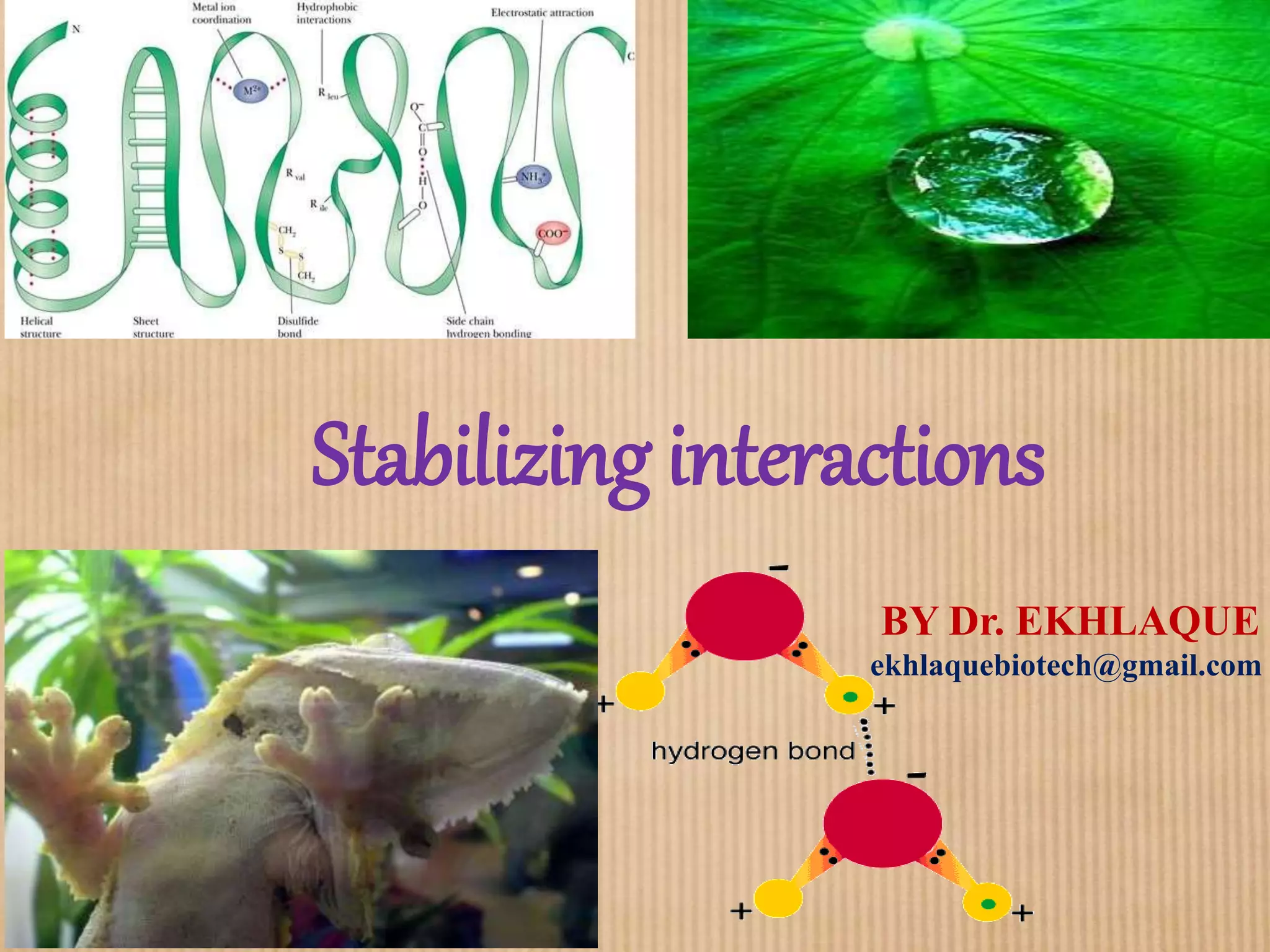



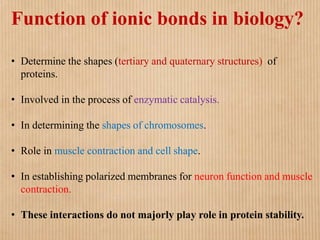


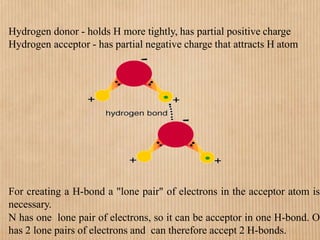


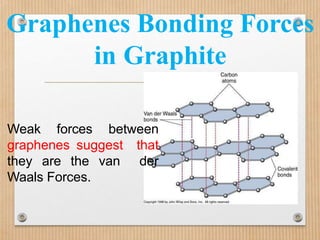
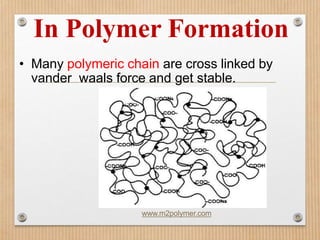





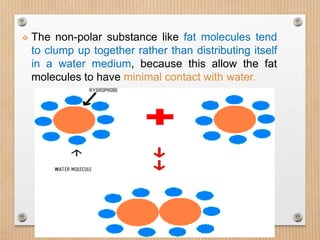

1. Non-covalent interactions like electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic interactions play important roles in stabilizing macromolecular structures like proteins. 2. These interactions are weak but numerous, allowing for spontaneous assembly of larger structures. They also allow conformational changes important for biochemical functions while maintaining overall structure. 3. Electrostatic interactions depend on distance between charges and the dielectric constant of the medium, with an optimal distance of around 2.8 Angstroms. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds but important in structures. Van der Waals forces and hydrophobic interactions also contribute to stability.





















