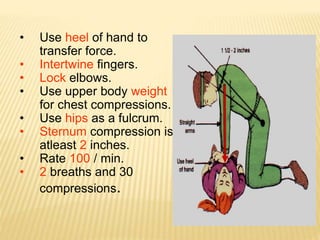
1. First aid involves providing immediate care for injuries and illnesses until full medical treatment can be received.
2. First aid kits should contain supplies to stop bleeding, treat wounds, prevent infection, immobilize fractures, and address other common medical emergencies.
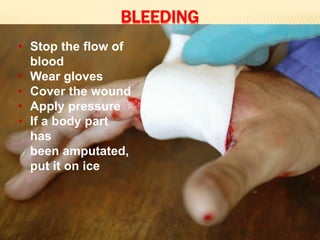
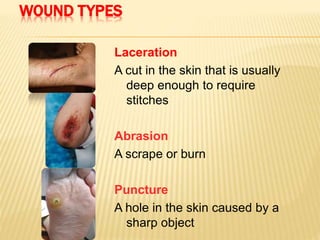
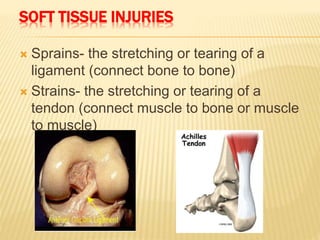
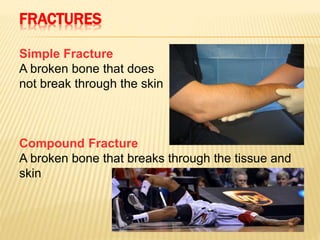
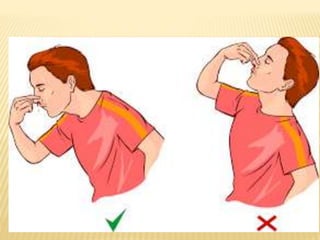
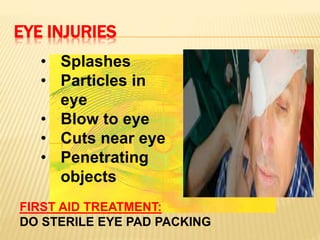
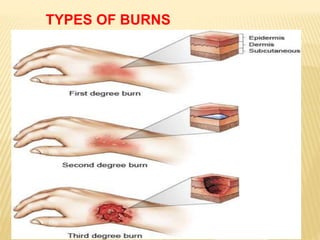
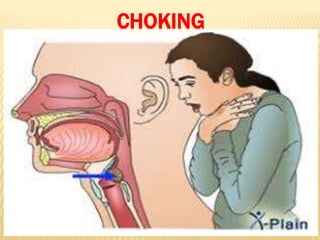
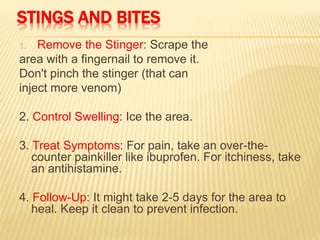
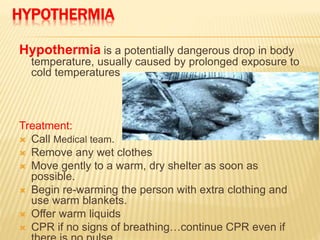
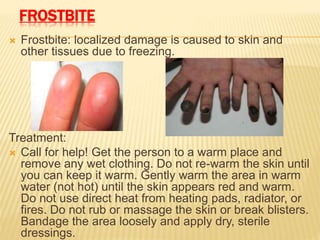
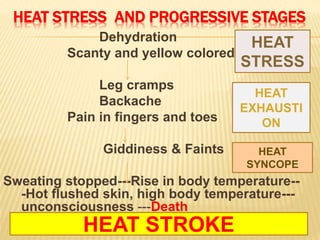
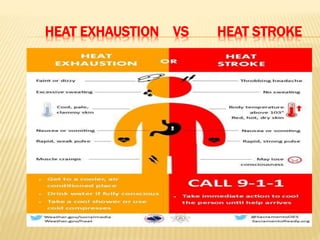
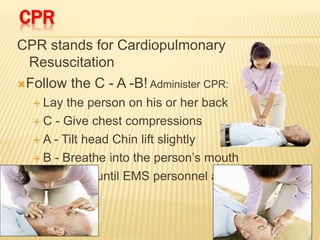
3. Proper first aid procedures exist for injuries and conditions like bleeding, sprains, burns, choking, shock, and heat/cold exposure. The goal is to stabilize the patient and reduce further harm until emergency help arrives.