Here are the key points about healthy eating habits:
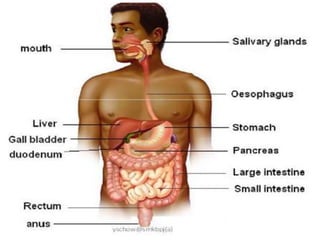
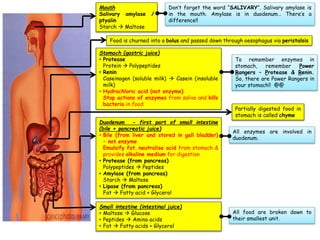
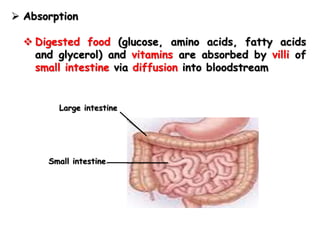
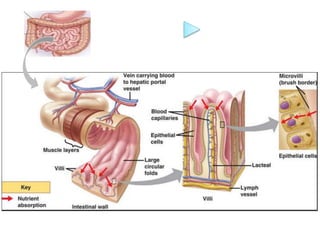
- Healthy eating provides the body with nutrients for growth, energy, and overall well-being. It involves consuming a variety of foods in appropriate portions from each of the major food groups.
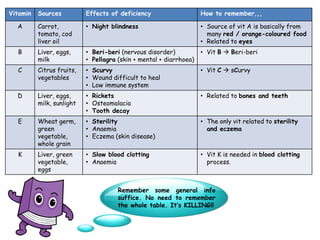
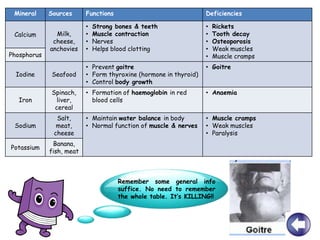
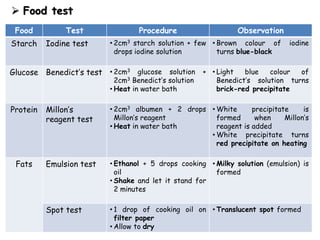
- A balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats promotes health and reduces risk of diseases. Limiting sugar, salt and unhealthy fats is also important.
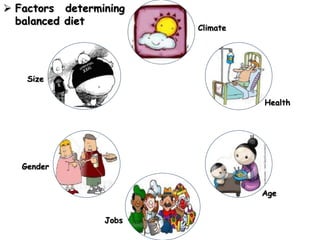
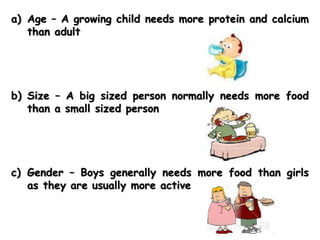
- Factors like one's lifestyle, medical conditions and cultural/religious beliefs should be considered to determine an individual's healthy eating plan. Vegetarians and those with allergies require alternative sources for some nutrients.
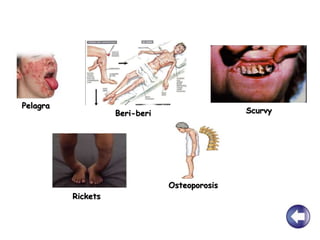
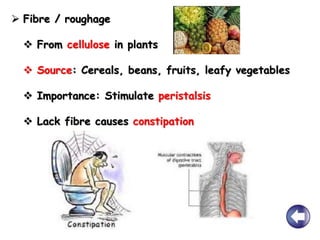
- Unhealthy eating with excessive calories or nutrients can