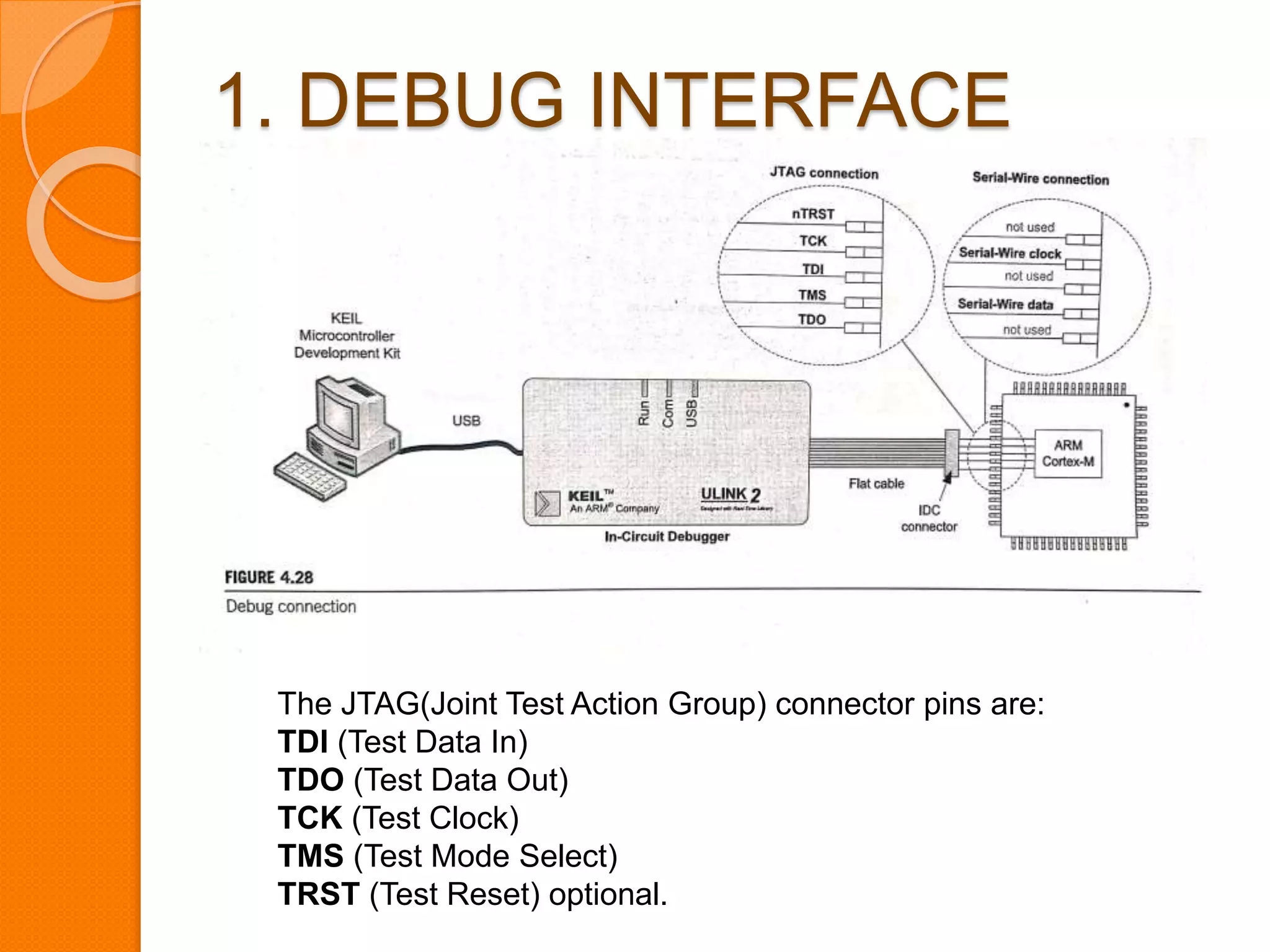
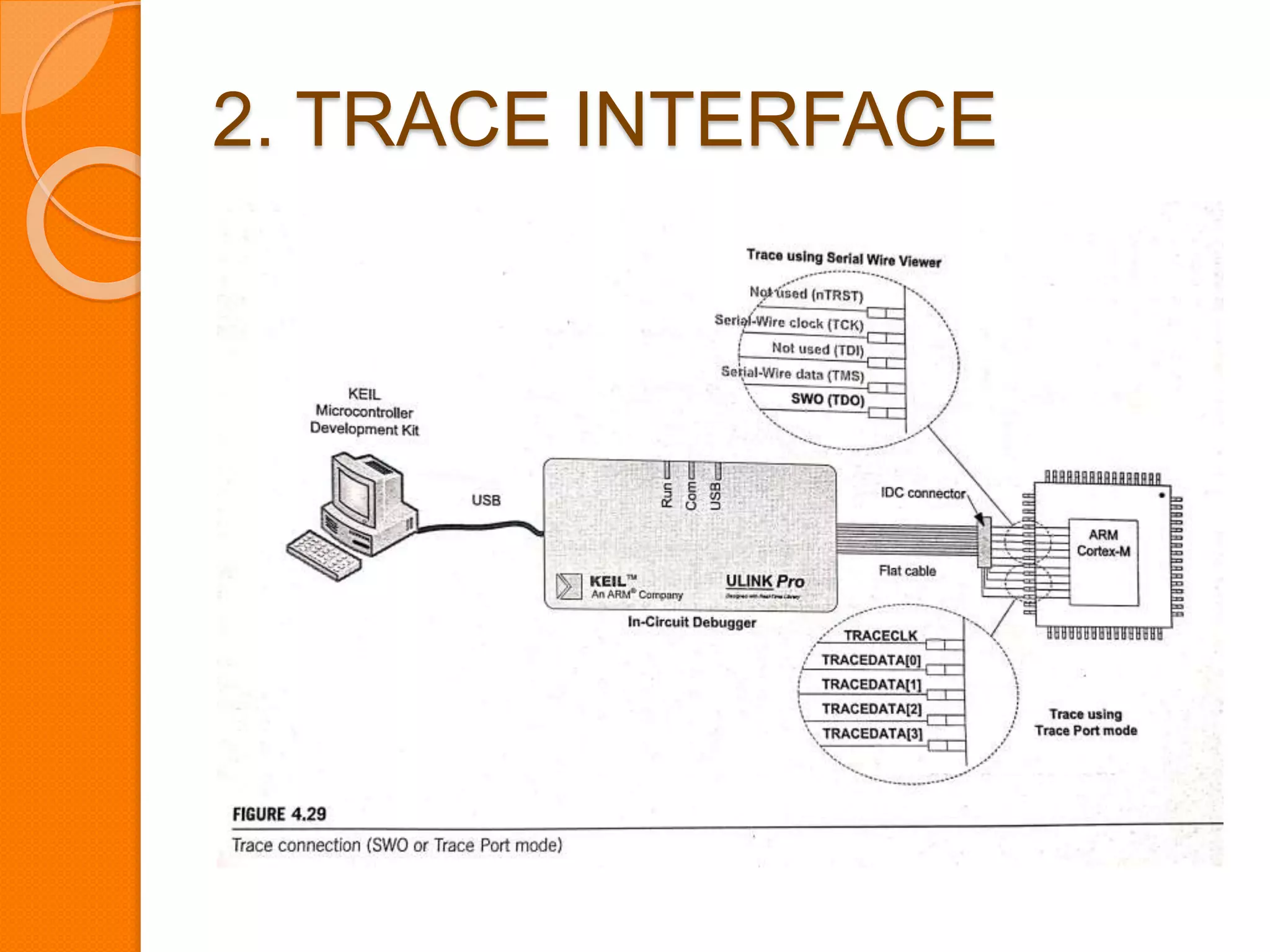
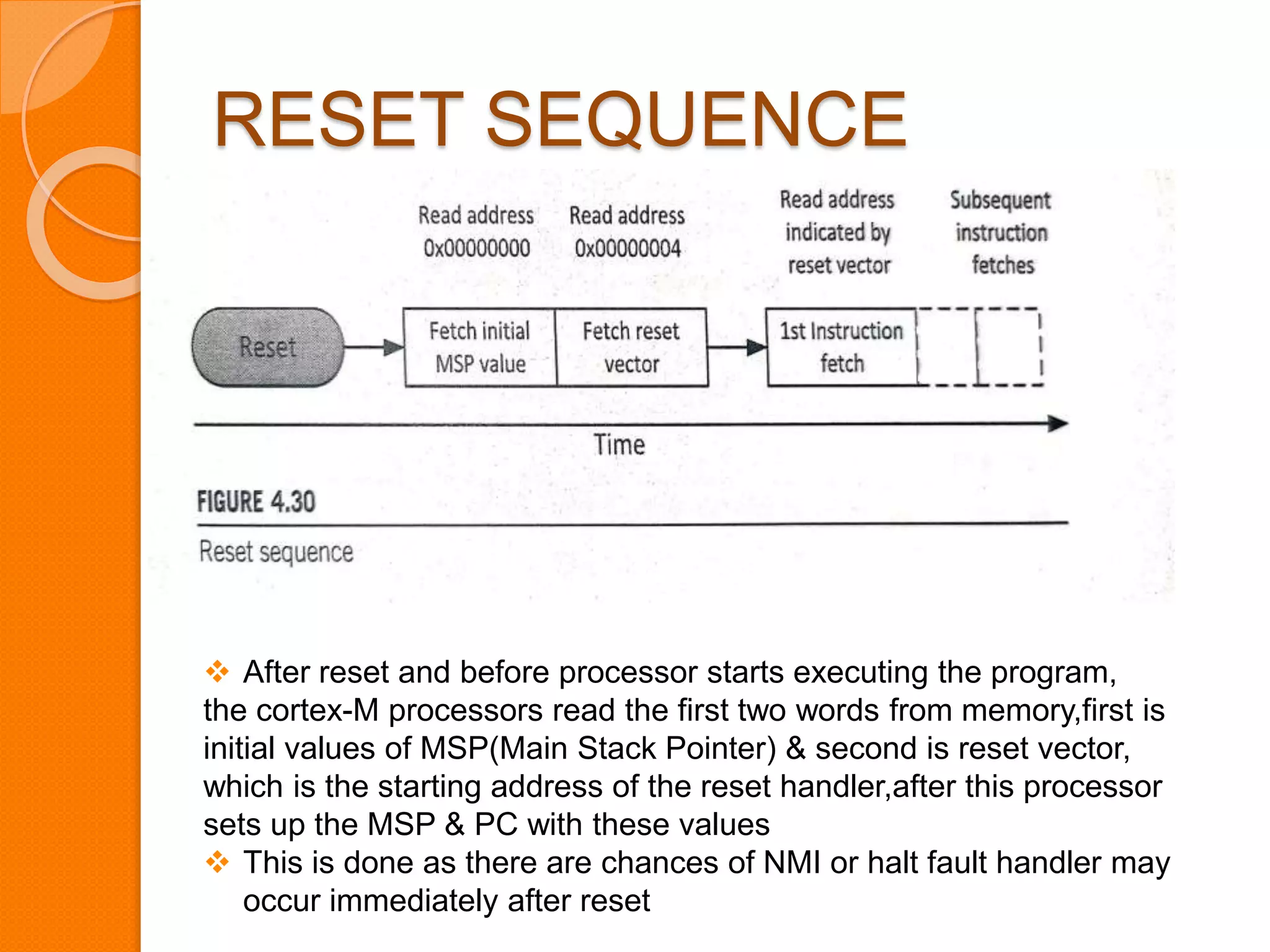
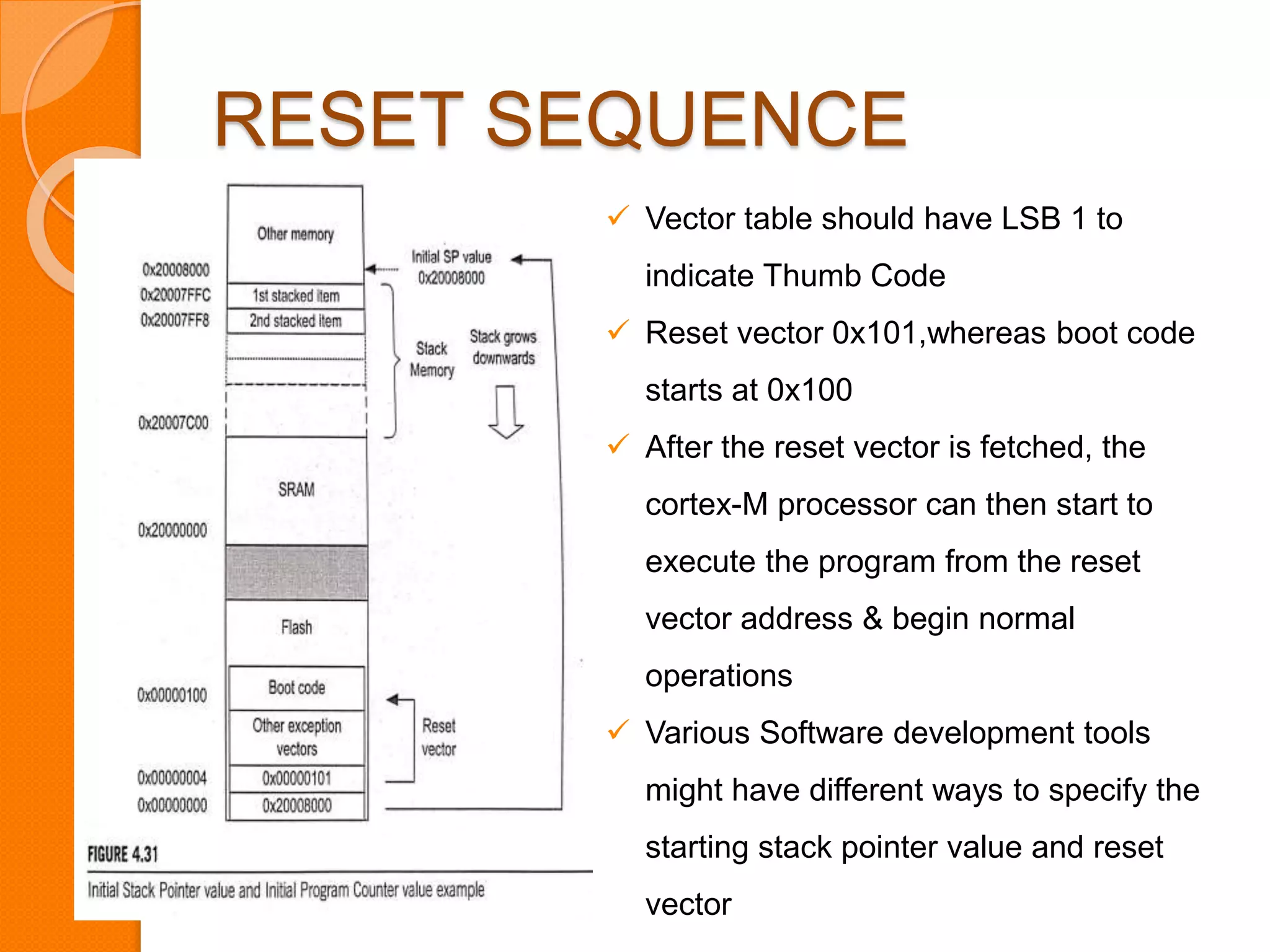
The document discusses system control block (SCB), debug, and reset in ARM Cortex-M processors. SCB provides system configuration and control information. Debug allows identifying and correcting errors through features like halting, stepping, and accessing memory. There are two debug interfaces: JTAG and SWD. Reset resets the processor, peripherals, or both. After reset, the processor reads the main stack pointer and reset vector values to begin program execution from the reset handler.