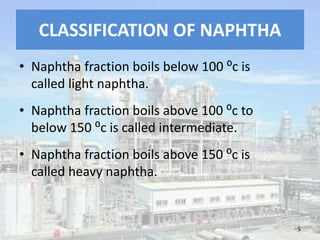
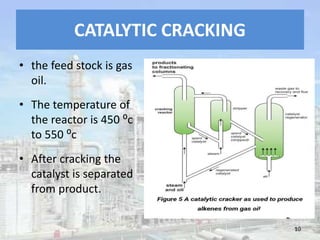
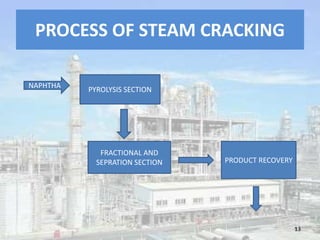
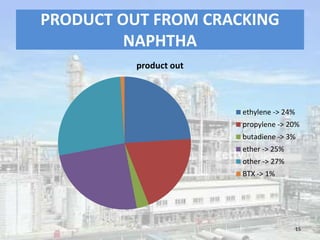
This document discusses naphtha cracking, which is the process of breaking long chain hydrocarbons in naphtha into lighter hydrocarbons. There are three main types of naphtha cracking: hydrocracking uses hydrogen and high pressure, catalytic cracking uses catalysts at 450-550°C, and steam cracking is the most complex using steam at 100-1400K. Steam cracking produces ethylene, propylene, butadiene and other products. Naphtha cracking is important for producing gasoline and solvents from naphtha.