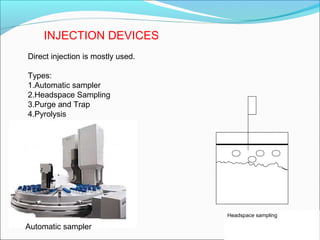
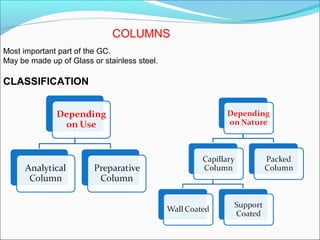
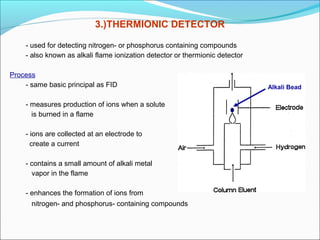
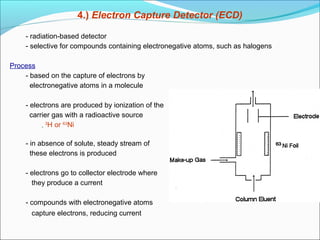
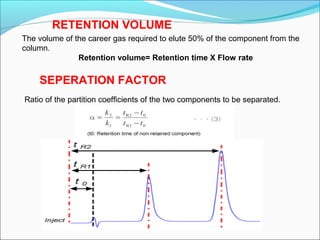
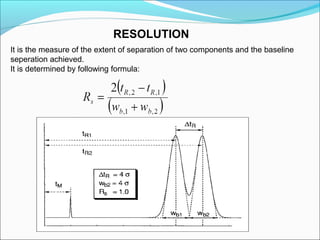
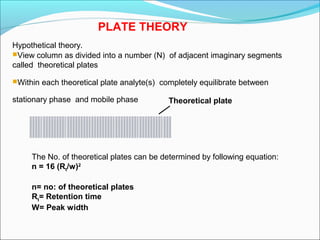
Gas chromatography is a technique used to separate and analyze mixtures that can be vaporized without decomposition. It works by partitioning components to be separated between a stationary phase and a mobile gas phase. The key components of a gas chromatography instrument are the carrier gas, injection port, column, temperature control system, and detector. Factors like temperature, flow rate, column length, and amount of sample injected can influence separation of the components. Gas chromatography has applications in qualitative and quantitative analysis and is used in quality control of pharmaceuticals.