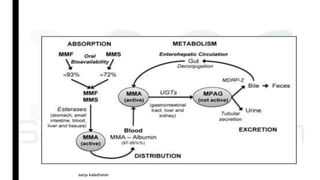
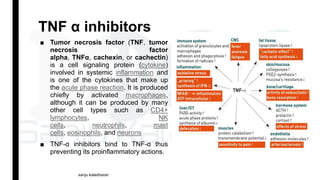
Immunosuppressants are drugs that inhibit immune responses and are used for organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases. The main classes of immunosuppressants discussed are calcineurin inhibitors like cyclosporine and tacrolimus which inhibit T-cell activation, mTOR inhibitors like sirolimus and everolimus, antiproliferative drugs like azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil which inhibit lymphocyte proliferation, glucocorticoids which inhibit cytokine production, and biological agents that target specific components of the immune system such as TNF inhibitors. Each drug has a specific mechanism of action to suppress immune responses through different pathways.









![Mechanism of action: Sirolimus
■ Sirolimus and tacrolimus bind to the
same cytoplasmic FK-binding protein,
but instead of forming a complex with
calcineurin, sirolimus binds to mTOR,
interfering with Signal 3.
■ The latter is a serine-threonine kinase.
[Note: TOR proteins are essential for
many cellular functions, such as cell-
cycle progression, DNA repair, and as
regulators involved in protein
translation.]
■ Binding of sirolimus to mTOR blocks the
progression of activated T cells from the
G1 to the S phase of the cell cycle and,
consequently, the proliferation of these
cells .
■ Unlike cyclosporine and tacrolimus,
sirolimus does not owe its effect to
lowering IL-2 production but, rather, to
inhibiting the cellular responses to IL-2.sanju kaladharan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immunosupressants1-190401101453/85/Immunosupressants-12-320.jpg)