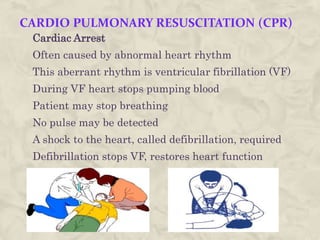
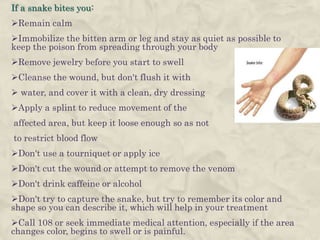
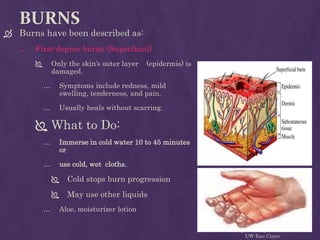
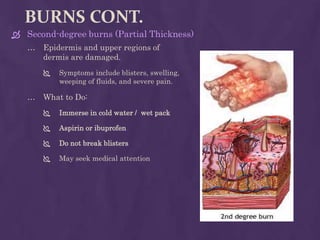
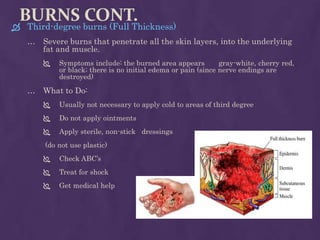
This document provides guidance on first aid for various injuries and medical emergencies. It discusses how to treat accidental trauma, burns/wounds, poisoning, electric shock, heart attacks, and animal bites. For each, it describes signs and symptoms and steps to take, such as calling for emergency help, monitoring breathing, preventing further harm, and promoting recovery. Procedures for performing CPR and treating shock are also outlined. The aim of first aid is to preserve life, prevent further harm, and promote recovery from illness or injury.