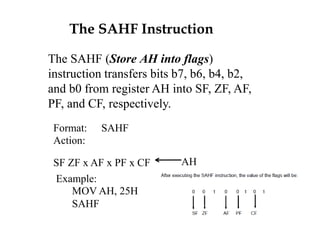
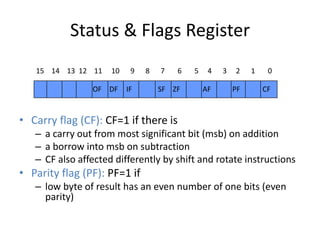
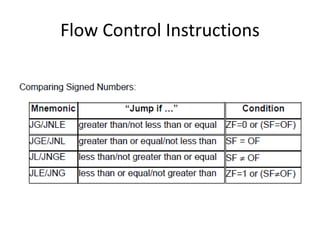
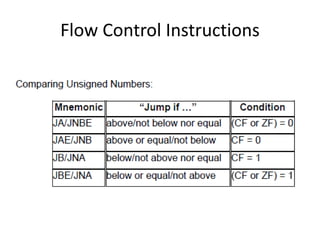
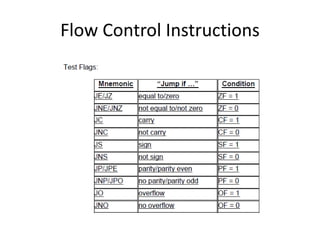
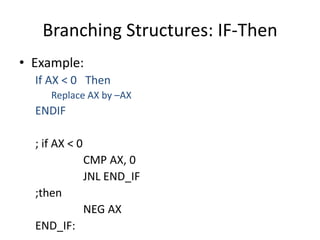
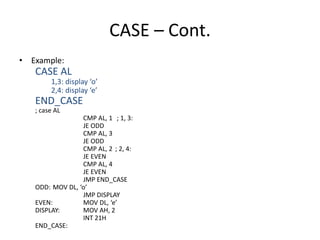
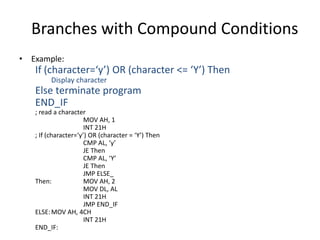
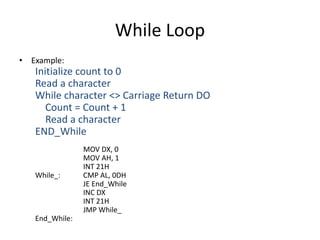
The document discusses various flag control and flow control instructions in the 8086/8088 architecture. It describes instructions like LAHF, SAHF, CLC, STC, CMC, PUSHF, and POPF that directly affect the status of flags. It also explains conditional jump instructions, loop instructions, and how to implement control structures like IF-THEN, IF-THEN-ELSE, CASE, and loops using these instructions. Examples are provided to illustrate different branching scenarios and loop implementations.







![The PUSHF Instruction
The PUSHF (Push Status Register onto Stack)
instruction pushes the flag register onto the stack.
PUSHF decrements SP by 2 and then moves the
flag register to the top of the stack.
Format: PUSHF
Action: SP SP - 2
SP [flag register]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flagcontrol-150309201516-conversion-gate01/85/Flag-control-10-320.jpg)
![The POPF Instruction
The POPF (Pop Flags off the Stack)
instruction transfers the word pointed to by
SP to the status register, thereby altering
the value of the flags.
POPF
Format:
Action:
status register
SP
[SP]
SP + 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flagcontrol-150309201516-conversion-gate01/85/Flag-control-11-320.jpg)
![Stack Instructions
• SP points at the the top of the stack
• .STACK 100H
– SP is initialized to 100H
• PUSH operand
– SP SP - 2
– [SP+1:SP] operand
• POP operand
– Operand [SP+1:SP]
– SP SP + 2
• PUSHF
– SP SP - 2
– [SP+1:SP] flags register
• POPF
– Flags register [SP+1:SP]
– SP SP + 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flagcontrol-150309201516-conversion-gate01/85/Flag-control-12-320.jpg)









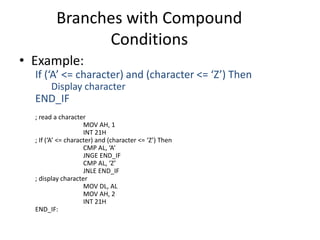



![Application of Loope
• Example: Search for a number in a Table
Table DB 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
XOR SI, SI
MOV CX, 9
Next: INC SI
CMP Table[SI-1], 7
Loopne Next](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flagcontrol-150309201516-conversion-gate01/85/Flag-control-33-320.jpg)