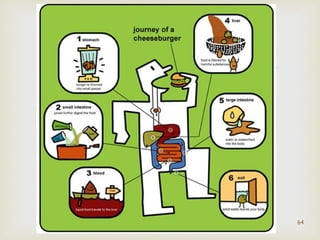
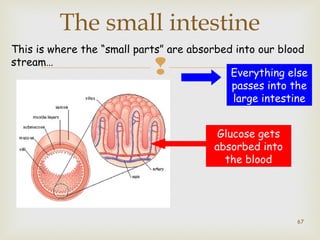
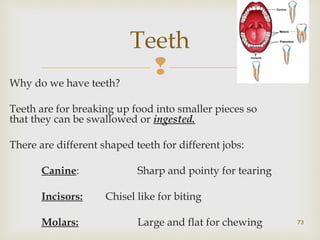
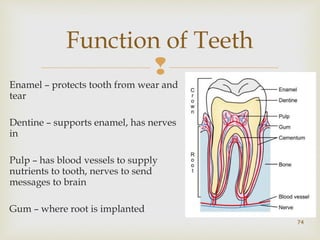
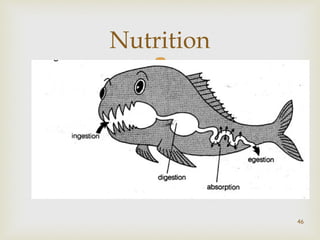
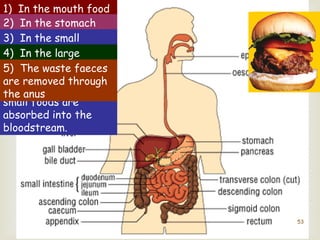
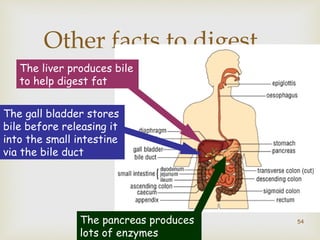
The document provides information about the digestive system and nutrition. It begins with an introduction to the digestive system and explains the four main stages of nutrition: ingestion, digestion, absorption, and excretion. It then discusses the process of digestion in more detail, explaining that digestion breaks down food into smaller particles that can be absorbed and passed through cell membranes. Various digestive organs like the mouth, stomach, and small intestine are involved in digestion. Tests are also described to identify different food types like starch, sugar, protein, and fat. Maintaining a balanced diet with a variety of food groups is emphasized as important for health.
























































![Rat Dissection
Animated Rat dissection [www.keepvid.com].mp4
Complete Scipad 157-158,
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/foodanddigestion2013-140922161325-phpapp02/85/Food-and-Digestion-Year-9-62-320.jpg)