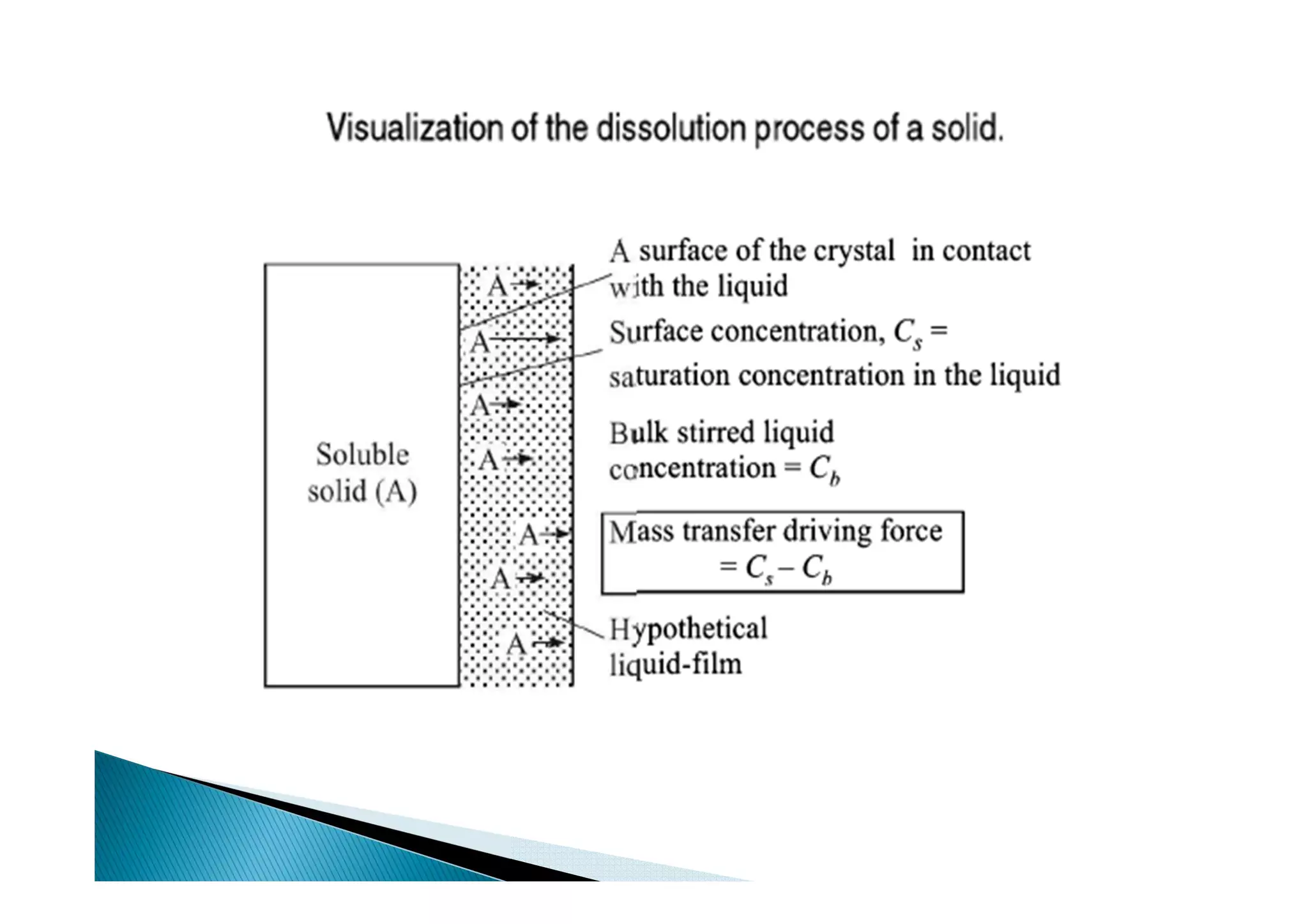
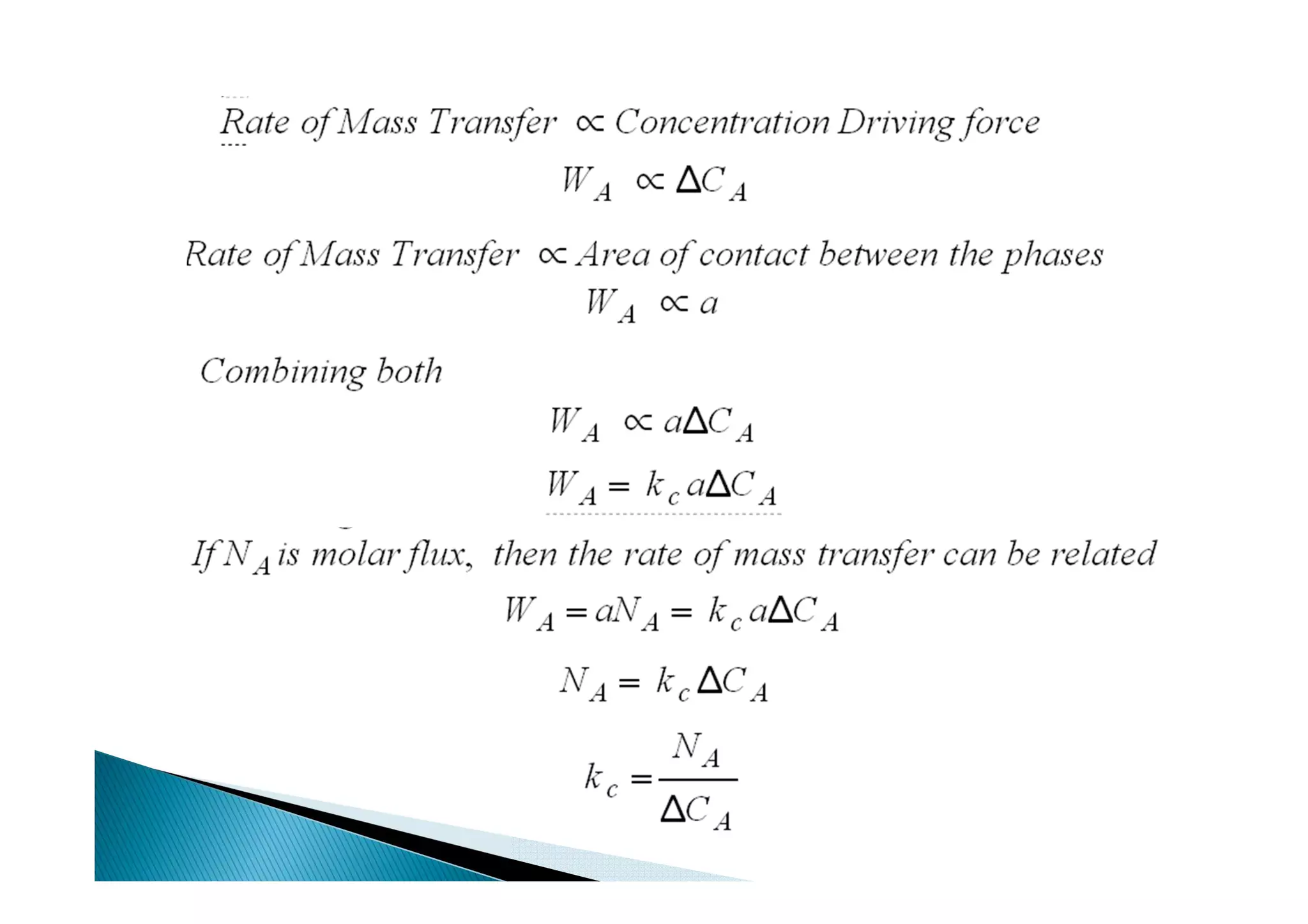
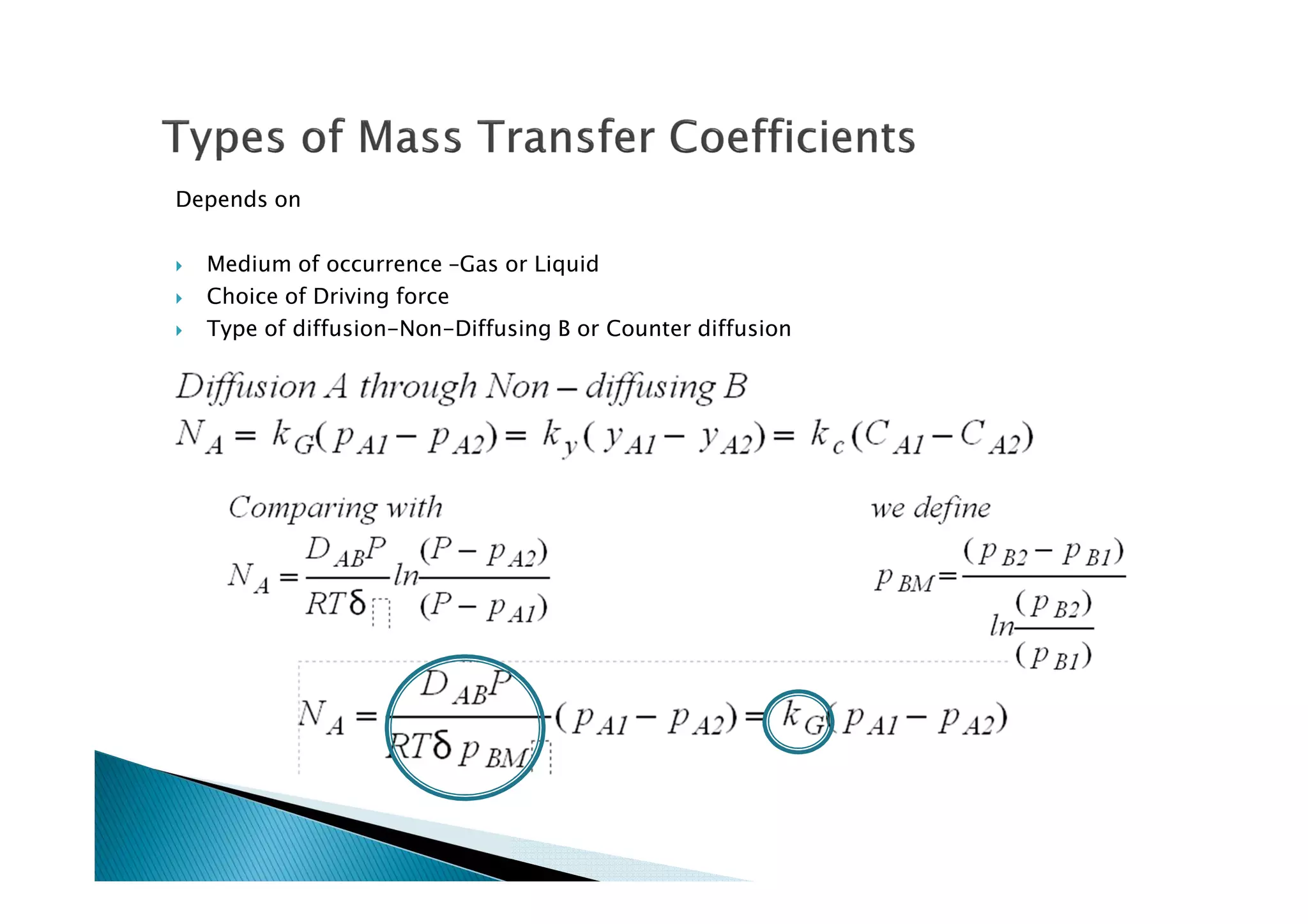
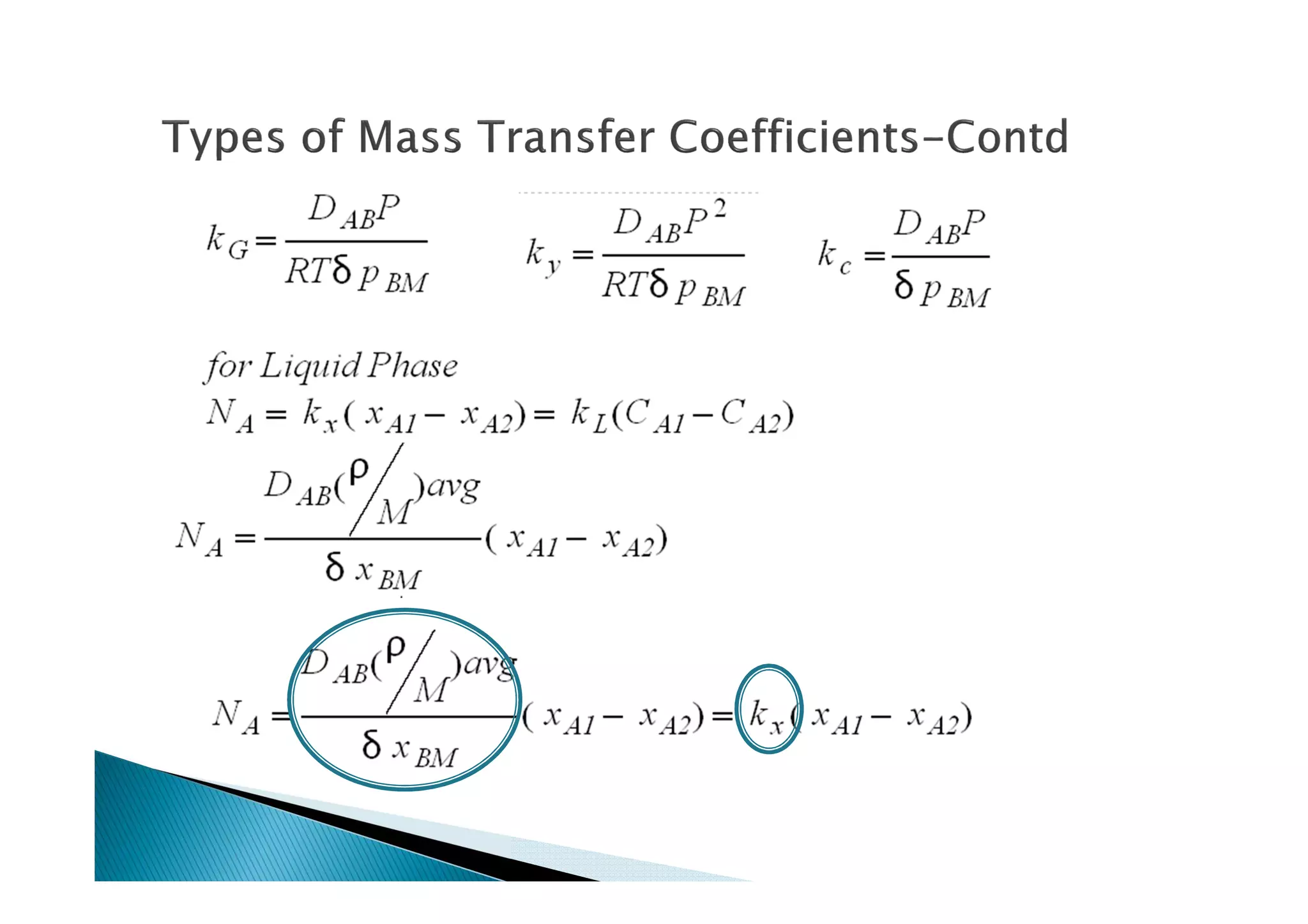
