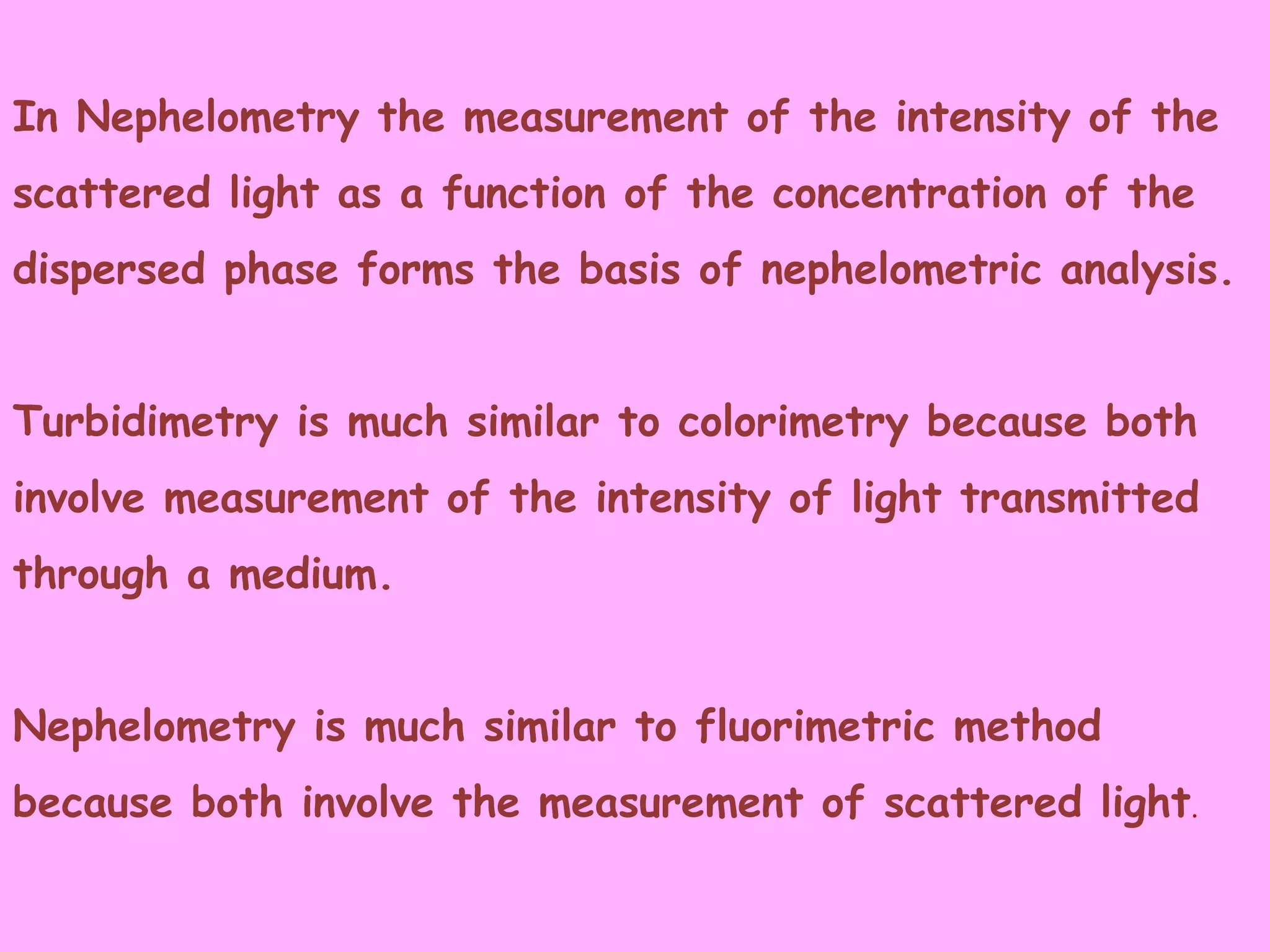
Nephelometry and turbidimetry are techniques used to analyze suspended particles in liquids or gases. Nephelometry measures the intensity of scattered light from a sample, while turbidimetry measures the intensity of transmitted light. Both techniques can be used to determine properties like concentration, particle size, and molecular weight. They have a variety of applications, including inorganic analysis, organic analysis, biochemical analysis, and monitoring air and water pollution. Choice between the two techniques depends on factors like the concentration and size of suspended particles in the sample.




















![APPLICATIONS
Turbidimetry and nephelometry can be used on
gaseous,liquid or even transparent solid samples in greatly
varying proportions.The various applications of both these
techniques are as follows
1]Inorganic Analysis
2]Organic Analysis
3]Biochemical Analysis
4]Air and Water Pollution
5]TurbidimetricTitration
6]Determination of Molecular weights of High
polymers
7]Atmosphoric pollution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nephelometry-180511150134/75/Nephelometry-and-Turbidimetry-22-2048.jpg)
![1]Inorganic Analysis
The important uses of nephelomery and turbidimetry are
the determination of sulphate as BaSO4,carbonate as
BaCO3,chloride as AgCl,fluoride as CaF2,cyanide as
AgCN,calciumas oxalate.
Out of these,sulphate determination is a particular
importance and serves for the routine determination of
total sulphur in coke,coal,oils,rubbers,plastics etc
Another important application of nephelometry and
turbiditimetry is the determination of carbon dioxide.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nephelometry-180511150134/75/Nephelometry-and-Turbidimetry-23-2048.jpg)
![2]Organic Analysis
In food and bevarages,turbidimeter is used for analysis of
turbidity in sugar products,and clarity of citrus
juices.Another intresting application is the determination of
benzene in alcohol by dilution with water to make an
immiscible suspension.
3]Biochemical Analysis
An important application of turbidimetry is to measure the
amount of growth of a test bacterium in a liquid nutrient
medium.It is also used to find out the amount of amino
acid, vitamins and antibiotics.
Nephelometry has been used for the determination of
protein and the determination of yeast,glycogen and of
beta and gamma globulin in blood serum and plasma.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nephelometry-180511150134/75/Nephelometry-and-Turbidimetry-24-2048.jpg)
![4]Air and Water Pollution
Turbidimetry and nephelometry are used for the continuous
monitoring of air and water pollution.
In air,dust and smoke are monitored whereas in
water,turbidity is monitored.
5]TurbidimetricTitration
These titration may be carried out in a manner analogous
to photometric titrations. In these titrations, the
absorbance is to be plotted against the volume of titrant
added.With the increase in the volume of titrant,the
concentration of precipitate increases and hence the
absorbance increases.When all the substances get
precipitated,the absorbance become constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nephelometry-180511150134/75/Nephelometry-and-Turbidimetry-25-2048.jpg)
![6]Determination of Molecular weights of High
polymers
In order to determine molecular weight of polymer
turbidity is measured at different concentrations of its
solution in a suitable medium.
7]Atmospheric pollution
Smoke and fogs are visible largely due to light scattering
effects.
Thus these effects are useful in monitoring atmospheric
pollution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nephelometry-180511150134/75/Nephelometry-and-Turbidimetry-26-2048.jpg)

