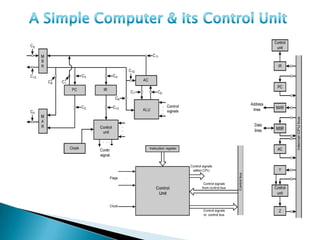
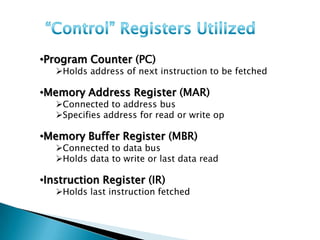
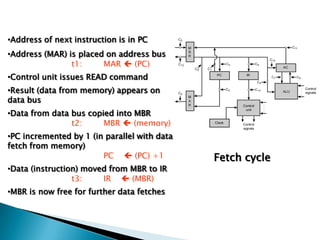
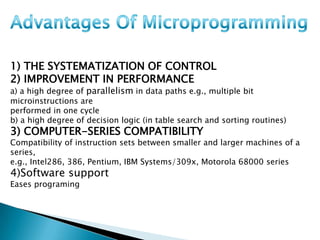
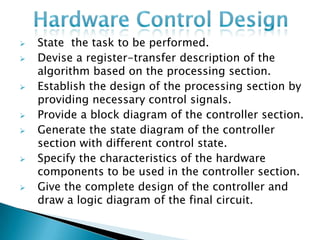
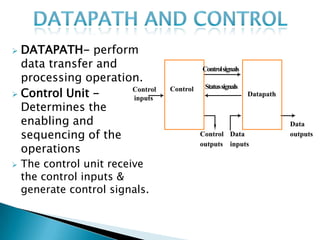
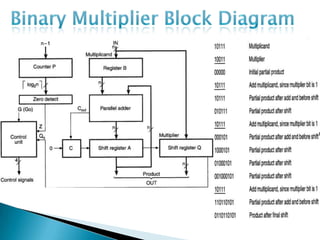
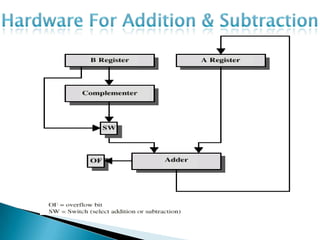
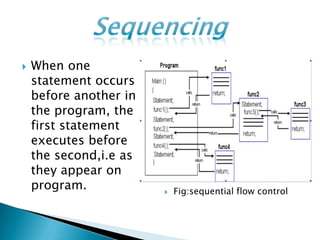
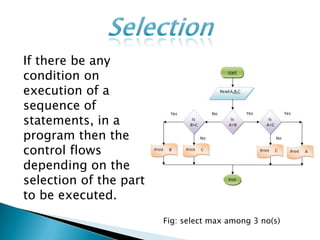
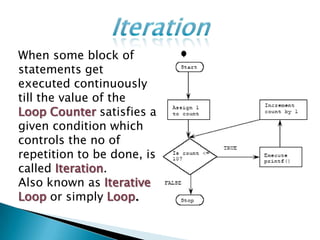
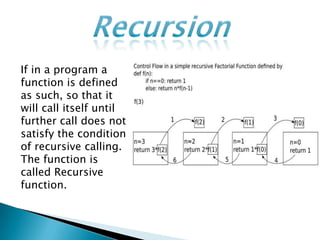
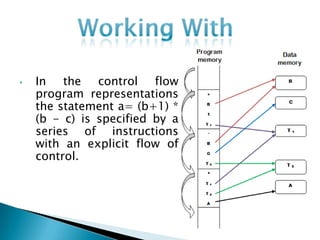
The document discusses different types of control flow in computer programs including sequential, selection, iteration, and recursion. It explains that in a control flow computer, instructions are executed sequentially based on the program counter. Shared memory is used to pass data between instructions by reference. Control flow computers perform computations synchronously using centralized control.