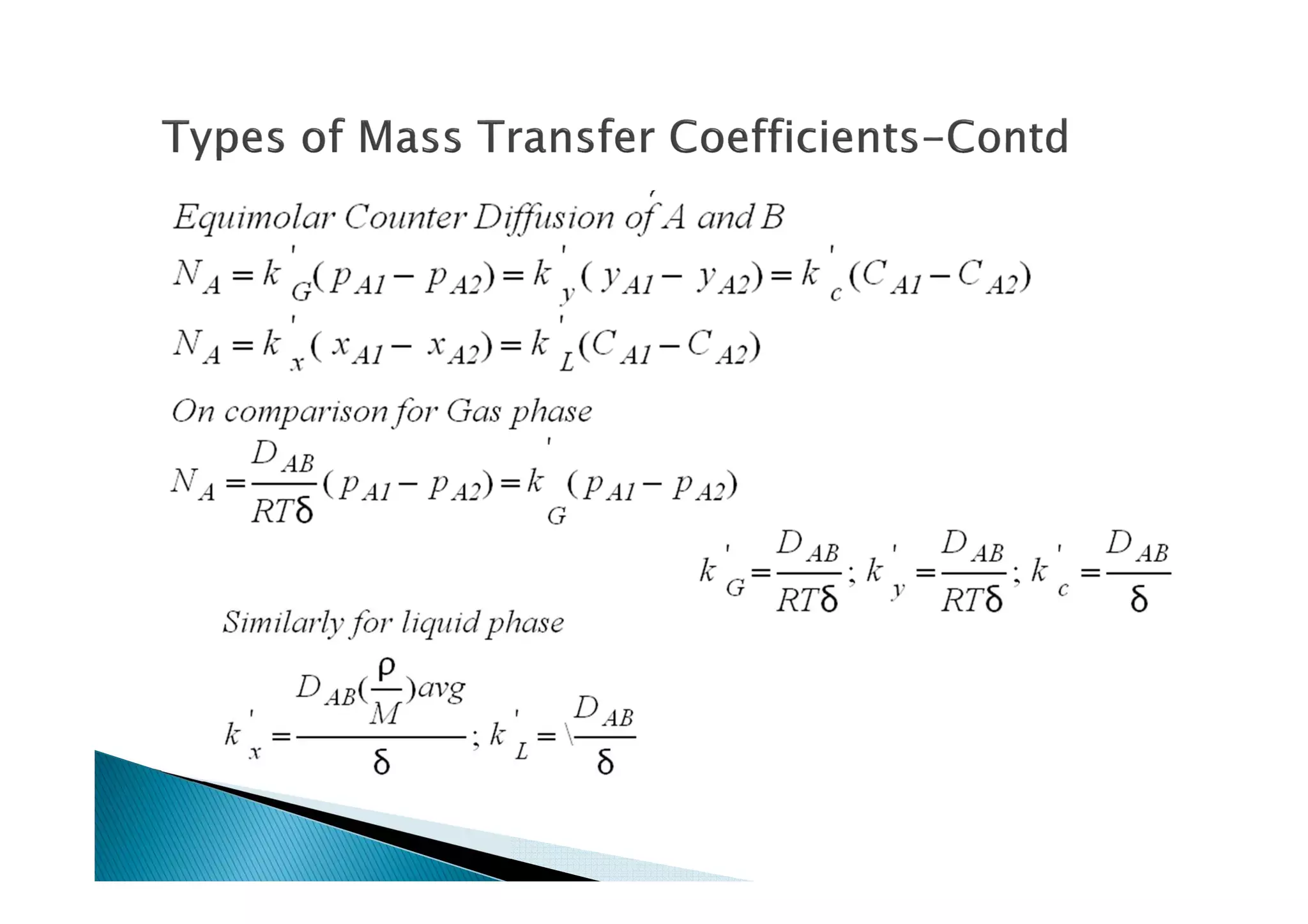
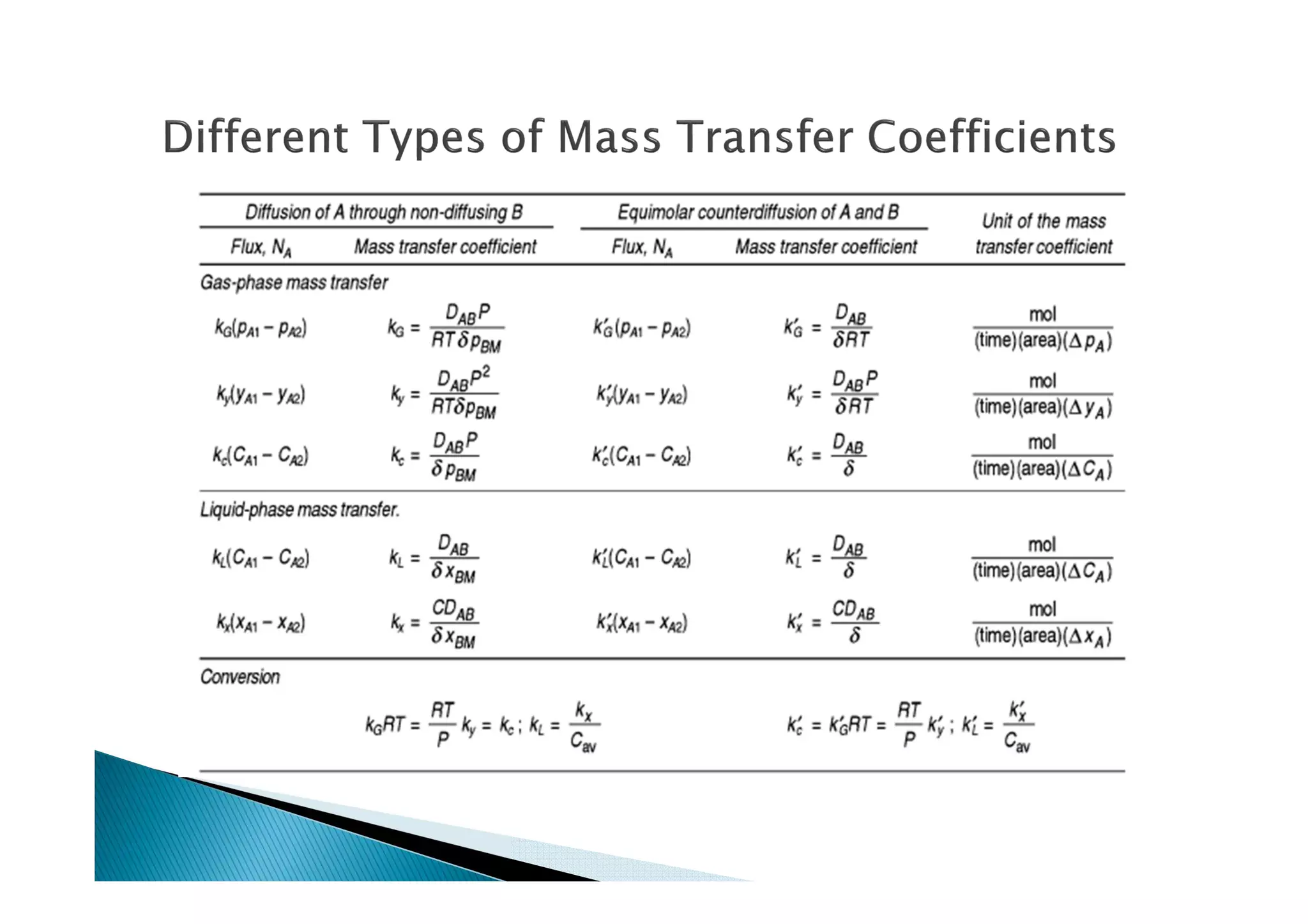
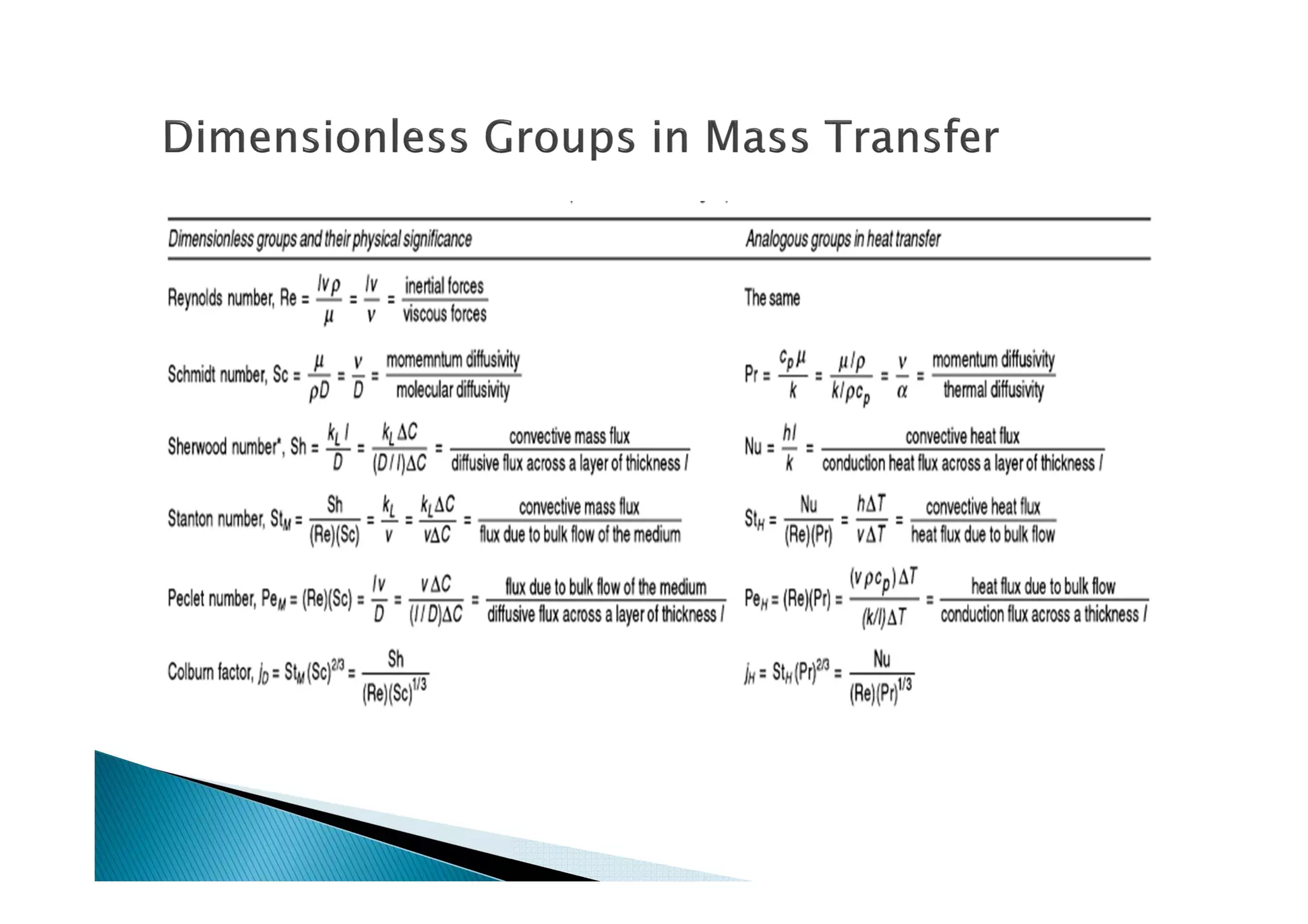
