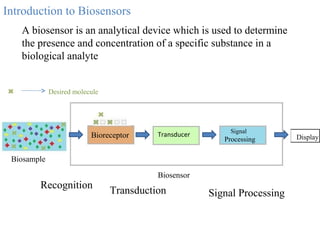
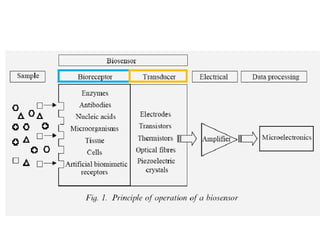
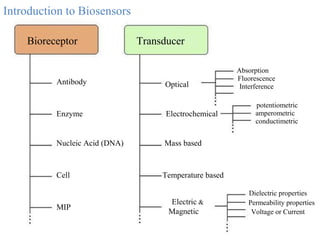
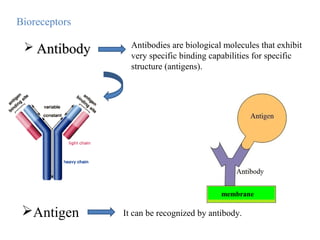
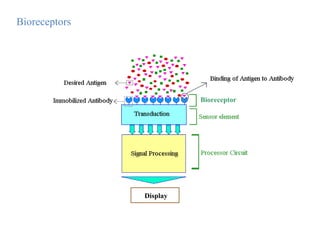
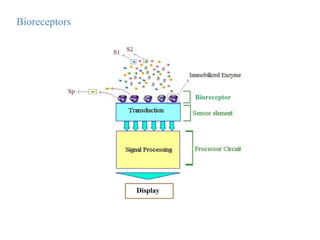
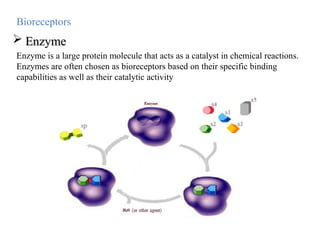
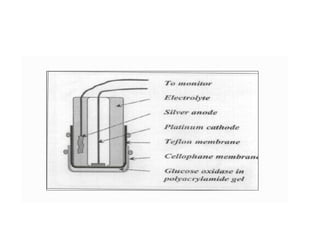
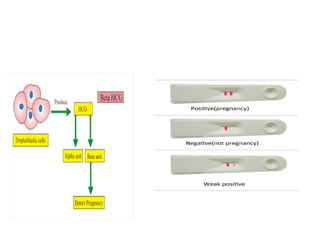
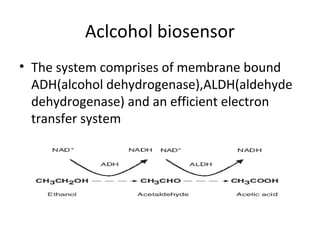
A biosensor is an analytical device that uses a bioreceptor to detect a specific substance. It contains a bioreceptor, transducer, and processing system. Common bioreceptors include antibodies, enzymes, nucleic acids, cells, and molecularly imprinted polymers. The bioreceptor interacts with the target analyte and the transducer converts the interaction signal into an electrical signal that is processed. Examples of biosensors include glucose biosensors, which detect glucose using the enzyme glucose oxidase, and pregnancy tests, which detect human chorionic gonadotropin hormone using antibodies.