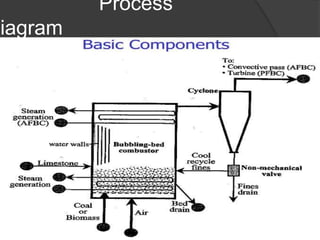
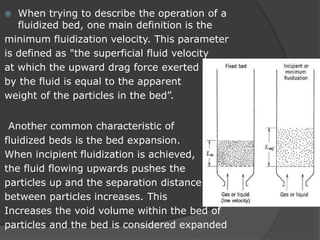
This document provides an overview of fluidization, which refers to transforming fine solids into a fluid-like state through contact with gas or liquid. Fluidization occurs when the drag forces from the fluid counteract gravitational forces on the particles, causing the bed to expand and behave like a liquid or gas. Examples where fluidization is used include fluidized bed reactors and combustion. The document discusses the minimum fluidization velocity and bed expansion during fluidization. Fluidized beds offer advantages like compact design and continuous operation but also challenges like non-uniform flow patterns.