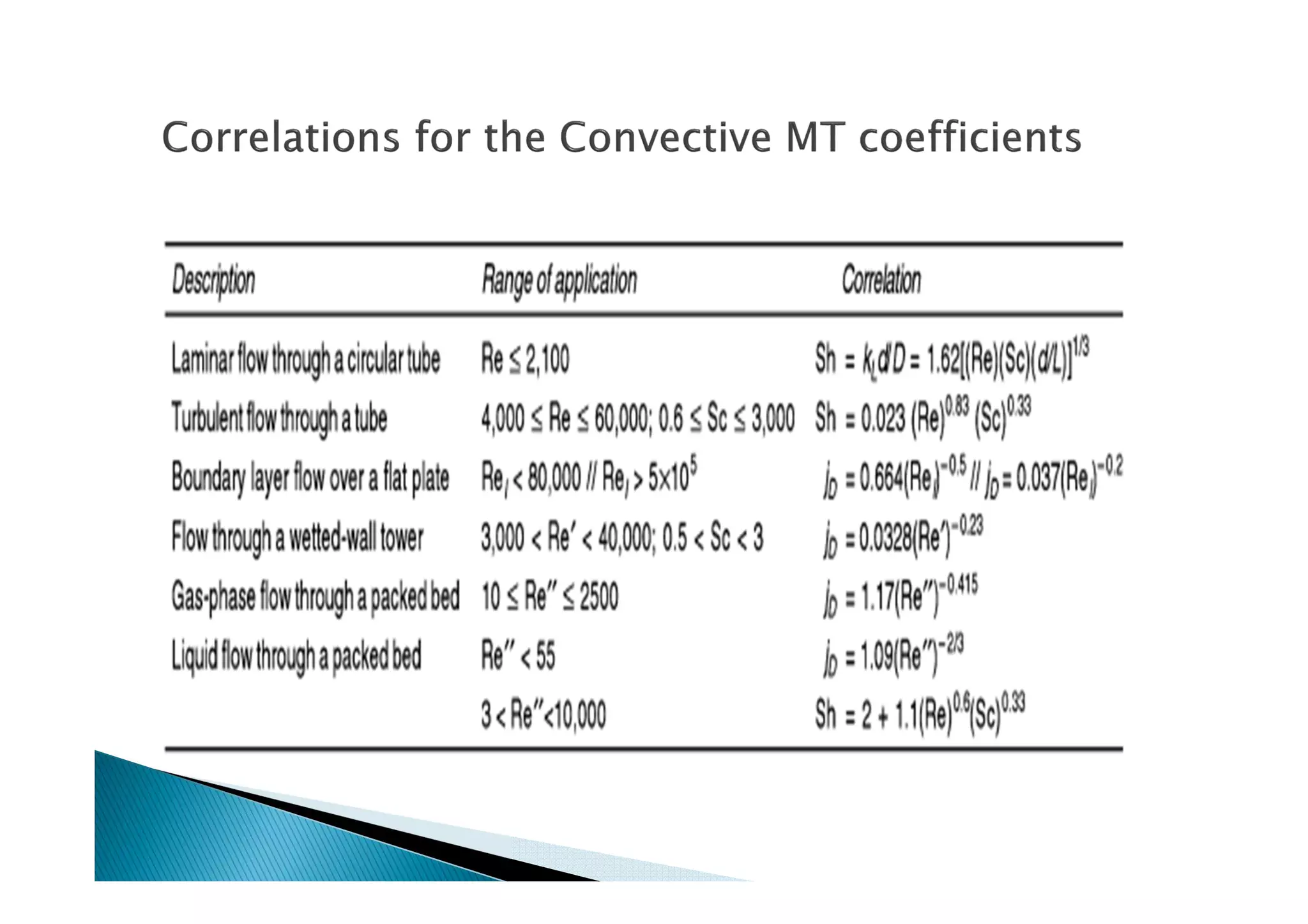
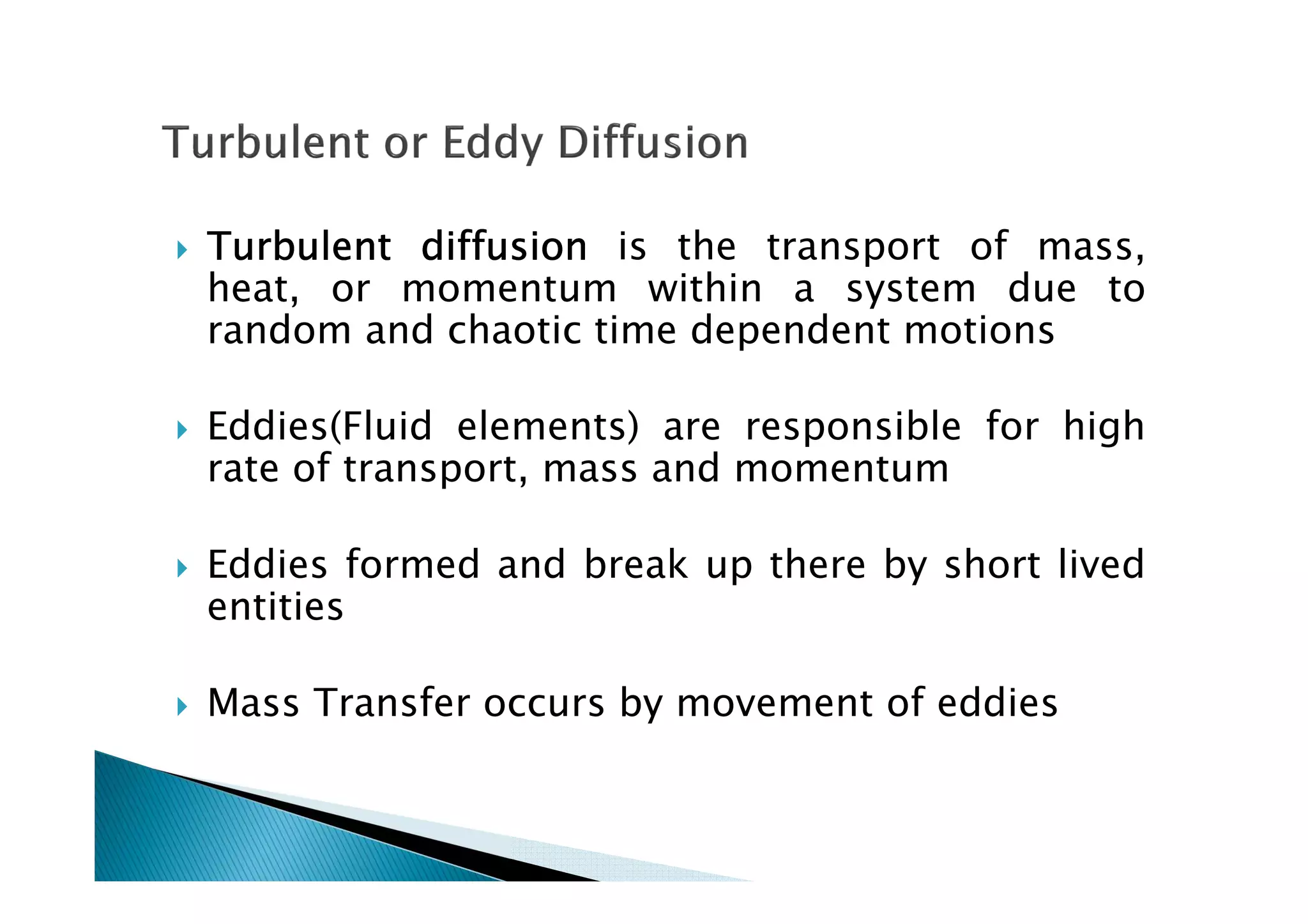
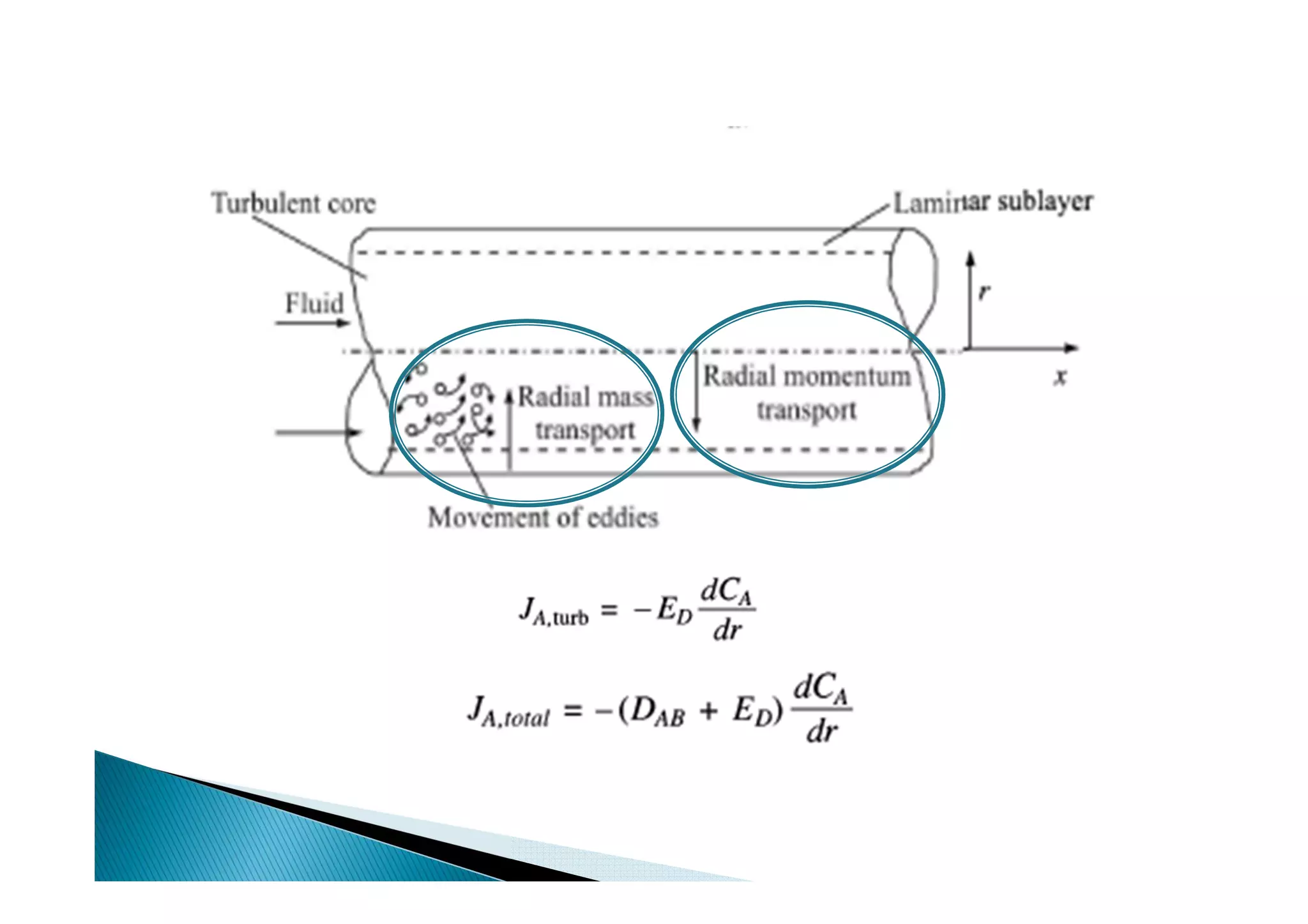
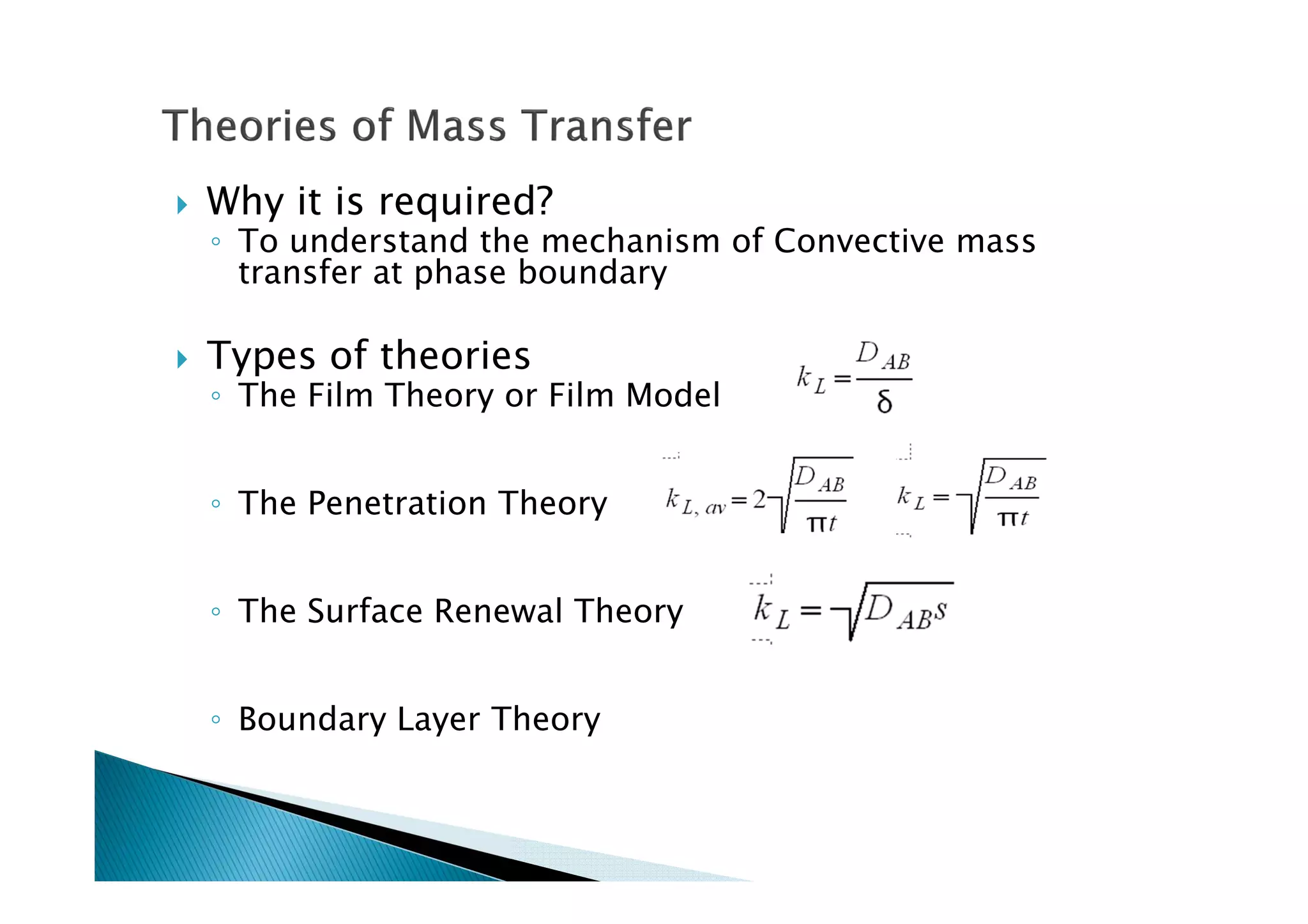
