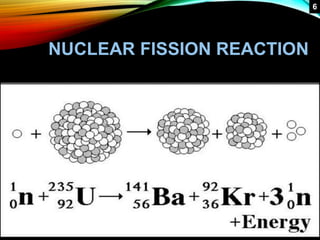
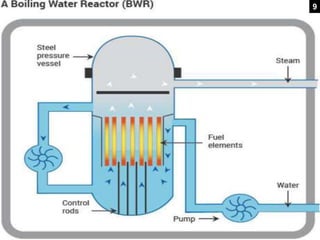
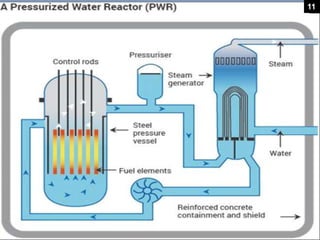
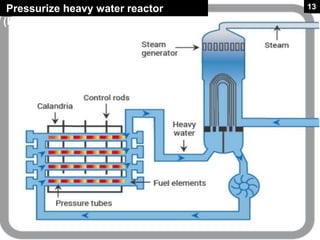
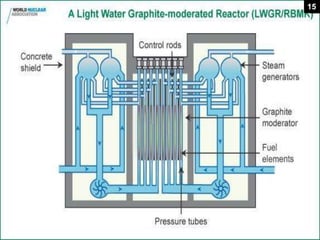
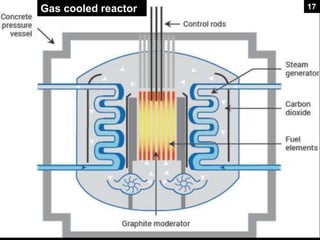
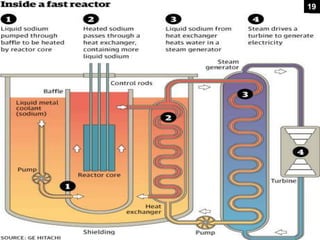
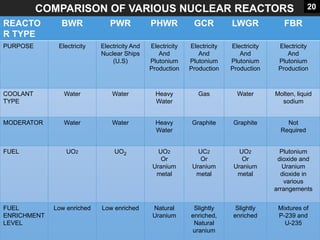
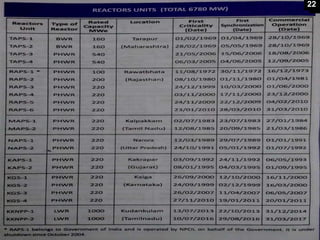
This document provides an overview of nuclear reactors, including their classification, main components, the nuclear fission reaction, and different reactor types. It discusses reactors based on neutron energy, coolant used, moderator, and fuel enrichment. The main components of a nuclear reactor are described as the fuel, moderator, coolant, control rods, and shielding. Examples of reactor types are provided and compared such as BWR, PWR, PHWR, GCR, LWGR, and FBR. Current and planned nuclear reactor units in India are also listed.