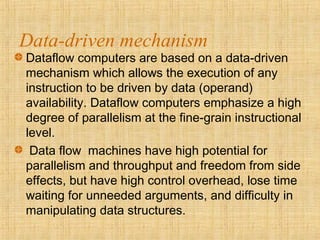
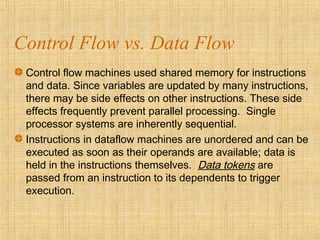
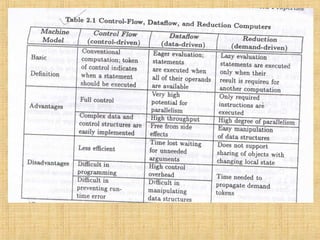
The document discusses three mechanisms for program flow in computer architecture: control flow, data-driven, and demand-driven mechanisms. Control flow uses a program counter for sequential instruction execution, while data-driven and demand-driven mechanisms emphasize parallelism with different execution approaches based on operand availability. Each mechanism has its advantages and disadvantages, affecting efficiency, parallelism potential, and the handling of data structures.








![example
Consider the following example of a arithmetic
expression :
a=[(b+1) * c – (d / e)]
The data-driven computation chooses a bottom-up
approach , starting from b+1 and d / e then
proceding to the ‘*’ operation finally to the
outermost operation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1-programflowmechanisms-190323082253/85/program-flow-mechanisms-advanced-computer-architecture-12-320.jpg)