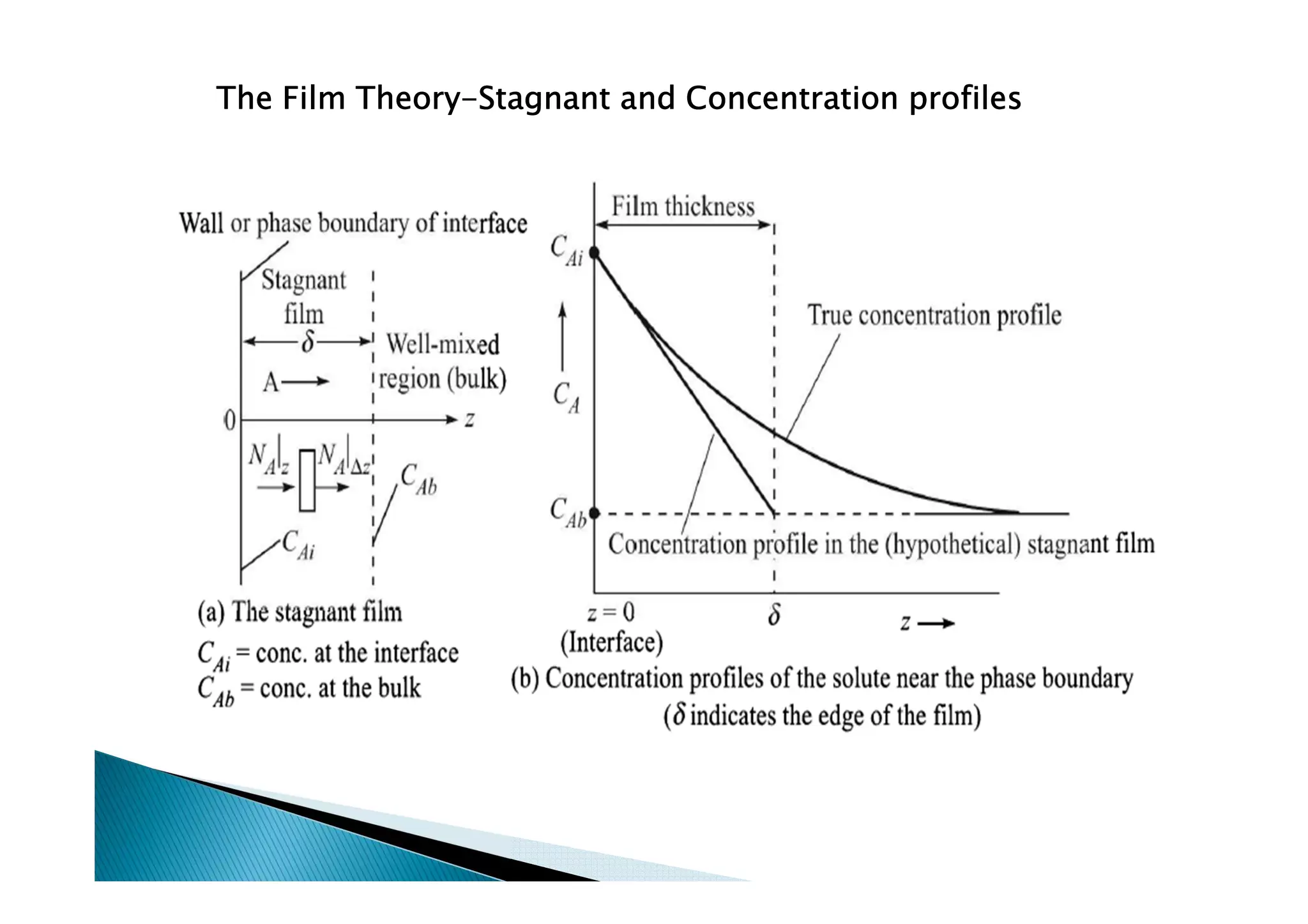
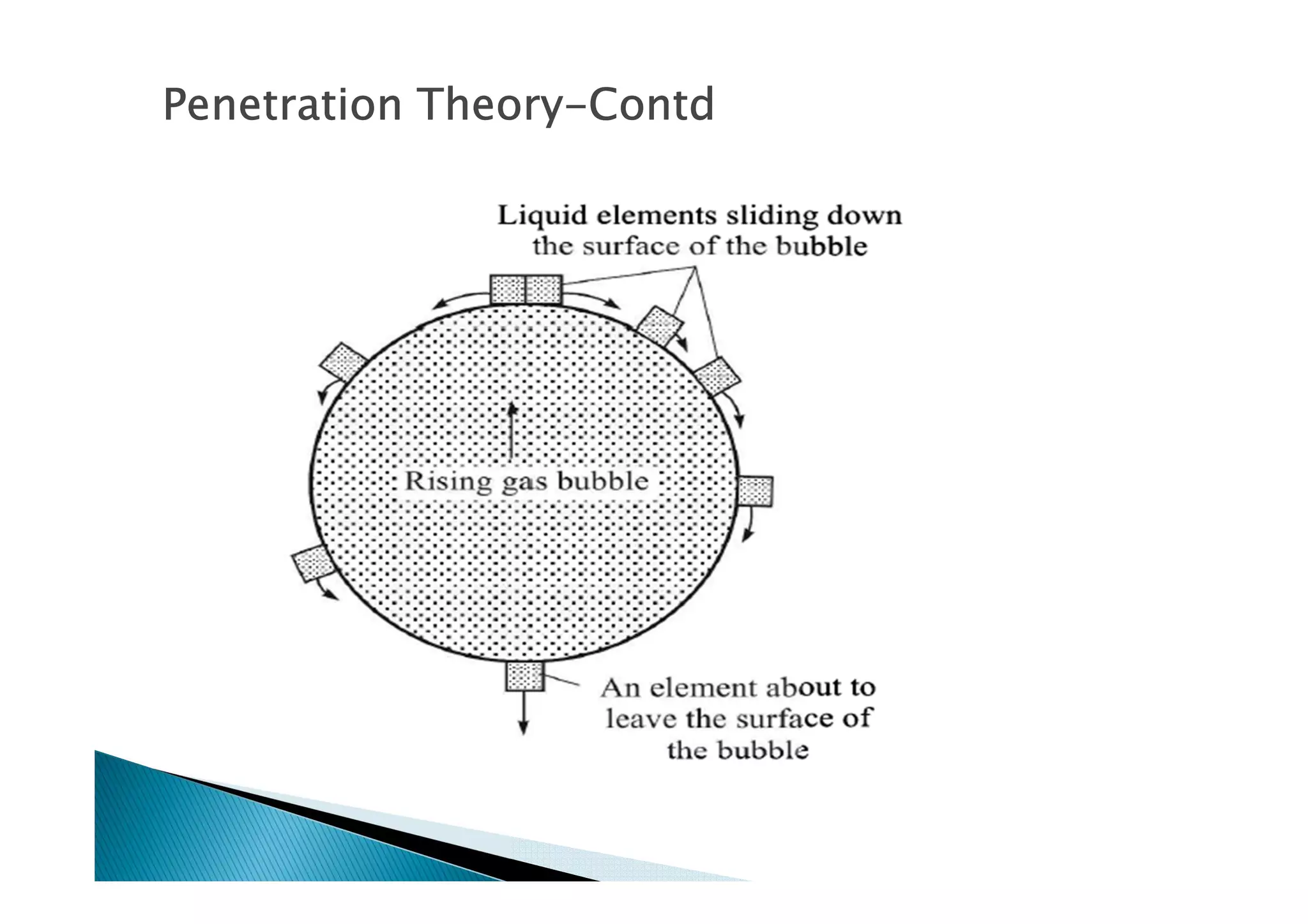
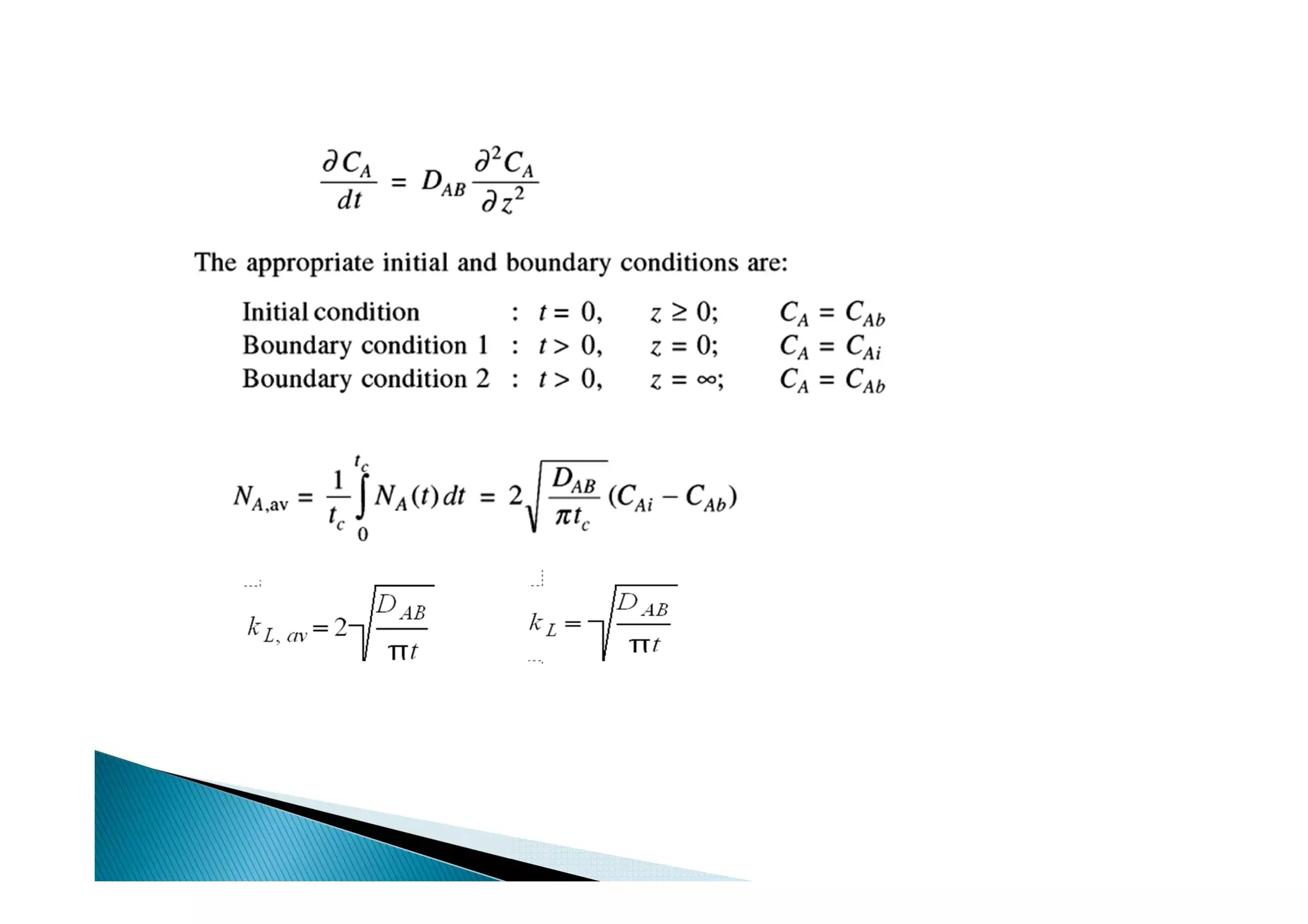
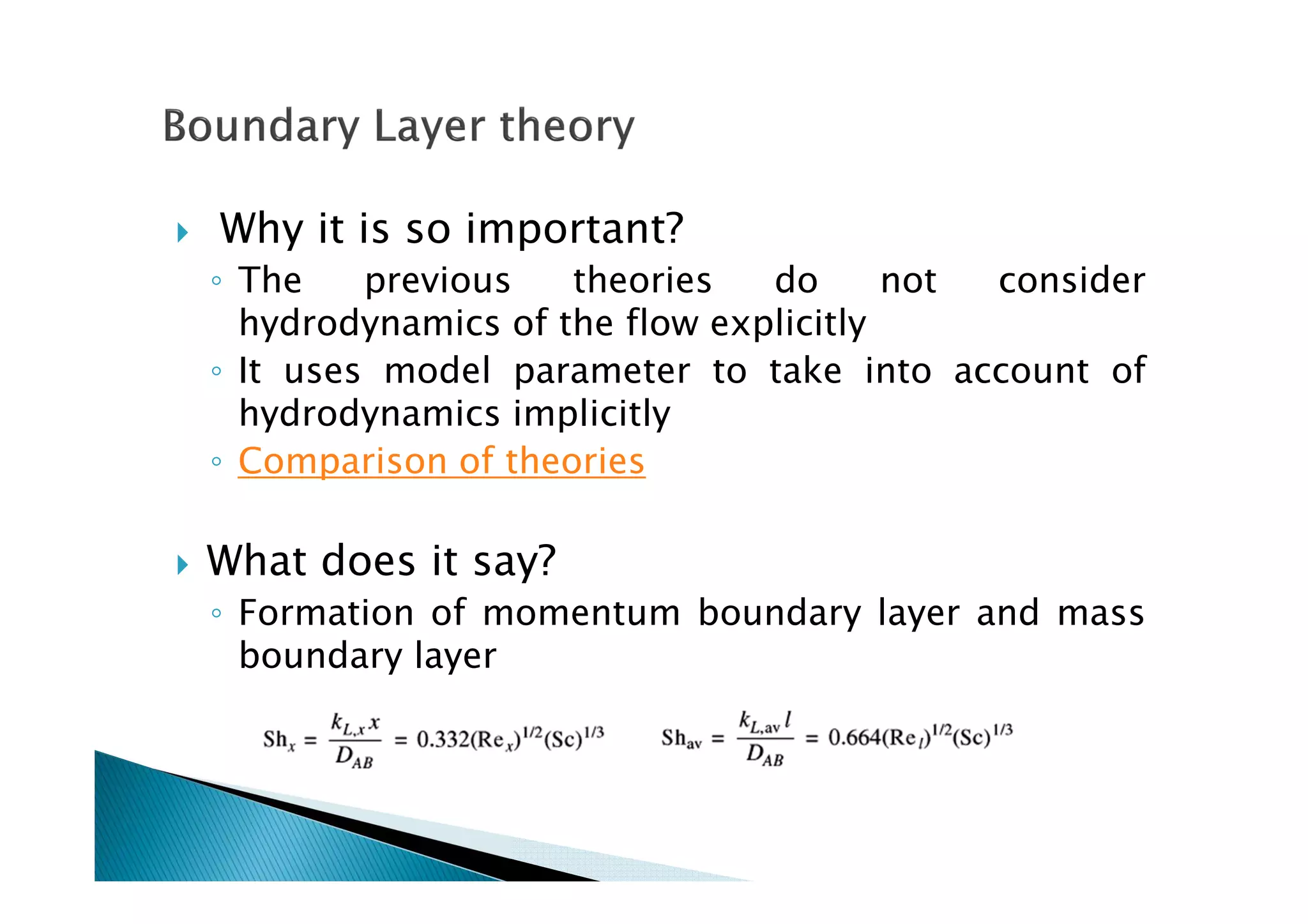
