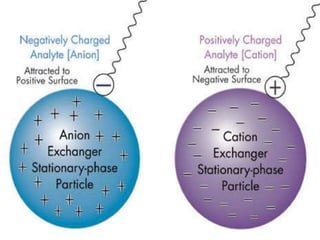
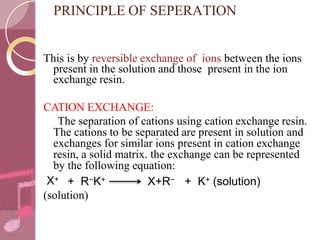
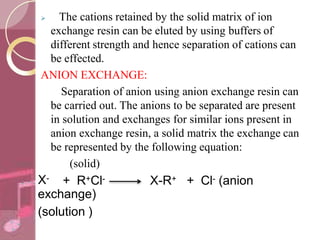
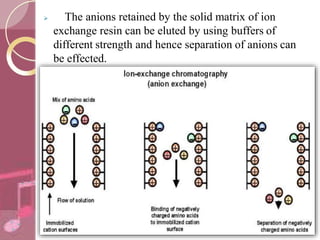
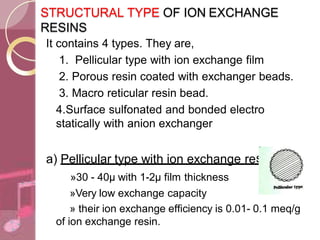
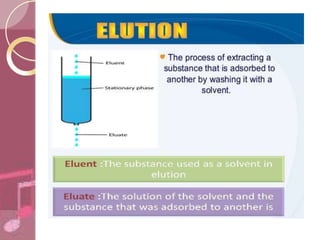
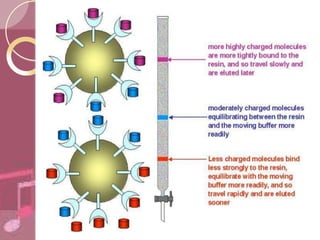
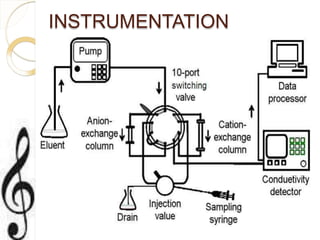
This document discusses ion exchange chromatography, including its principle, types of ion exchange resins, practical requirements, factors affecting separation, and applications. Ion exchange chromatography separates similar charged ions through reversible ion exchange between ions in solution and ions on an ion exchange resin. There are two main types of resins: cation exchange resins that separate cations, and anion exchange resins that separate anions. Key factors that affect ion exchange separation include the nature and properties of the resin, and the nature of the exchanging ions. Ion exchange chromatography has applications in water softening, producing deionized water, separating and purifying metals and ions, and analysis and purification of biomolecules.