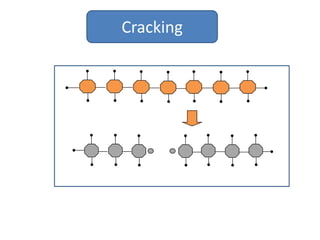
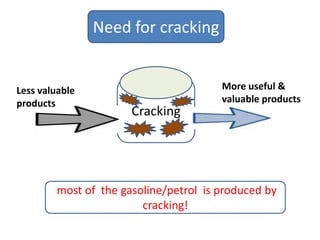
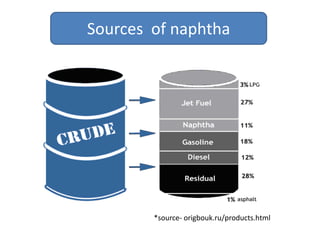
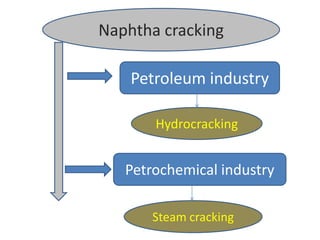
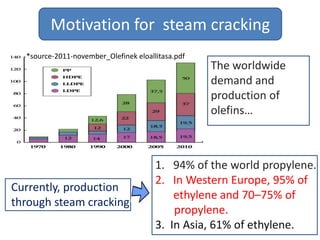
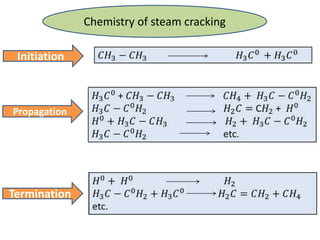
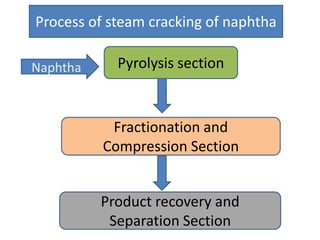
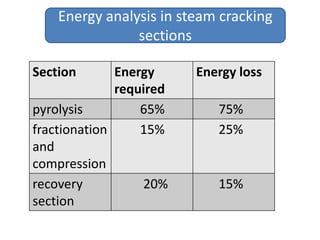
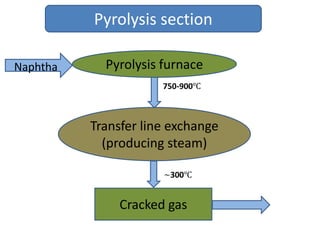
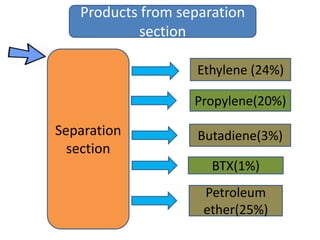
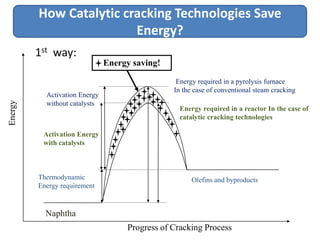
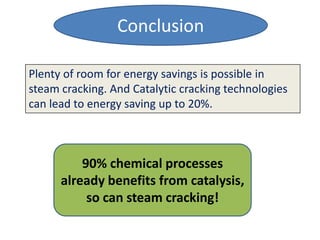
Naphtha cracking is the most energy intensive process in the chemical industry. It involves thermally cracking naphtha at high temperatures to produce more useful and valuable products like ethylene, propylene and gasoline. The presentation discusses the history of naphtha cracking, the steam cracking process, products obtained and latest developments to reduce energy usage like advanced furnace materials and distillation columns. Catalytic cracking technologies can lead to energy savings of up to 20% compared to steam cracking by reducing activation energy requirements and selectively removing coke. Overall, plenty of opportunities exist to improve the energy efficiency of naphtha cracking through technological advancements.