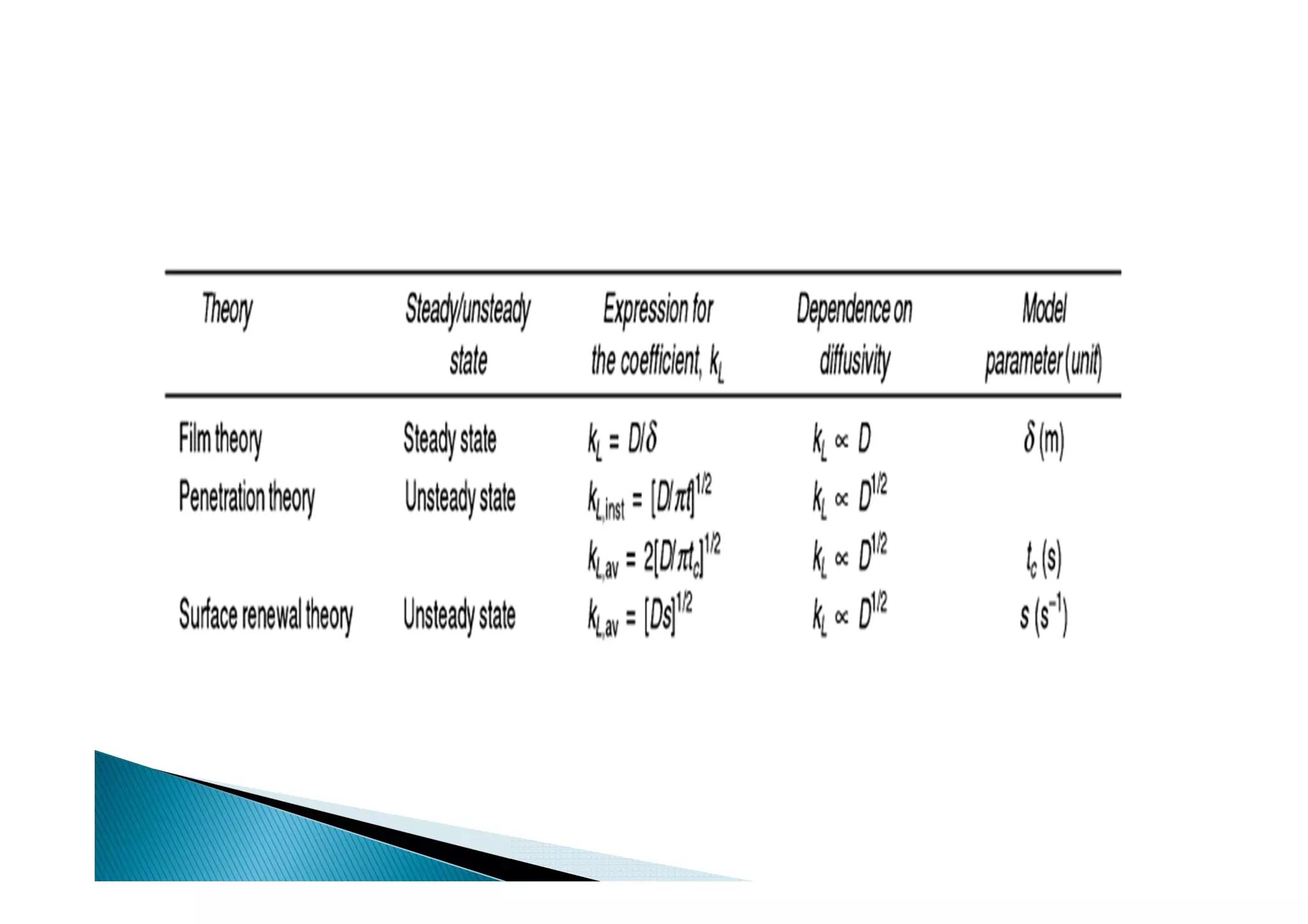
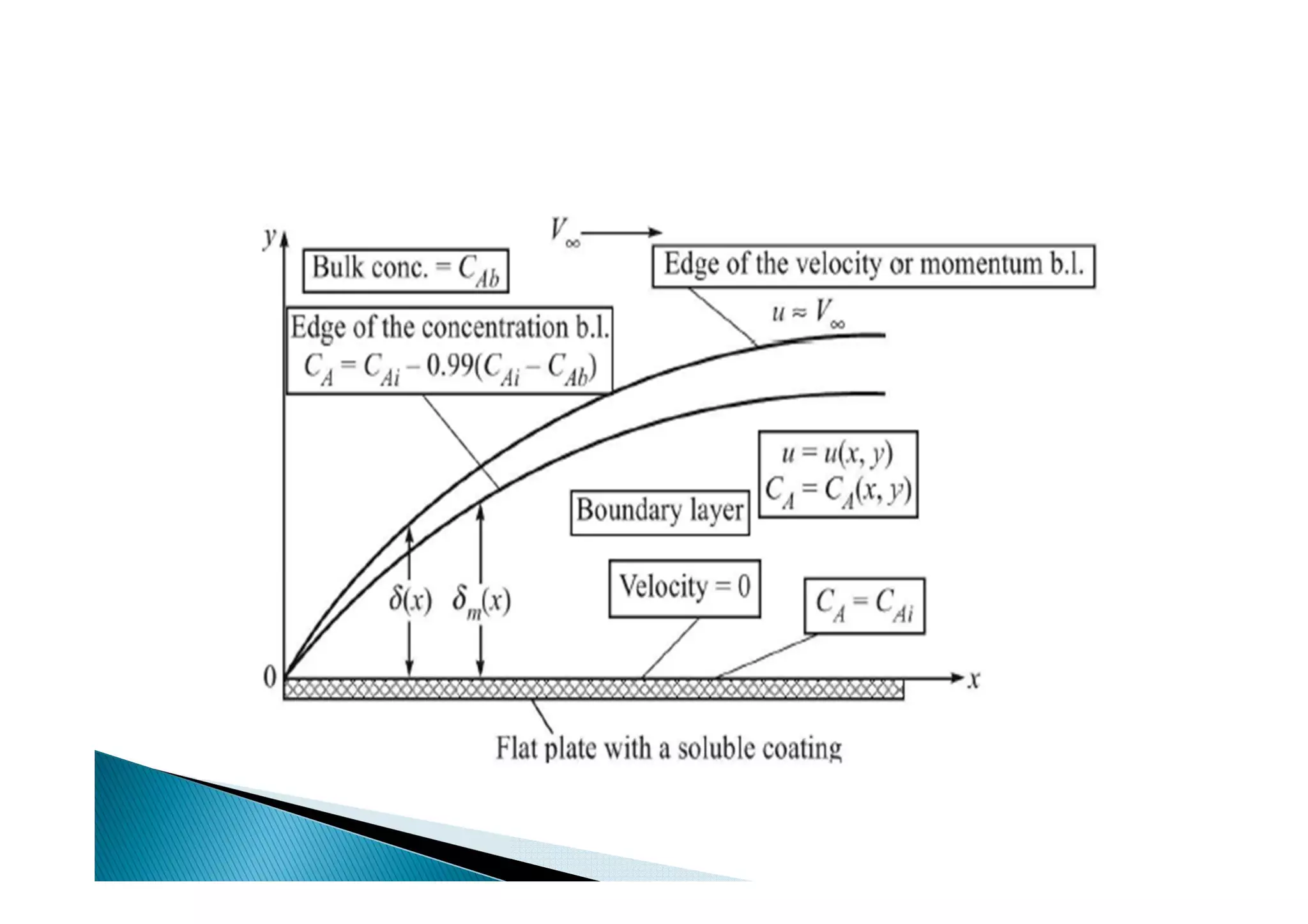
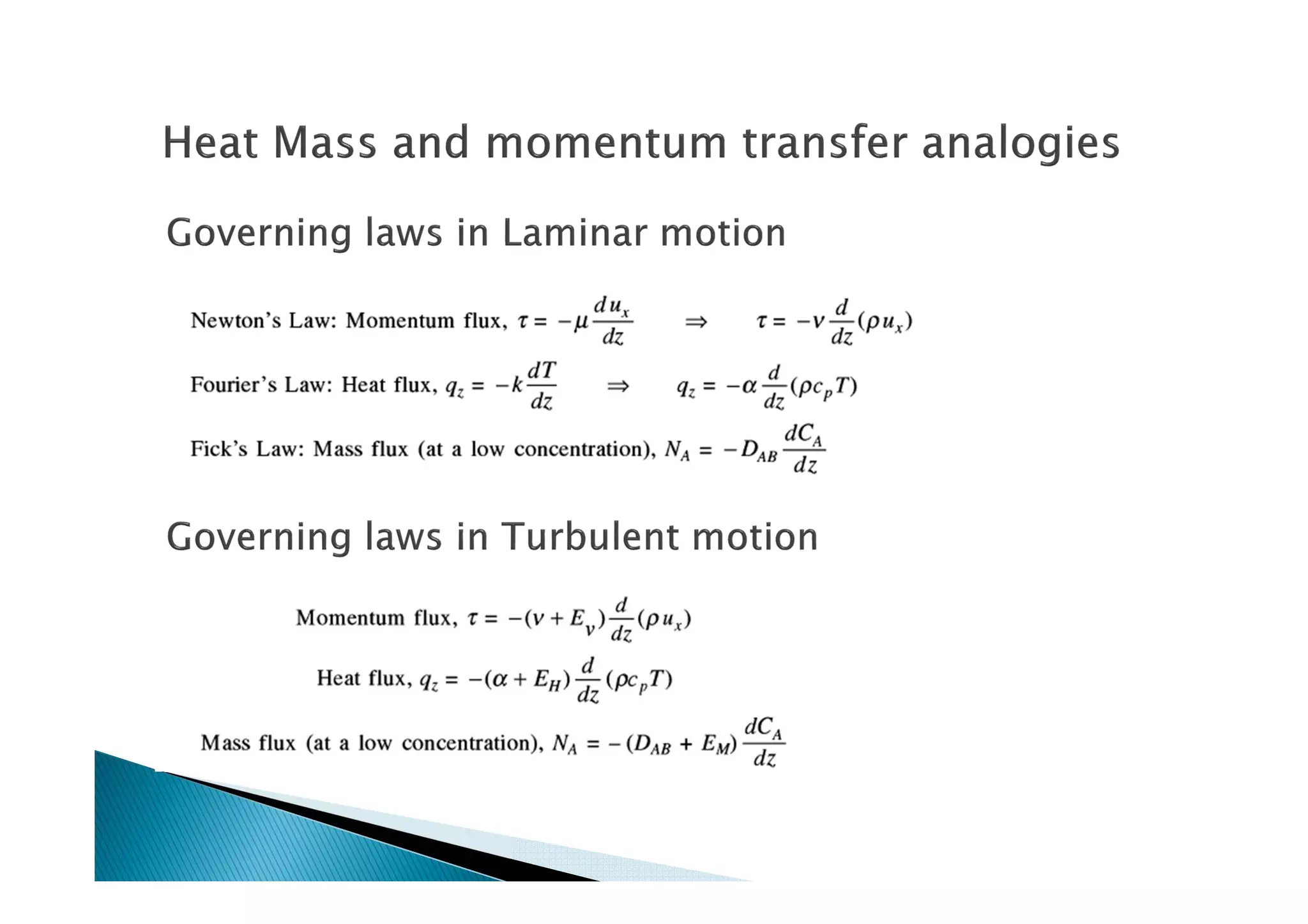
