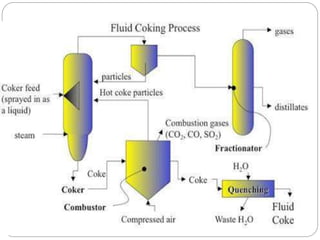
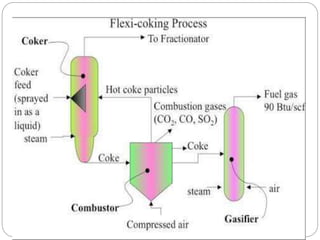
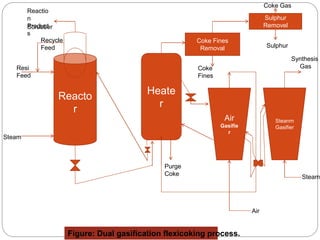
Fluid coking is a continuous process that thermally converts heavy hydrocarbons like residue into lighter products using two fluidized bed vessels, a reactor and a burner. In the reactor, feedstock is cracked into vapor and coke deposits on circulating coke particles, which transfer heat to the reactor. Flexicoking integrates fluid coking with coke gasification to upgrade residues. It uses an air gasifier to burn coke for heat and a steam gasifier to produce syngas that can be further processed. Dual gasification flexicoking employs both gasifiers, with the air gasifier providing heat and the steam gasifier generating syngas for downstream use or hydrogen production.