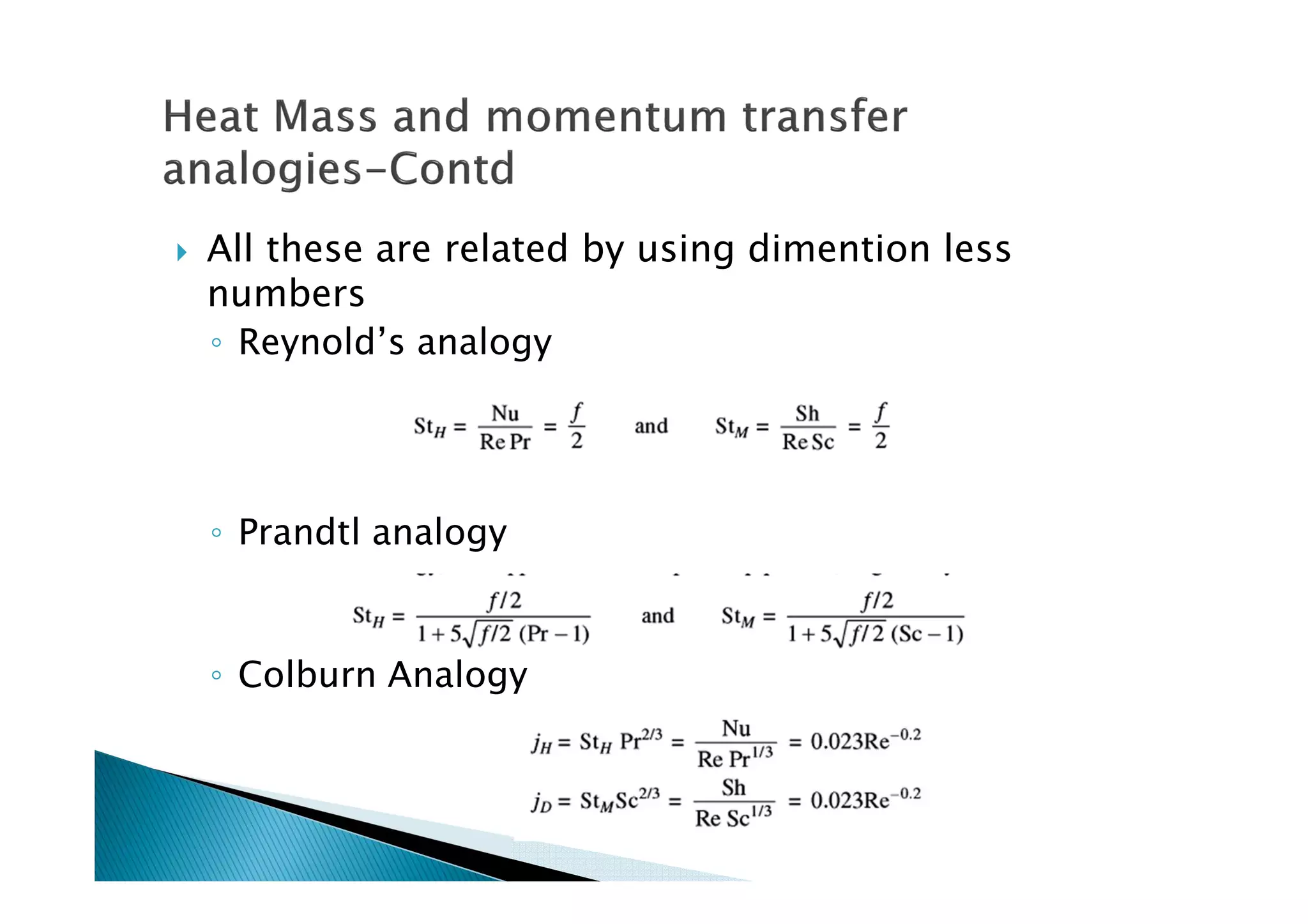
This document provides an overview of key concepts in mass transfer and diffusion processes. It discusses Fick's laws of diffusion, various diffusion mechanisms in different materials, and theories of mass transfer including the film theory, penetration theory, and surface renewal theory. It also covers convective mass transfer, turbulent diffusion, and dimensionless numbers that relate heat and mass transfer processes.